He Qu
Boosting Code-Switching ASR with Mixture of Experts Enhanced Speech-Conditioned LLM
Sep 24, 2024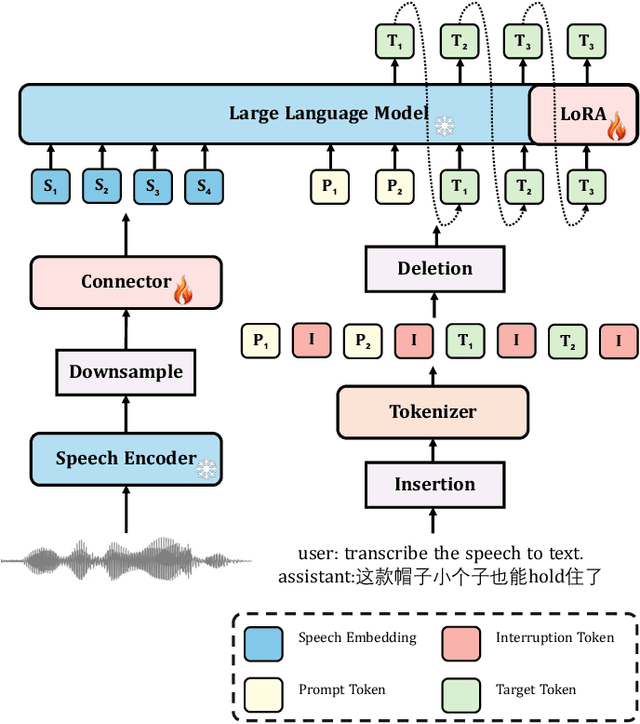
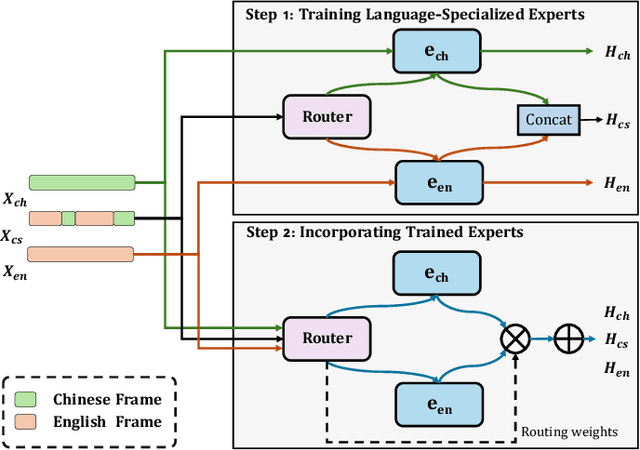
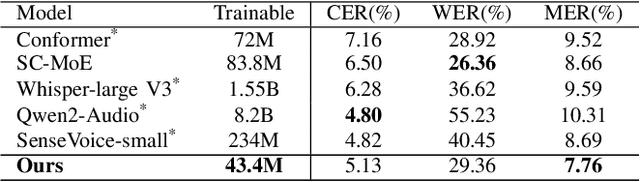
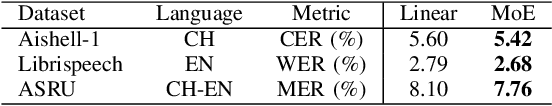
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce a speech-conditioned Large Language Model (LLM) integrated with a Mixture of Experts (MoE) based connector to address the challenge of Code-Switching (CS) in Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR). Specifically, we propose an Insertion and Deletion of Interruption Token (IDIT) mechanism for better transfer text generation ability of LLM to speech recognition task. We also present a connecter with MoE architecture that manages multiple languages efficiently. To further enhance the collaboration of multiple experts and leverage the understanding capabilities of LLM, we propose a two-stage progressive training strategy: 1) The connector is unfrozen and trained with language-specialized experts to map speech representations to the text space. 2) The connector and LLM LoRA adaptor are trained with the proposed IDIT mechanism and all experts are activated to learn general representations. Experimental results demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms state-of-the-art models, including end-to-end and large-scale audio-language models.
Zero-Shot Sing Voice Conversion: built upon clustering-based phoneme representations
Sep 12, 2024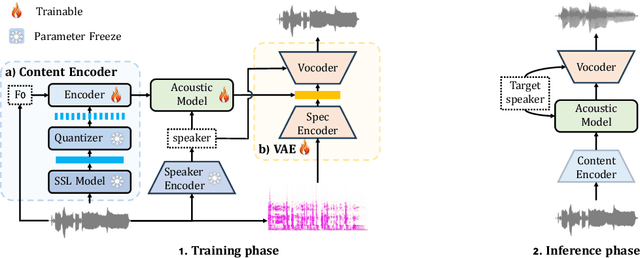
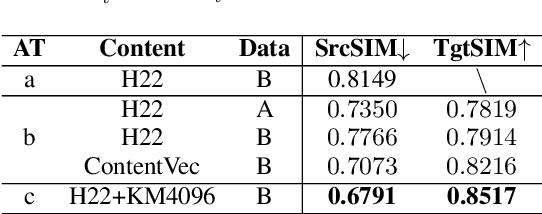
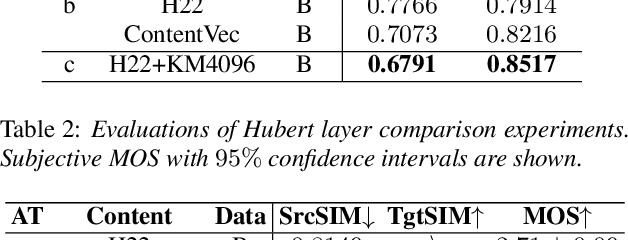
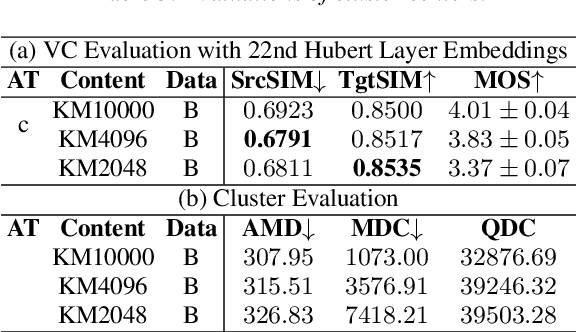
Abstract:This study presents an innovative Zero-Shot any-to-any Singing Voice Conversion (SVC) method, leveraging a novel clustering-based phoneme representation to effectively separate content, timbre, and singing style. This approach enables precise voice characteristic manipulation. We discovered that datasets with fewer recordings per artist are more susceptible to timbre leakage. Extensive testing on over 10,000 hours of singing and user feedback revealed our model significantly improves sound quality and timbre accuracy, aligning with our objectives and advancing voice conversion technology. Furthermore, this research advances zero-shot SVC and sets the stage for future work on discrete speech representation, emphasizing the preservation of rhyme.
Dynamic Language Group-Based MoE: Enhancing Efficiency and Flexibility for Code-Switching Speech Recognition
Jul 26, 2024



Abstract:The Mixture of Experts (MoE) approach is ideally suited for tackling multilingual and code-switching (CS) challenges due to its multi-expert architecture. This work introduces the DLG-MoE, which is optimized for bilingual and CS scenarios. Our novel Dynamic Language Group-based MoE layer features a language router with shared weights for explicit language modeling, while independent unsupervised routers within the language group handle attributes beyond language. This structure not only enhances expert extension capabilities but also supports dynamic top-k training, allowing for flexible inference across various top-k values and improving overall performance. The model requires no pre-training and supports streaming recognition, achieving state-of-the-art (SOTA) results with unmatched flexibility compared to other methods. The Code will be released.
Minimally-Supervised Speech Synthesis with Conditional Diffusion Model and Language Model: A Comparative Study of Semantic Coding
Jul 28, 2023Abstract:Recently, there has been a growing interest in text-to-speech (TTS) methods that can be trained with minimal supervision by combining two types of discrete speech representations and using two sequence-to-sequence tasks to decouple TTS. To address the challenges associated with high dimensionality and waveform distortion in discrete representations, we propose Diff-LM-Speech, which models semantic embeddings into mel-spectrogram based on diffusion models and introduces a prompt encoder structure based on variational autoencoders and prosody bottlenecks to improve prompt representation capabilities. Autoregressive language models often suffer from missing and repeated words, while non-autoregressive frameworks face expression averaging problems due to duration prediction models. To address these issues, we propose Tetra-Diff-Speech, which designs a duration diffusion model to achieve diverse prosodic expressions. While we expect the information content of semantic coding to be between that of text and acoustic coding, existing models extract semantic coding with a lot of redundant information and dimensionality explosion. To verify that semantic coding is not necessary, we propose Tri-Diff-Speech. Experimental results show that our proposed methods outperform baseline methods. We provide a website with audio samples.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge