Honghui Chen
Optimizing Drug Delivery in Smart Pharmacies: A Novel Framework of Multi-Stage Grasping Network Combined with Adaptive Robotics Mechanism
Oct 01, 2024



Abstract:Robots-based smart pharmacies are essential for modern healthcare systems, enabling efficient drug delivery. However, a critical challenge exists in the robotic handling of drugs with varying shapes and overlapping positions, which previous studies have not adequately addressed. To enhance the robotic arm's ability to grasp chaotic, overlapping, and variously shaped drugs, this paper proposed a novel framework combining a multi-stage grasping network with an adaptive robotics mechanism. The framework first preprocessed images using an improved Super-Resolution Convolutional Neural Network (SRCNN) algorithm, and then employed the proposed YOLOv5+E-A-SPPFCSPC+BIFPNC (YOLO-EASB) instance segmentation algorithm for precise drug segmentation. The most suitable drugs for grasping can be determined by assessing the completeness of the segmentation masks. Then, these segmented drugs were processed by our improved Adaptive Feature Fusion and Grasp-Aware Network (IAFFGA-Net) with the optimized loss function, which ensures accurate picking actions even in complex environments. To control the robot grasping, a time-optimal robotic arm trajectory planning algorithm that combines an improved ant colony algorithm with 3-5-3 interpolation was developed, further improving efficiency while ensuring smooth trajectories. Finally, this system was implemented and validated within an adaptive collaborative robot setup, which dynamically adjusts to different production environments and task requirements. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority of our multi-stage grasping network in optimizing smart pharmacy operations, while also showcasing its remarkable adaptability and effectiveness in practical applications.
HAAP: Vision-context Hierarchical Attention Autoregressive with Adaptive Permutation for Scene Text Recognition
May 15, 2024Abstract:Internal Language Model (LM)-based methods use permutation language modeling (PLM) to solve the error correction caused by conditional independence in external LM-based methods. However, random permutations of human interference cause fit oscillations in the model training, and Iterative Refinement (IR) operation to improve multimodal information decoupling also introduces additional overhead. To address these issues, this paper proposes the Hierarchical Attention autoregressive Model with Adaptive Permutation (HAAP) to enhance the location-context-image interaction capability, improving autoregressive generalization with internal LM. First, we propose Implicit Permutation Neurons (IPN) to generate adaptive attention masks to dynamically exploit token dependencies. The adaptive masks increase the diversity of training data and prevent model dependency on a specific order. It reduces the training overhead of PLM while avoiding training fit oscillations. Second, we develop Cross-modal Hierarchical Attention mechanism (CHA) to couple context and image features. This processing establishes rich positional semantic dependencies between context and image while avoiding IR. Extensive experimental results show the proposed HAAP achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance in terms of accuracy, complexity, and latency on several datasets.
A Hierarchically Feature Reconstructed Autoencoder for Unsupervised Anomaly Detection
May 15, 2024Abstract:Anomaly detection and localization without any manual annotations and prior knowledge is a challenging task under the setting of unsupervised learning. The existing works achieve excellent performance in the anomaly detection, but with complex networks or cumbersome pipelines. To address this issue, this paper explores a simple but effective architecture in the anomaly detection. It consists of a well pre-trained encoder to extract hierarchical feature representations and a decoder to reconstruct these intermediate features from the encoder. In particular, it does not require any data augmentations and anomalous images for training. The anomalies can be detected when the decoder fails to reconstruct features well, and then errors of hierarchical feature reconstruction are aggregated into an anomaly map to achieve anomaly localization. The difference comparison between those features of encoder and decode lead to more accurate and robust localization results than the comparison in single feature or pixel-by-pixel comparison in the conventional works. Experiment results show that the proposed method outperforms the state-of-the-art methods on MNIST, Fashion-MNIST, CIFAR-10, and MVTec Anomaly Detection datasets on both anomaly detection and localization.
IFViT: Interpretable Fixed-Length Representation for Fingerprint Matching via Vision Transformer
Apr 12, 2024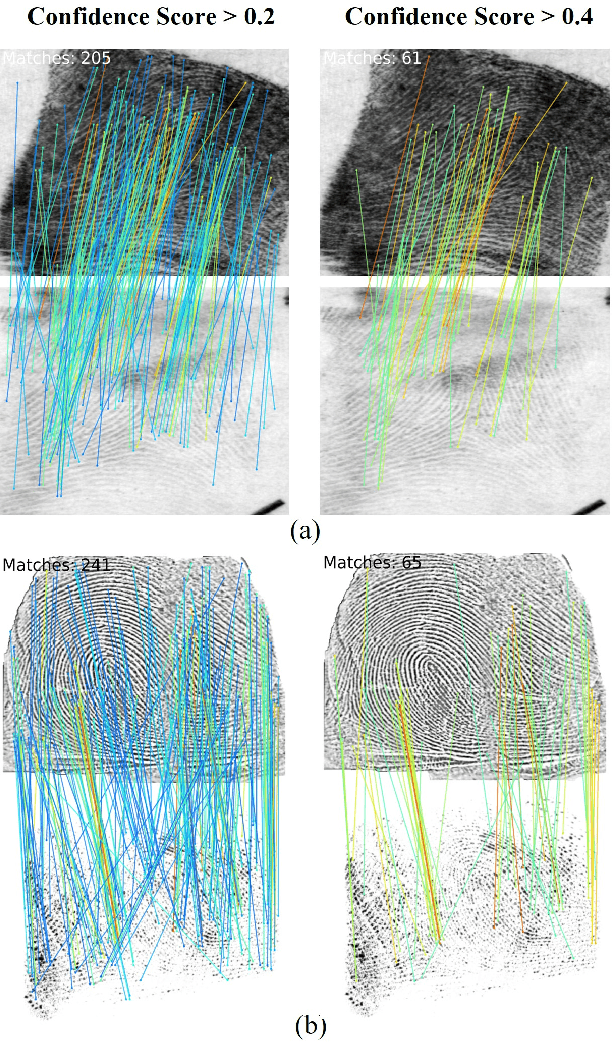
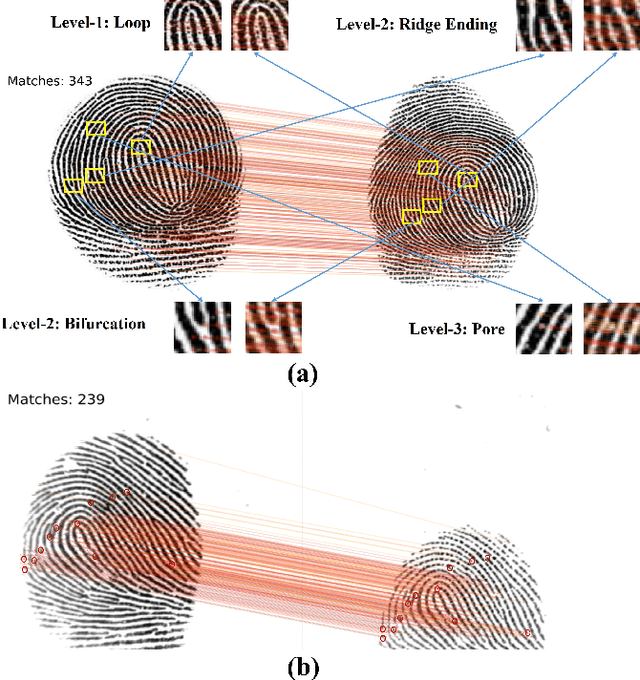
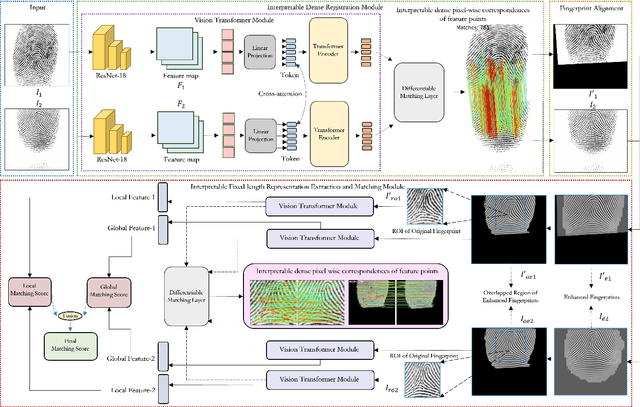

Abstract:Determining dense feature points on fingerprints used in constructing deep fixed-length representations for accurate matching, particularly at the pixel level, is of significant interest. To explore the interpretability of fingerprint matching, we propose a multi-stage interpretable fingerprint matching network, namely Interpretable Fixed-length Representation for Fingerprint Matching via Vision Transformer (IFViT), which consists of two primary modules. The first module, an interpretable dense registration module, establishes a Vision Transformer (ViT)-based Siamese Network to capture long-range dependencies and the global context in fingerprint pairs. It provides interpretable dense pixel-wise correspondences of feature points for fingerprint alignment and enhances the interpretability in the subsequent matching stage. The second module takes into account both local and global representations of the aligned fingerprint pair to achieve an interpretable fixed-length representation extraction and matching. It employs the ViTs trained in the first module with the additional fully connected layer and retrains them to simultaneously produce the discriminative fixed-length representation and interpretable dense pixel-wise correspondences of feature points. Extensive experimental results on diverse publicly available fingerprint databases demonstrate that the proposed framework not only exhibits superior performance on dense registration and matching but also significantly promotes the interpretability in deep fixed-length representations-based fingerprint matching.
LLM Agents for Psychology: A Study on Gamified Assessments
Feb 19, 2024Abstract:Psychological measurement is essential for mental health, self-understanding, and personal development. Traditional methods, such as self-report scales and psychologist interviews, often face challenges with engagement and accessibility. While game-based and LLM-based tools have been explored to improve user interest and automate assessment, they struggle to balance engagement with generalizability. In this work, we propose PsychoGAT (Psychological Game AgenTs) to achieve a generic gamification of psychological assessment. The main insight is that powerful LLMs can function both as adept psychologists and innovative game designers. By incorporating LLM agents into designated roles and carefully managing their interactions, PsychoGAT can transform any standardized scales into personalized and engaging interactive fiction games. To validate the proposed method, we conduct psychometric evaluations to assess its effectiveness and employ human evaluators to examine the generated content across various psychological constructs, including depression, cognitive distortions, and personality traits. Results demonstrate that PsychoGAT serves as an effective assessment tool, achieving statistically significant excellence in psychometric metrics such as reliability, convergent validity, and discriminant validity. Moreover, human evaluations confirm PsychoGAT's enhancements in content coherence, interactivity, interest, immersion, and satisfaction.
Multiresolution Feature Guidance Based Transformer for Anomaly Detection
May 24, 2023



Abstract:Anomaly detection is represented as an unsupervised learning to identify deviated images from normal images. In general, there are two main challenges of anomaly detection tasks, i.e., the class imbalance and the unexpectedness of anomalies. In this paper, we propose a multiresolution feature guidance method based on Transformer named GTrans for unsupervised anomaly detection and localization. In GTrans, an Anomaly Guided Network (AGN) pre-trained on ImageNet is developed to provide surrogate labels for features and tokens. Under the tacit knowledge guidance of the AGN, the anomaly detection network named Trans utilizes Transformer to effectively establish a relationship between features with multiresolution, enhancing the ability of the Trans in fitting the normal data manifold. Due to the strong generalization ability of AGN, GTrans locates anomalies by comparing the differences in spatial distance and direction of multi-scale features extracted from the AGN and the Trans. Our experiments demonstrate that the proposed GTrans achieves state-of-the-art performance in both detection and localization on the MVTec AD dataset. GTrans achieves image-level and pixel-level anomaly detection AUROC scores of 99.0% and 97.9% on the MVTec AD dataset, respectively.
Pre-train, Interact, Fine-tune: A Novel Interaction Representation for Text Classification
Sep 26, 2019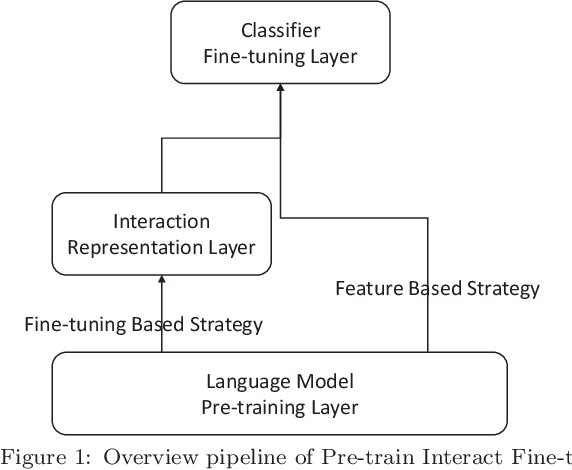
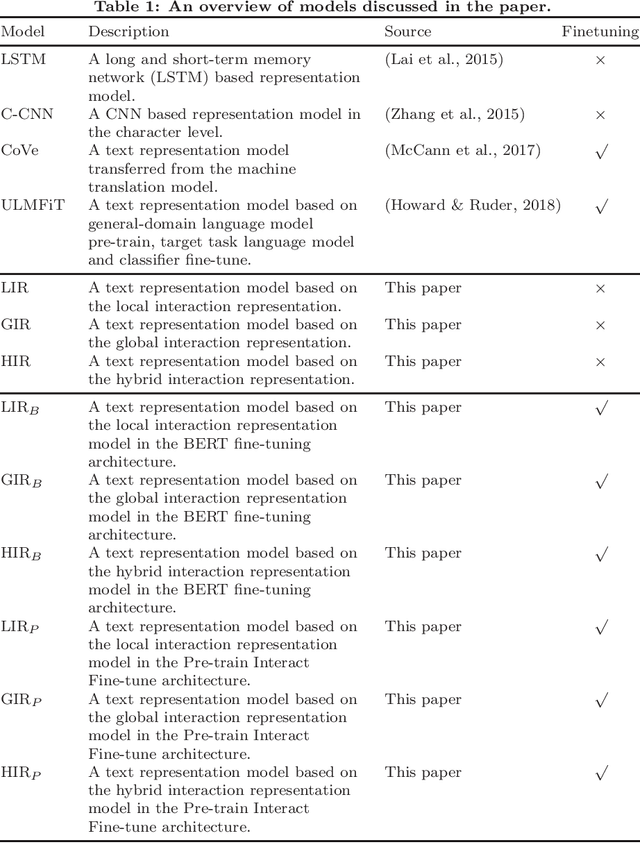
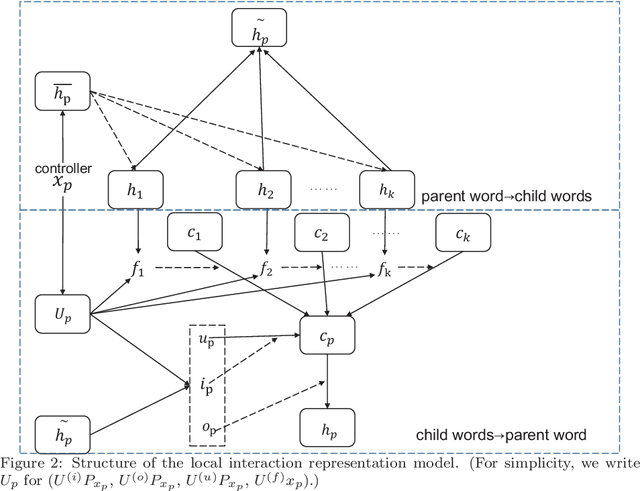
Abstract:Text representation can aid machines in understanding text. Previous work on text representation often focuses on the so-called forward implication, i.e., preceding words are taken as the context of later words for creating representations, thus ignoring the fact that the semantics of a text segment is a product of the mutual implication of words in the text: later words contribute to the meaning of preceding words. We introduce the concept of interaction and propose a two-perspective interaction representation, that encapsulates a local and a global interaction representation. Here, a local interaction representation is one that interacts among words with parent-children relationships on the syntactic trees and a global interaction interpretation is one that interacts among all the words in a sentence. We combine the two interaction representations to develop a Hybrid Interaction Representation (HIR). Inspired by existing feature-based and fine-tuning-based pretrain-finetuning approaches to language models, we integrate the advantages of feature-based and fine-tuning-based methods to propose the Pre-train, Interact, Fine-tune (PIF) architecture. We evaluate our proposed models on five widely-used datasets for text classification tasks. Our ensemble method, outperforms state-of-the-art baselines with improvements ranging from 2.03% to 3.15% in terms of error rate. In addition, we find that, the improvements of PIF against most state-of-the-art methods is not affected by increasing of the length of the text.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge