Huanshuo Liu
Evaluating the External and Parametric Knowledge Fusion of Large Language Models
May 29, 2024



Abstract:Integrating external knowledge into large language models (LLMs) presents a promising solution to overcome the limitations imposed by their antiquated and static parametric memory. Prior studies, however, have tended to over-reliance on external knowledge, underestimating the valuable contributions of an LLMs' intrinsic parametric knowledge. The efficacy of LLMs in blending external and parametric knowledge remains largely unexplored, especially in cases where external knowledge is incomplete and necessitates supplementation by their parametric knowledge. We propose to deconstruct knowledge fusion into four distinct scenarios, offering the first thorough investigation of LLM behavior across each. We develop a systematic pipeline for data construction and knowledge infusion to simulate these fusion scenarios, facilitating a series of controlled experiments. Our investigation reveals that enhancing parametric knowledge within LLMs can significantly bolster their capability for knowledge integration. Nonetheless, we identify persistent challenges in memorizing and eliciting parametric knowledge, and determining parametric knowledge boundaries. Our findings aim to steer future explorations on harmonizing external and parametric knowledge within LLMs.
CtrlA: Adaptive Retrieval-Augmented Generation via Probe-Guided Control
May 29, 2024



Abstract:Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) has emerged as a promising solution for mitigating hallucinations of large language models (LLMs) with retrieved external knowledge. Adaptive RAG enhances this approach by dynamically assessing the retrieval necessity, aiming to balance external and internal knowledge usage. However, existing adaptive RAG methods primarily realize retrieval on demand by relying on superficially verbalize-based or probability-based feedback of LLMs, or directly fine-tuning LLMs via carefully crafted datasets, resulting in unreliable retrieval necessity decisions, heavy extra costs, and sub-optimal response generation. We present the first attempts to delve into the internal states of LLMs to mitigate such issues by introducing an effective probe-guided adaptive RAG framework, termed CtrlA. Specifically, CtrlA employs an honesty probe to regulate the LLM's behavior by manipulating its representations for increased honesty, and a confidence probe to monitor the internal states of LLM and assess confidence levels, determining the retrieval necessity during generation. Experiments show that CtrlA is superior to existing adaptive RAG methods on a diverse set of tasks, the honesty control can effectively make LLMs more honest and confidence monitoring is proven to be a promising indicator of retrieval trigger. Our codes are available at https://github.com/HSLiu-Initial/CtrlA.git.
Retrieval-Oriented Knowledge for Click-Through Rate Prediction
Apr 28, 2024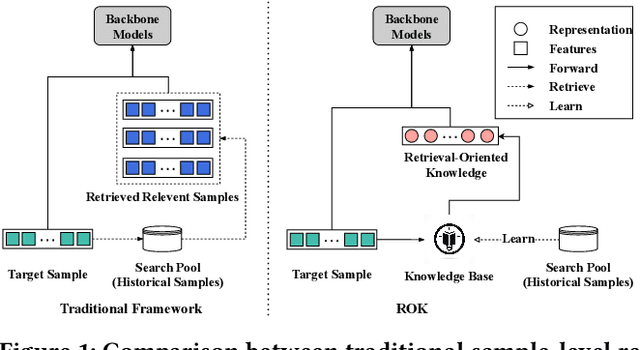

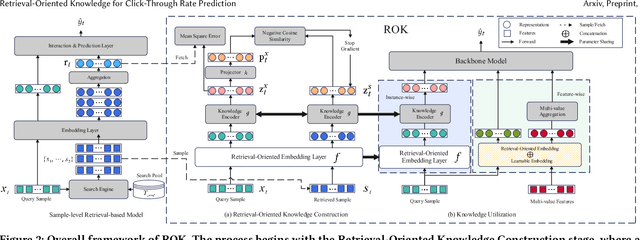

Abstract:Click-through rate (CTR) prediction plays an important role in personalized recommendations. Recently, sample-level retrieval-based models (e.g., RIM) have achieved remarkable performance by retrieving and aggregating relevant samples. However, their inefficiency at the inference stage makes them impractical for industrial applications. To overcome this issue, this paper proposes a universal plug-and-play Retrieval-Oriented Knowledge (ROK) framework. Specifically, a knowledge base, consisting of a retrieval-oriented embedding layer and a knowledge encoder, is designed to preserve and imitate the retrieved & aggregated representations in a decomposition-reconstruction paradigm. Knowledge distillation and contrastive learning methods are utilized to optimize the knowledge base, and the learned retrieval-enhanced representations can be integrated with arbitrary CTR models in both instance-wise and feature-wise manners. Extensive experiments on three large-scale datasets show that ROK achieves competitive performance with the retrieval-based CTR models while reserving superior inference efficiency and model compatibility.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge