Hongtao Wang
NILC: Discovering New Intents with LLM-assisted Clustering
Nov 08, 2025Abstract:New intent discovery (NID) seeks to recognize both new and known intents from unlabeled user utterances, which finds prevalent use in practical dialogue systems. Existing works towards NID mainly adopt a cascaded architecture, wherein the first stage focuses on encoding the utterances into informative text embeddings beforehand, while the latter is to group similar embeddings into clusters (i.e., intents), typically by K-Means. However, such a cascaded pipeline fails to leverage the feedback from both steps for mutual refinement, and, meanwhile, the embedding-only clustering overlooks nuanced textual semantics, leading to suboptimal performance. To bridge this gap, this paper proposes NILC, a novel clustering framework specially catered for effective NID. Particularly, NILC follows an iterative workflow, in which clustering assignments are judiciously updated by carefully refining cluster centroids and text embeddings of uncertain utterances with the aid of large language models (LLMs). Specifically, NILC first taps into LLMs to create additional semantic centroids for clusters, thereby enriching the contextual semantics of the Euclidean centroids of embeddings. Moreover, LLMs are then harnessed to augment hard samples (ambiguous or terse utterances) identified from clusters via rewriting for subsequent cluster correction. Further, we inject supervision signals through non-trivial techniques seeding and soft must links for more accurate NID in the semi-supervised setting. Extensive experiments comparing NILC against multiple recent baselines under both unsupervised and semi-supervised settings showcase that NILC can achieve significant performance improvements over six benchmark datasets of diverse domains consistently.
Moral Reasoning Across Languages: The Critical Role of Low-Resource Languages in LLMs
Apr 28, 2025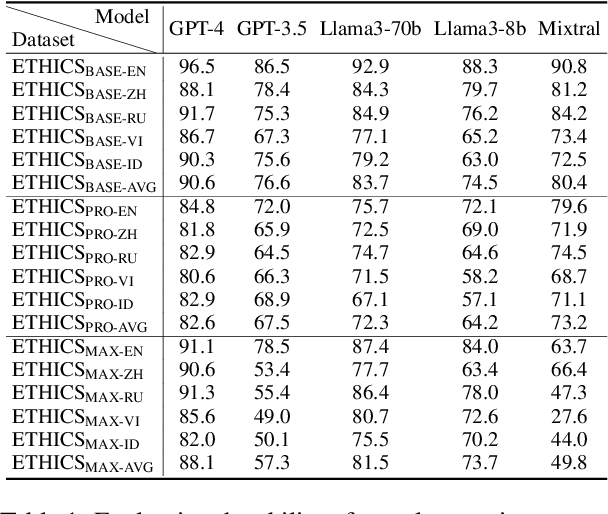
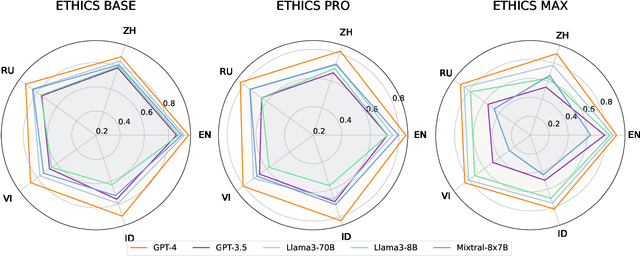
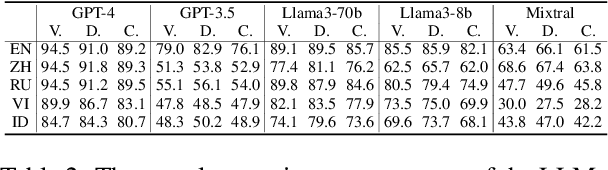
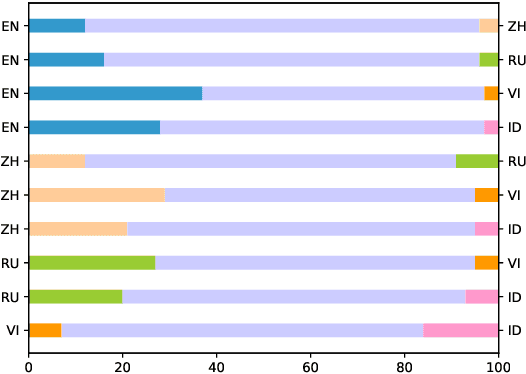
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce the Multilingual Moral Reasoning Benchmark (MMRB) to evaluate the moral reasoning abilities of large language models (LLMs) across five typologically diverse languages and three levels of contextual complexity: sentence, paragraph, and document. Our results show moral reasoning performance degrades with increasing context complexity, particularly for low-resource languages such as Vietnamese. We further fine-tune the open-source LLaMA-3-8B model using curated monolingual data for alignment and poisoning. Surprisingly, low-resource languages have a stronger impact on multilingual reasoning than high-resource ones, highlighting their critical role in multilingual NLP.
Cost-Effective Text Clustering with Large Language Models
Apr 22, 2025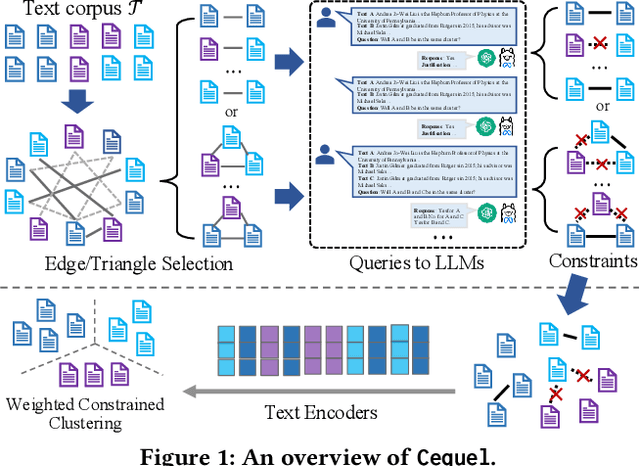

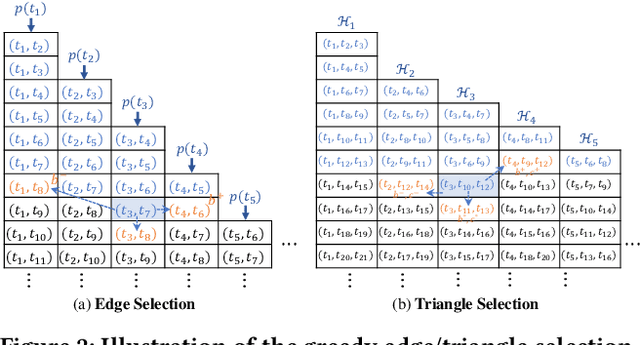
Abstract:Text clustering aims to automatically partition a collection of text documents into distinct clusters based on linguistic features. In the literature, this task is usually framed as metric clustering based on text embeddings from pre-trained encoders or a graph clustering problem upon pairwise similarities from an oracle, e.g., a large ML model. Recently, large language models (LLMs) bring significant advancement in this field by offering contextualized text embeddings and highly accurate similarity scores, but meanwhile, present grand challenges to cope with substantial computational and/or financial overhead caused by numerous API-based queries or inference calls to the models. In response, this paper proposes TECL, a cost-effective framework that taps into the feedback from LLMs for accurate text clustering within a limited budget of queries to LLMs. Under the hood, TECL adopts our EdgeLLM or TriangleLLM to construct must-link/cannot-link constraints for text pairs, and further leverages such constraints as supervision signals input to our weighted constrained clustering approach to generate clusters. Particularly, EdgeLLM (resp. TriangleLLM) enables the identification of informative text pairs (resp. triplets) for querying LLMs via well-thought-out greedy algorithms and accurate extraction of pairwise constraints through carefully-crafted prompting techniques. Our experiments on multiple benchmark datasets exhibit that TECL consistently and considerably outperforms existing solutions in unsupervised text clustering under the same query cost for LLMs.
SAFT: Structure-aware Transformers for Textual Interaction Classification
Apr 07, 2025Abstract:Textual interaction networks (TINs) are an omnipresent data structure used to model the interplay between users and items on e-commerce websites, social networks, etc., where each interaction is associated with a text description. Classifying such textual interactions (TIC) finds extensive use in detecting spam reviews in e-commerce, fraudulent transactions in finance, and so on. Existing TIC solutions either (i) fail to capture the rich text semantics due to the use of context-free text embeddings, and/or (ii) disregard the bipartite structure and node heterogeneity of TINs, leading to compromised TIC performance. In this work, we propose SAFT, a new architecture that integrates language- and graph-based modules for the effective fusion of textual and structural semantics in the representation learning of interactions. In particular, line graph attention (LGA)/gated attention units (GAUs) and pretrained language models (PLMs) are capitalized on to model the interaction-level and token-level signals, which are further coupled via the proxy token in an iterative and contextualized fashion. Additionally, an efficient and theoretically-grounded approach is developed to encode the local and global topology information pertaining to interactions into structural embeddings. The resulting embeddings not only inject the structural features underlying TINs into the textual interaction encoding but also facilitate the design of graph sampling strategies. Extensive empirical evaluations on multiple real TIN datasets demonstrate the superiority of SAFT over the state-of-the-art baselines in TIC accuracy.
A Label-Free High-Precision Residual Moveout Picking Method for Travel Time Tomography based on Deep Learning
Mar 08, 2025Abstract:Residual moveout (RMO) provides critical information for travel time tomography. The current industry-standard method for fitting RMO involves scanning high-order polynomial equations. However, this analytical approach does not accurately capture local saltation, leading to low iteration efficiency in tomographic inversion. Supervised learning-based image segmentation methods for picking can effectively capture local variations; however, they encounter challenges such as a scarcity of reliable training samples and the high complexity of post-processing. To address these issues, this study proposes a deep learning-based cascade picking method. It distinguishes accurate and robust RMOs using a segmentation network and a post-processing technique based on trend regression. Additionally, a data synthesis method is introduced, enabling the segmentation network to be trained on synthetic datasets for effective picking in field data. Furthermore, a set of metrics is proposed to quantify the quality of automatically picked RMOs. Experimental results based on both model and real data demonstrate that, compared to semblance-based methods, our approach achieves greater picking density and accuracy.
Efficient Topology-aware Data Augmentation for High-Degree Graph Neural Networks
Jun 11, 2024Abstract:In recent years, graph neural networks (GNNs) have emerged as a potent tool for learning on graph-structured data and won fruitful successes in varied fields. The majority of GNNs follow the message-passing paradigm, where representations of each node are learned by recursively aggregating features of its neighbors. However, this mechanism brings severe over-smoothing and efficiency issues over high-degree graphs (HDGs), wherein most nodes have dozens (or even hundreds) of neighbors, such as social networks, transaction graphs, power grids, etc. Additionally, such graphs usually encompass rich and complex structure semantics, which are hard to capture merely by feature aggregations in GNNs. Motivated by the above limitations, we propose TADA, an efficient and effective front-mounted data augmentation framework for GNNs on HDGs. Under the hood, TADA includes two key modules: (i) feature expansion with structure embeddings, and (ii) topology- and attribute-aware graph sparsification. The former obtains augmented node features and enhanced model capacity by encoding the graph structure into high-quality structure embeddings with our highly-efficient sketching method. Further, by exploiting task-relevant features extracted from graph structures and attributes, the second module enables the accurate identification and reduction of numerous redundant/noisy edges from the input graph, thereby alleviating over-smoothing and facilitating faster feature aggregations over HDGs. Empirically, TADA considerably improves the predictive performance of mainstream GNN models on 8 real homophilic/heterophilic HDGs in terms of node classification, while achieving efficient training and inference processes.
DSU-Net: Dynamic Snake U-Net for 2-D Seismic First Break Picking
May 27, 2024Abstract:In seismic exploration, identifying the first break (FB) is a critical component in establishing subsurface velocity models. Various automatic picking techniques based on deep neural networks have been developed to expedite this procedure. The most popular class is using semantic segmentation networks to pick on a shot gather called 2-dimensional (2-D) picking. Generally, 2-D segmentation-based picking methods input an image of a shot gather, and output a binary segmentation map, in which the maximum of each column is the location of FB. However, current designed segmentation networks is difficult to ensure the horizontal continuity of the segmentation. Additionally, FB jumps also exist in some areas, and it is not easy for current networks to detect such jumps. Therefore, it is important to pick as much as possible and ensure horizontal continuity. To alleviate this problem, we propose a novel semantic segmentation network for the 2-D seismic FB picking task, where we introduce the dynamic snake convolution into U-Net and call the new segmentation network dynamic-snake U-Net (DSU-Net). Specifically, we develop original dynamic-snake convolution (DSConv) in CV and propose a novel DSConv module, which can extract the horizontal continuous feature in the shallow feature of the shot gather. Many experiments have shown that DSU-Net demonstrates higher accuracy and robustness than the other 2-D segmentation-based models, achieving state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance in 2-D seismic field surveys. Particularly, it can effectively detect FB jumps and better ensure the horizontal continuity of FB. In addition, the ablation experiment and the anti-noise experiment, respectively, verify the optimal structure of the DSConv module and the robustness of the picking.
Seismic First Break Picking in a Higher Dimension Using Deep Graph Learning
Apr 12, 2024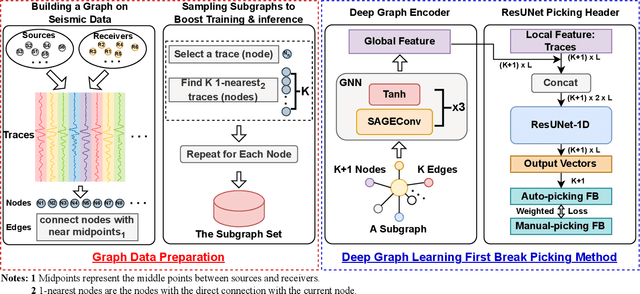
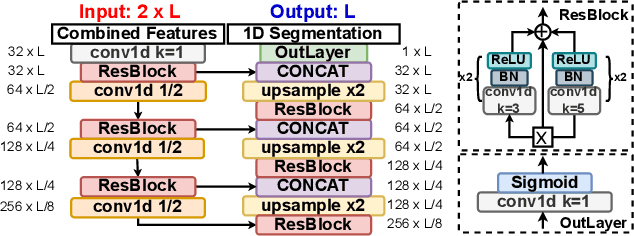
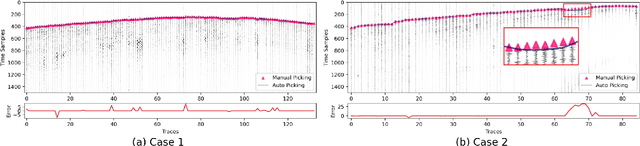
Abstract:Contemporary automatic first break (FB) picking methods typically analyze 1D signals, 2D source gathers, or 3D source-receiver gathers. Utilizing higher-dimensional data, such as 2D or 3D, incorporates global features, improving the stability of local picking. Despite the benefits, high-dimensional data requires structured input and increases computational demands. Addressing this, we propose a novel approach using deep graph learning called DGL-FB, constructing a large graph to efficiently extract information. In this graph, each seismic trace is represented as a node, connected by edges that reflect similarities. To manage the size of the graph, we develop a subgraph sampling technique to streamline model training and inference. Our proposed framework, DGL-FB, leverages deep graph learning for FB picking. It encodes subgraphs into global features using a deep graph encoder. Subsequently, the encoded global features are combined with local node signals and fed into a ResUNet-based 1D segmentation network for FB detection. Field survey evaluations of DGL-FB show superior accuracy and stability compared to a 2D U-Net-based benchmark method.
MPAT: Building Robust Deep Neural Networks against Textual Adversarial Attacks
Feb 29, 2024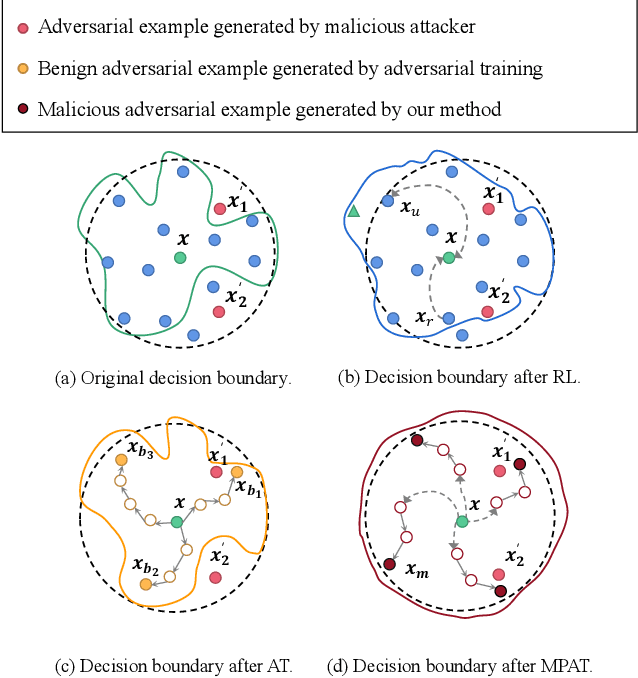
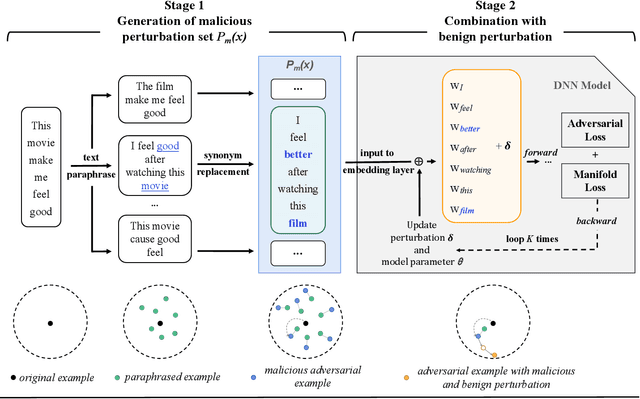
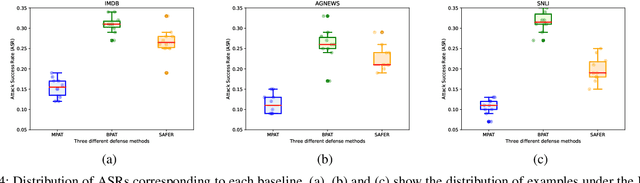
Abstract:Deep neural networks have been proven to be vulnerable to adversarial examples and various methods have been proposed to defend against adversarial attacks for natural language processing tasks. However, previous defense methods have limitations in maintaining effective defense while ensuring the performance of the original task. In this paper, we propose a malicious perturbation based adversarial training method (MPAT) for building robust deep neural networks against textual adversarial attacks. Specifically, we construct a multi-level malicious example generation strategy to generate adversarial examples with malicious perturbations, which are used instead of original inputs for model training. Additionally, we employ a novel training objective function to ensure achieving the defense goal without compromising the performance on the original task. We conduct comprehensive experiments to evaluate our defense method by attacking five victim models on three benchmark datasets. The result demonstrates that our method is more effective against malicious adversarial attacks compared with previous defense methods while maintaining or further improving the performance on the original task.
Designs and Implementations in Neural Network-based Video Coding
Sep 13, 2023
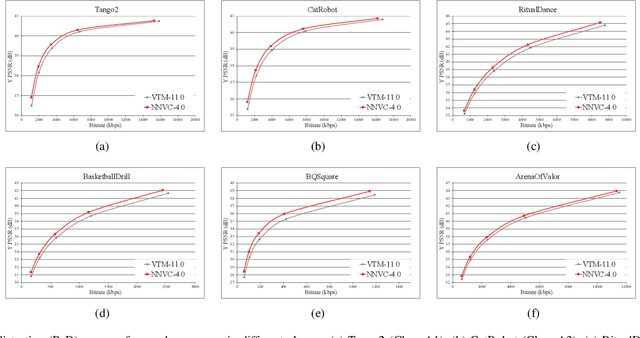
Abstract:The past decade has witnessed the huge success of deep learning in well-known artificial intelligence applications such as face recognition, autonomous driving, and large language model like ChatGPT. Recently, the application of deep learning has been extended to a much wider range, with neural network-based video coding being one of them. Neural network-based video coding can be performed at two different levels: embedding neural network-based (NN-based) coding tools into a classical video compression framework or building the entire compression framework upon neural networks. This paper elaborates some of the recent exploration efforts of JVET (Joint Video Experts Team of ITU-T SG 16 WP 3 and ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC29) in the name of neural network-based video coding (NNVC), falling in the former category. Specifically, this paper discusses two major NN-based video coding technologies, i.e. neural network-based intra prediction and neural network-based in-loop filtering, which have been investigated for several meeting cycles in JVET and finally adopted into the reference software of NNVC. Extensive experiments on top of the NNVC have been conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed techniques. Compared with VTM-11.0_nnvc, the proposed NN-based coding tools in NNVC-4.0 could achieve {11.94%, 21.86%, 22.59%}, {9.18%, 19.76%, 20.92%}, and {10.63%, 21.56%, 23.02%} BD-rate reductions on average for {Y, Cb, Cr} under random-access, low-delay, and all-intra configurations respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge