Fengrun Zhang
Boosting Code-Switching ASR with Mixture of Experts Enhanced Speech-Conditioned LLM
Sep 24, 2024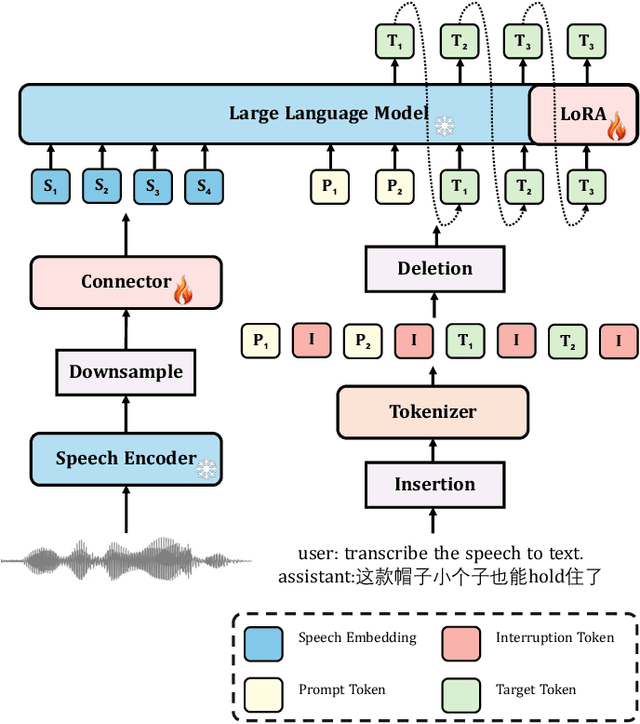
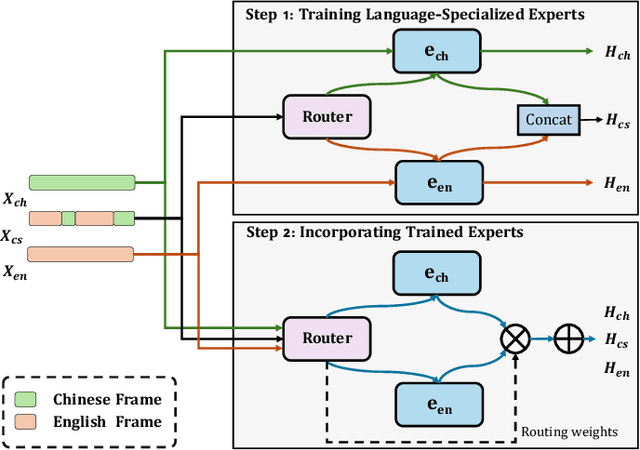
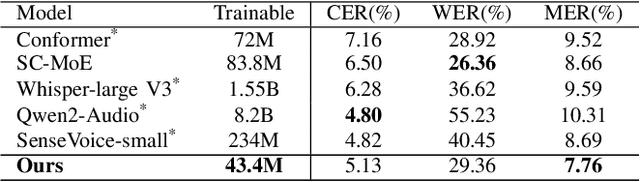
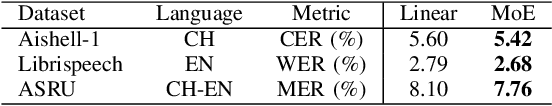
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce a speech-conditioned Large Language Model (LLM) integrated with a Mixture of Experts (MoE) based connector to address the challenge of Code-Switching (CS) in Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR). Specifically, we propose an Insertion and Deletion of Interruption Token (IDIT) mechanism for better transfer text generation ability of LLM to speech recognition task. We also present a connecter with MoE architecture that manages multiple languages efficiently. To further enhance the collaboration of multiple experts and leverage the understanding capabilities of LLM, we propose a two-stage progressive training strategy: 1) The connector is unfrozen and trained with language-specialized experts to map speech representations to the text space. 2) The connector and LLM LoRA adaptor are trained with the proposed IDIT mechanism and all experts are activated to learn general representations. Experimental results demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms state-of-the-art models, including end-to-end and large-scale audio-language models.
Disentangling Age and Identity with a Mutual Information Minimization Approach for Cross-Age Speaker Verification
Sep 24, 2024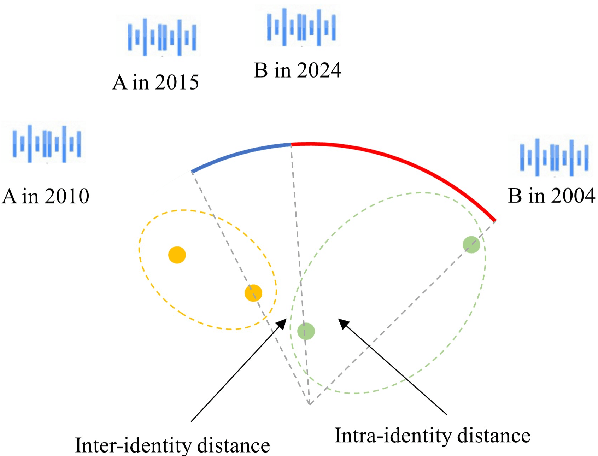
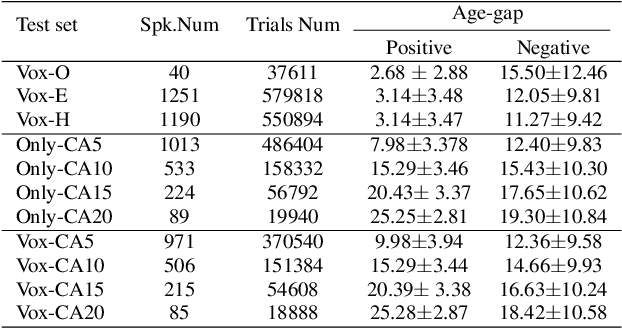
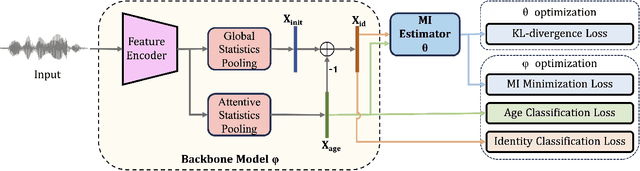
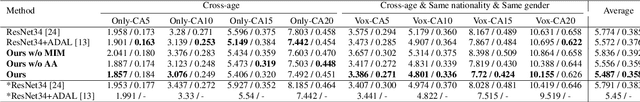
Abstract:There has been an increasing research interest in cross-age speaker verification~(CASV). However, existing speaker verification systems perform poorly in CASV due to the great individual differences in voice caused by aging. In this paper, we propose a disentangled representation learning framework for CASV based on mutual information~(MI) minimization. In our method, a backbone model is trained to disentangle the identity- and age-related embeddings from speaker information, and an MI estimator is trained to minimize the correlation between age- and identity-related embeddings via MI minimization, resulting in age-invariant speaker embeddings. Furthermore, by using the age gaps between positive and negative samples, we propose an aging-aware MI minimization loss function that allows the backbone model to focus more on the vocal changes with large age gaps. Experimental results show that the proposed method outperforms other methods on multiple Cross-Age test sets of Vox-CA.
ASD-Diffusion: Anomalous Sound Detection with Diffusion Models
Sep 24, 2024Abstract:Unsupervised Anomalous Sound Detection (ASD) aims to design a generalizable method that can be used to detect anomalies when only normal sounds are given. In this paper, Anomalous Sound Detection based on Diffusion Models (ASD-Diffusion) is proposed for ASD in real-world factories. In our pipeline, the anomalies in acoustic features are reconstructed from their noisy corrupted features into their approximate normal pattern. Secondly, a post-processing anomalies filter algorithm is proposed to detect anomalies that exhibit significant deviation from the original input after reconstruction. Furthermore, denoising diffusion implicit model is introduced to accelerate the inference speed by a longer sampling interval of the denoising process. The proposed method is innovative in the application of diffusion models as a new scheme. Experimental results on the development set of DCASE 2023 challenge task 2 outperform the baseline by 7.75%, demonstrating the effectiveness of the proposed method.
Zero-Shot Sing Voice Conversion: built upon clustering-based phoneme representations
Sep 12, 2024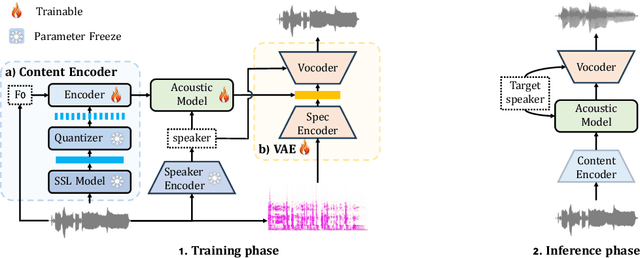
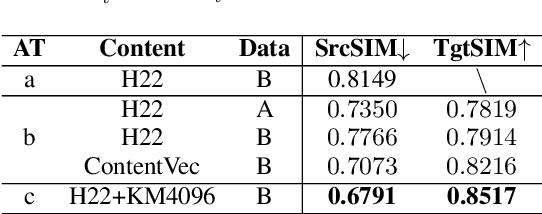
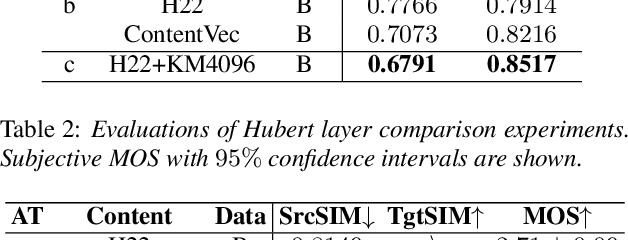
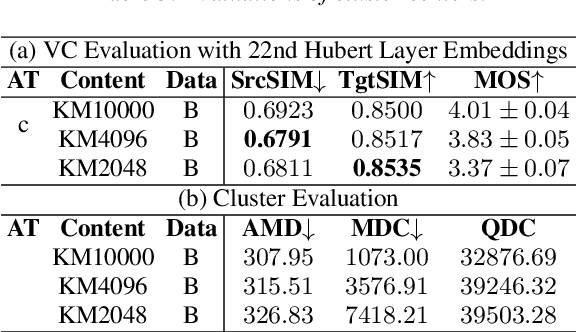
Abstract:This study presents an innovative Zero-Shot any-to-any Singing Voice Conversion (SVC) method, leveraging a novel clustering-based phoneme representation to effectively separate content, timbre, and singing style. This approach enables precise voice characteristic manipulation. We discovered that datasets with fewer recordings per artist are more susceptible to timbre leakage. Extensive testing on over 10,000 hours of singing and user feedback revealed our model significantly improves sound quality and timbre accuracy, aligning with our objectives and advancing voice conversion technology. Furthermore, this research advances zero-shot SVC and sets the stage for future work on discrete speech representation, emphasizing the preservation of rhyme.
Multimodal Emotion Recognition with Vision-language Prompting and Modality Dropout
Sep 11, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we present our solution for the Second Multimodal Emotion Recognition Challenge Track 1(MER2024-SEMI). To enhance the accuracy and generalization performance of emotion recognition, we propose several methods for Multimodal Emotion Recognition. Firstly, we introduce EmoVCLIP, a model fine-tuned based on CLIP using vision-language prompt learning, designed for video-based emotion recognition tasks. By leveraging prompt learning on CLIP, EmoVCLIP improves the performance of pre-trained CLIP on emotional videos. Additionally, to address the issue of modality dependence in multimodal fusion, we employ modality dropout for robust information fusion. Furthermore, to aid Baichuan in better extracting emotional information, we suggest using GPT-4 as the prompt for Baichuan. Lastly, we utilize a self-training strategy to leverage unlabeled videos. In this process, we use unlabeled videos with high-confidence pseudo-labels generated by our model and incorporate them into the training set. Experimental results demonstrate that our model ranks 1st in the MER2024-SEMI track, achieving an accuracy of 90.15% on the test set.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge