Hiroko H. Dodge
Detecting Cognitive Impairment and Psychological Well-being among Older Adults Using Facial, Acoustic, Linguistic, and Cardiovascular Patterns Derived from Remote Conversations
Dec 23, 2024



Abstract:The aging society urgently requires scalable methods to monitor cognitive decline and identify social and psychological factors indicative of dementia risk in older adults. Our machine learning (ML) models captured facial, acoustic, linguistic, and cardiovascular features from 39 individuals with normal cognition or Mild Cognitive Impairment derived from remote video conversations and classified cognitive status, social isolation, neuroticism, and psychological well-being. Our model could distinguish Clinical Dementia Rating Scale (CDR) of 0.5 (vs. 0) with 0.78 area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), social isolation with 0.75 AUC, neuroticism with 0.71 AUC, and negative affect scales with 0.79 AUC. Recent advances in machine learning offer new opportunities to remotely detect cognitive impairment and assess associated factors, such as neuroticism and psychological well-being. Our experiment showed that speech and language patterns were more useful for quantifying cognitive impairment, whereas facial expression and cardiovascular patterns using photoplethysmography (PPG) were more useful for quantifying personality and psychological well-being.
Augmented Risk Prediction for the Onset of Alzheimer's Disease from Electronic Health Records with Large Language Models
May 26, 2024



Abstract:Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the fifth-leading cause of death among Americans aged 65 and older. Screening and early detection of AD and related dementias (ADRD) are critical for timely intervention and for identifying clinical trial participants. The widespread adoption of electronic health records (EHRs) offers an important resource for developing ADRD screening tools such as machine learning based predictive models. Recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) demonstrate their unprecedented capability of encoding knowledge and performing reasoning, which offers them strong potential for enhancing risk prediction. This paper proposes a novel pipeline that augments risk prediction by leveraging the few-shot inference power of LLMs to make predictions on cases where traditional supervised learning methods (SLs) may not excel. Specifically, we develop a collaborative pipeline that combines SLs and LLMs via a confidence-driven decision-making mechanism, leveraging the strengths of SLs in clear-cut cases and LLMs in more complex scenarios. We evaluate this pipeline using a real-world EHR data warehouse from Oregon Health \& Science University (OHSU) Hospital, encompassing EHRs from over 2.5 million patients and more than 20 million patient encounters. Our results show that our proposed approach effectively combines the power of SLs and LLMs, offering significant improvements in predictive performance. This advancement holds promise for revolutionizing ADRD screening and early detection practices, with potential implications for better strategies of patient management and thus improving healthcare.
Detection of Mild Cognitive Impairment Using Facial Features in Video Conversations
Aug 29, 2023



Abstract:Early detection of Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) leads to early interventions to slow the progression from MCI into dementia. Deep Learning (DL) algorithms could help achieve early non-invasive, low-cost detection of MCI. This paper presents the detection of MCI in older adults using DL models based only on facial features extracted from video-recorded conversations at home. We used the data collected from the I-CONECT behavioral intervention study (NCT02871921), where several sessions of semi-structured interviews between socially isolated older individuals and interviewers were video recorded. We develop a framework that extracts spatial holistic facial features using a convolutional autoencoder and temporal information using transformers. Our proposed DL model was able to detect the I-CONECT study participants' cognitive conditions (MCI vs. those with normal cognition (NC)) using facial features. The segments and sequence information of the facial features improved the prediction performance compared with the non-temporal features. The detection accuracy using this combined method reached 88% whereas 84% is the accuracy without applying the segments and sequences information of the facial features within a video on a certain theme.
MC-ViViT: Multi-branch Classifier-ViViT to Detect Mild Cognitive Impairment in Older Adults using Facial Videos
Apr 11, 2023Abstract:Deep machine learning models including Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) have been successful in the detection of Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) using medical images, questionnaires, and videos. This paper proposes a novel Multi-branch Classifier-Video Vision Transformer (MC-ViViT) model to distinguish MCI from those with normal cognition by analyzing facial features. The data comes from the I-CONECT, a behavioral intervention trial aimed at improving cognitive function by providing frequent video chats. MC-ViViT extracts spatiotemporal features of videos in one branch and augments representations by the MC module. The I-CONECT dataset is challenging as the dataset is imbalanced containing Hard-Easy and Positive-Negative samples, which impedes the performance of MC-ViViT. We propose a loss function for Hard-Easy and Positive-Negative Samples (HP Loss) by combining Focal loss and AD-CORRE loss to address the imbalanced problem. Our experimental results on the I-CONECT dataset show the great potential of MC-ViViT in predicting MCI with a high accuracy of 90.63\% accuracy on some of the interview videos.
Improving Mild Cognitive Impairment Prediction via Reinforcement Learning and Dialogue Simulation
Feb 18, 2018
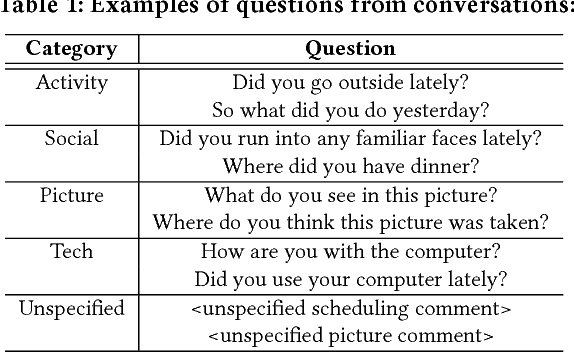


Abstract:Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is a prodromal phase in the progression from normal aging to dementia, especially Alzheimers disease. Even though there is mild cognitive decline in MCI patients, they have normal overall cognition and thus is challenging to distinguish from normal aging. Using transcribed data obtained from recorded conversational interactions between participants and trained interviewers, and applying supervised learning models to these data, a recent clinical trial has shown a promising result in differentiating MCI from normal aging. However, the substantial amount of interactions with medical staff can still incur significant medical care expenses in practice. In this paper, we propose a novel reinforcement learning (RL) framework to train an efficient dialogue agent on existing transcripts from clinical trials. Specifically, the agent is trained to sketch disease-specific lexical probability distribution, and thus to converse in a way that maximizes the diagnosis accuracy and minimizes the number of conversation turns. We evaluate the performance of the proposed reinforcement learning framework on the MCI diagnosis from a real clinical trial. The results show that while using only a few turns of conversation, our framework can significantly outperform state-of-the-art supervised learning approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge