Guangyuan Wang
Wan-Animate: Unified Character Animation and Replacement with Holistic Replication
Sep 17, 2025
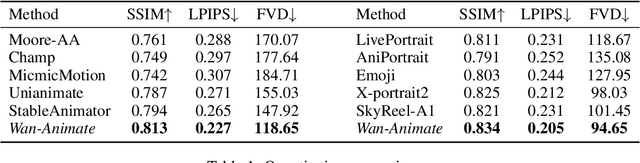
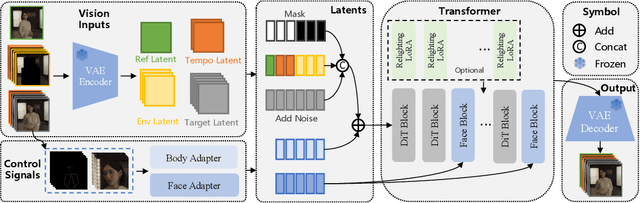
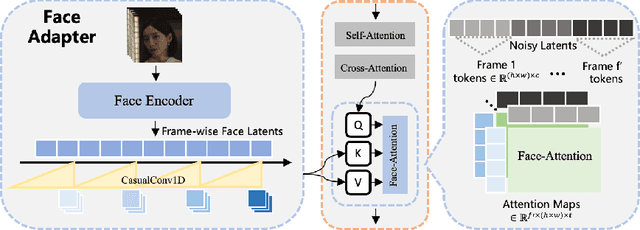
Abstract:We introduce Wan-Animate, a unified framework for character animation and replacement. Given a character image and a reference video, Wan-Animate can animate the character by precisely replicating the expressions and movements of the character in the video to generate high-fidelity character videos. Alternatively, it can integrate the animated character into the reference video to replace the original character, replicating the scene's lighting and color tone to achieve seamless environmental integration. Wan-Animate is built upon the Wan model. To adapt it for character animation tasks, we employ a modified input paradigm to differentiate between reference conditions and regions for generation. This design unifies multiple tasks into a common symbolic representation. We use spatially-aligned skeleton signals to replicate body motion and implicit facial features extracted from source images to reenact expressions, enabling the generation of character videos with high controllability and expressiveness. Furthermore, to enhance environmental integration during character replacement, we develop an auxiliary Relighting LoRA. This module preserves the character's appearance consistency while applying the appropriate environmental lighting and color tone. Experimental results demonstrate that Wan-Animate achieves state-of-the-art performance. We are committed to open-sourcing the model weights and its source code.
Animate Anyone 2: High-Fidelity Character Image Animation with Environment Affordance
Feb 10, 2025



Abstract:Recent character image animation methods based on diffusion models, such as Animate Anyone, have made significant progress in generating consistent and generalizable character animations. However, these approaches fail to produce reasonable associations between characters and their environments. To address this limitation, we introduce Animate Anyone 2, aiming to animate characters with environment affordance. Beyond extracting motion signals from source video, we additionally capture environmental representations as conditional inputs. The environment is formulated as the region with the exclusion of characters and our model generates characters to populate these regions while maintaining coherence with the environmental context. We propose a shape-agnostic mask strategy that more effectively characterizes the relationship between character and environment. Furthermore, to enhance the fidelity of object interactions, we leverage an object guider to extract features of interacting objects and employ spatial blending for feature injection. We also introduce a pose modulation strategy that enables the model to handle more diverse motion patterns. Experimental results demonstrate the superior performance of the proposed method.
Langevin Soft Actor-Critic: Efficient Exploration through Uncertainty-Driven Critic Learning
Jan 29, 2025



Abstract:Existing actor-critic algorithms, which are popular for continuous control reinforcement learning (RL) tasks, suffer from poor sample efficiency due to lack of principled exploration mechanism within them. Motivated by the success of Thompson sampling for efficient exploration in RL, we propose a novel model-free RL algorithm, Langevin Soft Actor Critic (LSAC), which prioritizes enhancing critic learning through uncertainty estimation over policy optimization. LSAC employs three key innovations: approximate Thompson sampling through distributional Langevin Monte Carlo (LMC) based $Q$ updates, parallel tempering for exploring multiple modes of the posterior of the $Q$ function, and diffusion synthesized state-action samples regularized with $Q$ action gradients. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that LSAC outperforms or matches the performance of mainstream model-free RL algorithms for continuous control tasks. Notably, LSAC marks the first successful application of an LMC based Thompson sampling in continuous control tasks with continuous action spaces.
High-Resolution Volumetric Reconstruction for Clothed Humans
Jul 25, 2023



Abstract:We present a novel method for reconstructing clothed humans from a sparse set of, e.g., 1 to 6 RGB images. Despite impressive results from recent works employing deep implicit representation, we revisit the volumetric approach and demonstrate that better performance can be achieved with proper system design. The volumetric representation offers significant advantages in leveraging 3D spatial context through 3D convolutions, and the notorious quantization error is largely negligible with a reasonably large yet affordable volume resolution, e.g., 512. To handle memory and computation costs, we propose a sophisticated coarse-to-fine strategy with voxel culling and subspace sparse convolution. Our method starts with a discretized visual hull to compute a coarse shape and then focuses on a narrow band nearby the coarse shape for refinement. Once the shape is reconstructed, we adopt an image-based rendering approach, which computes the colors of surface points by blending input images with learned weights. Extensive experimental results show that our method significantly reduces the mean point-to-surface (P2S) precision of state-of-the-art methods by more than 50% to achieve approximately 2mm accuracy with a 512 volume resolution. Additionally, images rendered from our textured model achieve a higher peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) compared to state-of-the-art methods.
Cluster Contrast for Unsupervised Person Re-Identification
Apr 12, 2021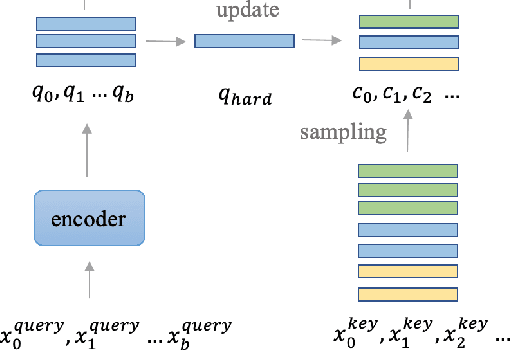
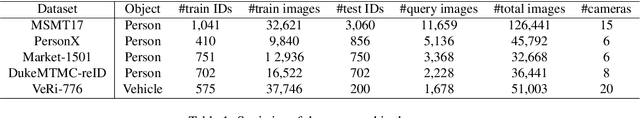
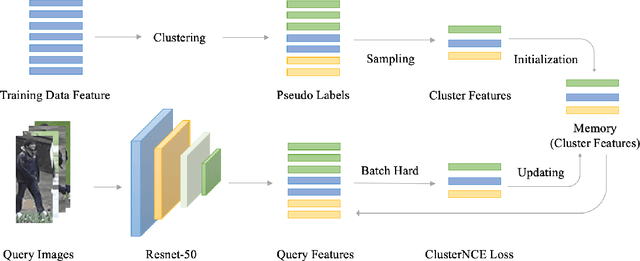
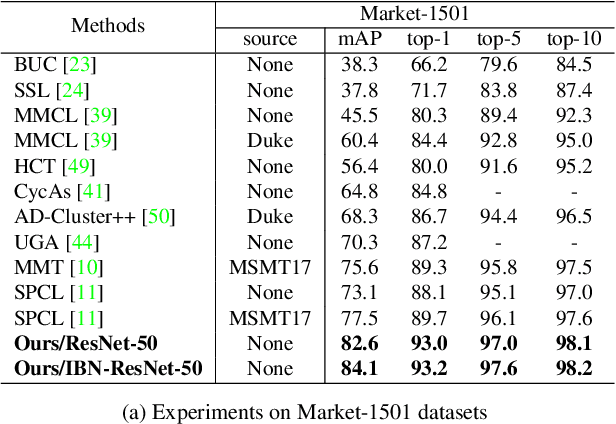
Abstract:Unsupervised person re-identification (re-ID) attracts increasing attention due to its practical applications in industry. State-of-the-art unsupervised re-ID methods train the neural networks using a memory-based non-parametric softmax loss. They store the pre-computed instance feature vectors inside the memory, assign pseudo labels to them us-ing clustering algorithm, and compare the query instances to the cluster using a form of contrastive loss. During training, the instance feature vectors are updated. How-ever, due to the varying cluster size, the updating progress for each cluster is inconsistent. To solve this problem, we present Cluster Contrast which stores feature vectors and computes contrast loss in the cluster level. We demonstrate that the inconsistency problem for cluster feature representation can be solved by the cluster-level memory dictionary.By straightforwardly applying Cluster Contrast to a standard unsupervised re-ID pipeline, it achieves considerable improvements of 9.5%, 7.5%, 6.6% compared to state-of-the-art purely unsupervised re-ID methods and 5.1%, 4.0%,6.5% mAP compared to the state-of-the-art unsupervised domain adaptation re-ID methods on the Market, Duke, andMSMT17 datasets.Our source code is available at https://github.com/alibaba/cluster-contrast.
Spherical Text Embedding
Nov 04, 2019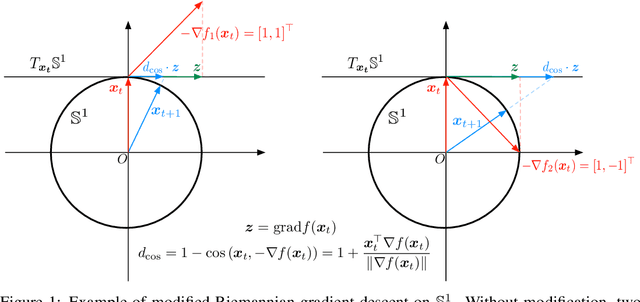
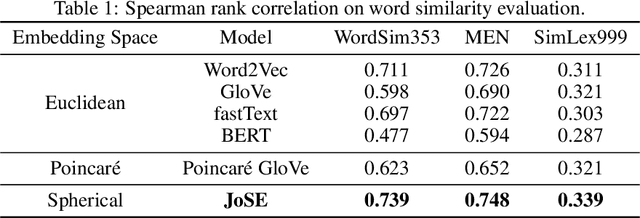


Abstract:Unsupervised text embedding has shown great power in a wide range of NLP tasks. While text embeddings are typically learned in the Euclidean space, directional similarity is often more effective in tasks such as word similarity and document clustering, which creates a gap between the training stage and usage stage of text embedding. To close this gap, we propose a spherical generative model based on which unsupervised word and paragraph embeddings are jointly learned. To learn text embeddings in the spherical space, we develop an efficient optimization algorithm with convergence guarantee based on Riemannian optimization. Our model enjoys high efficiency and achieves state-of-the-art performances on various text embedding tasks including word similarity and document clustering.
CatE: Category-Name GuidedWord Embedding
Aug 20, 2019



Abstract:Unsupervised word embedding has benefited a wide spectrum of NLP tasks due to its effectiveness of encoding word semantics in distributed word representations. However, unsupervised word embedding is a generic representation, not optimized for specific tasks. In this work, we propose a weakly-supervised word embedding framework, CatE. It uses category names to guide word embedding and effectively selects category representative words to regularize the embedding space where the categories are well separated. Experiments show that our model outperforms unsupervised word embedding models significantly on both document classification and category representative words retrieval tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge