Gilles Hacheme
Optimizing Cloud-to-GPU Throughput for Deep Learning With Earth Observation Data
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:Training deep learning models on petabyte-scale Earth observation (EO) data requires separating compute resources from data storage. However, standard PyTorch data loaders cannot keep modern GPUs utilized when streaming GeoTIFF files directly from cloud storage. In this work, we benchmark GeoTIFF loading throughput from both cloud object storage and local SSD, systematically testing different loader configurations and data parameters. We focus on tile-aligned reads and worker thread pools, using Bayesian optimization to find optimal settings for each storage type. Our optimized configurations increase remote data loading throughput by 20x and local throughput by 4x compared to default settings. On three public EO benchmarks, models trained with optimized remote loading achieve the same accuracy as local training within identical time budgets. We improve validation IoU by 6-15% and maintain 85-95% GPU utilization versus 0-30% with standard configurations. Code is publicly available at https://github.com/microsoft/pytorch-cloud-geotiff-optimization
Distribution Shifts at Scale: Out-of-distribution Detection in Earth Observation
Dec 18, 2024Abstract:Training robust deep learning models is critical in Earth Observation, where globally deployed models often face distribution shifts that degrade performance, especially in low-data regions. Out-of-distribution (OOD) detection addresses this challenge by identifying inputs that differ from in-distribution (ID) data. However, existing methods either assume access to OOD data or compromise primary task performance, making them unsuitable for real-world deployment. We propose TARDIS, a post-hoc OOD detection method for scalable geospatial deployments. The core novelty lies in generating surrogate labels by integrating information from ID data and unknown distributions, enabling OOD detection at scale. Our method takes a pre-trained model, ID data, and WILD samples, disentangling the latter into surrogate ID and surrogate OOD labels based on internal activations, and fits a binary classifier as an OOD detector. We validate TARDIS on EuroSAT and xBD datasets, across 17 experimental setups covering covariate and semantic shifts, showing that it performs close to the theoretical upper bound in assigning surrogate ID and OOD samples in 13 cases. To demonstrate scalability, we deploy TARDIS on the Fields of the World dataset, offering actionable insights into pre-trained model behavior for large-scale deployments. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/microsoft/geospatial-ood-detection.
FonMTL: Towards Multitask Learning for the Fon Language
Sep 11, 2023



Abstract:The Fon language, spoken by an average 2 million of people, is a truly low-resourced African language, with a limited online presence, and existing datasets (just to name but a few). Multitask learning is a learning paradigm that aims to improve the generalization capacity of a model by sharing knowledge across different but related tasks: this could be prevalent in very data-scarce scenarios. In this paper, we present the first explorative approach to multitask learning, for model capabilities enhancement in Natural Language Processing for the Fon language. Specifically, we explore the tasks of Named Entity Recognition (NER) and Part of Speech Tagging (POS) for Fon. We leverage two language model heads as encoders to build shared representations for the inputs, and we use linear layers blocks for classification relative to each task. Our results on the NER and POS tasks for Fon, show competitive (or better) performances compared to several multilingual pretrained language models finetuned on single tasks. Additionally, we perform a few ablation studies to leverage the efficiency of two different loss combination strategies and find out that the equal loss weighting approach works best in our case. Our code is open-sourced at https://github.com/bonaventuredossou/multitask_fon.
AfriQA: Cross-lingual Open-Retrieval Question Answering for African Languages
May 11, 2023



Abstract:African languages have far less in-language content available digitally, making it challenging for question answering systems to satisfy the information needs of users. Cross-lingual open-retrieval question answering (XOR QA) systems -- those that retrieve answer content from other languages while serving people in their native language -- offer a means of filling this gap. To this end, we create AfriQA, the first cross-lingual QA dataset with a focus on African languages. AfriQA includes 12,000+ XOR QA examples across 10 African languages. While previous datasets have focused primarily on languages where cross-lingual QA augments coverage from the target language, AfriQA focuses on languages where cross-lingual answer content is the only high-coverage source of answer content. Because of this, we argue that African languages are one of the most important and realistic use cases for XOR QA. Our experiments demonstrate the poor performance of automatic translation and multilingual retrieval methods. Overall, AfriQA proves challenging for state-of-the-art QA models. We hope that the dataset enables the development of more equitable QA technology.
A Few Thousand Translations Go a Long Way! Leveraging Pre-trained Models for African News Translation
May 04, 2022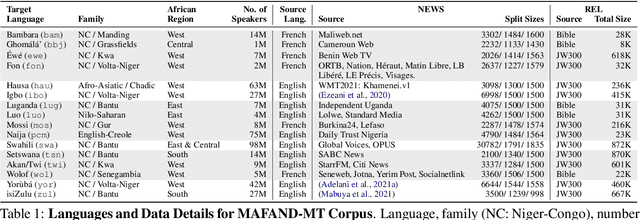
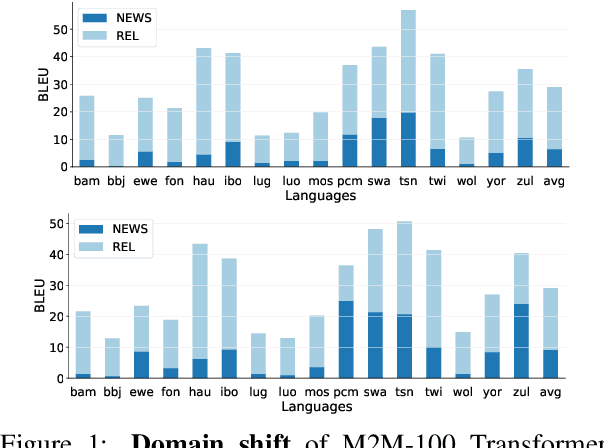
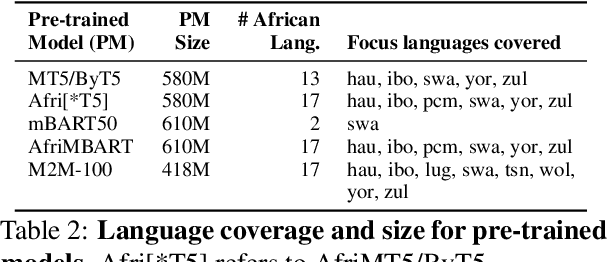
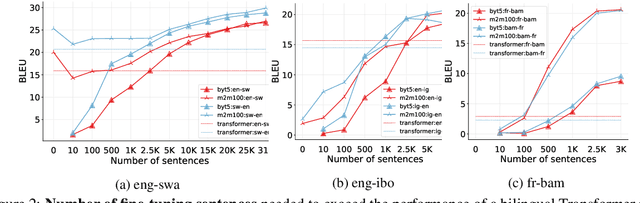
Abstract:Recent advances in the pre-training of language models leverage large-scale datasets to create multilingual models. However, low-resource languages are mostly left out in these datasets. This is primarily because many widely spoken languages are not well represented on the web and therefore excluded from the large-scale crawls used to create datasets. Furthermore, downstream users of these models are restricted to the selection of languages originally chosen for pre-training. This work investigates how to optimally leverage existing pre-trained models to create low-resource translation systems for 16 African languages. We focus on two questions: 1) How can pre-trained models be used for languages not included in the initial pre-training? and 2) How can the resulting translation models effectively transfer to new domains? To answer these questions, we create a new African news corpus covering 16 languages, of which eight languages are not part of any existing evaluation dataset. We demonstrate that the most effective strategy for transferring both to additional languages and to additional domains is to fine-tune large pre-trained models on small quantities of high-quality translation data.
GAM(L)A: An econometric model for interpretable Machine Learning
Mar 17, 2022



Abstract:Despite their high predictive performance, random forest and gradient boosting are often considered as black boxes or uninterpretable models which has raised concerns from practitioners and regulators. As an alternative, we propose in this paper to use partial linear models that are inherently interpretable. Specifically, this article introduces GAM-lasso (GAMLA) and GAM-autometrics (GAMA), denoted as GAM(L)A in short. GAM(L)A combines parametric and non-parametric functions to accurately capture linearities and non-linearities prevailing between dependent and explanatory variables, and a variable selection procedure to control for overfitting issues. Estimation relies on a two-step procedure building upon the double residual method. We illustrate the predictive performance and interpretability of GAM(L)A on a regression and a classification problem. The results show that GAM(L)A outperforms parametric models augmented by quadratic, cubic and interaction effects. Moreover, the results also suggest that the performance of GAM(L)A is not significantly different from that of random forest and gradient boosting.
English2Gbe: A multilingual machine translation model for {Fon/Ewe}Gbe
Dec 13, 2021


Abstract:Language is an essential factor of emancipation. Unfortunately, most of the more than 2,000 African languages are low-resourced. The community has recently used machine translation to revive and strengthen several African languages. However, the trained models are often bilingual, resulting in a potentially exponential number of models to train and maintain to cover all possible translation directions. Additionally, bilingual models do not leverage the similarity between some of the languages. Consequently, multilingual neural machine translation (NMT) is gaining considerable interest, especially for low-resourced languages. Nevertheless, its adoption by the community is still limited. This paper introduces English2Gbe, a multilingual NMT model capable of translating from English to Ewe or Fon. Using the BLEU, CHRF, and TER scores computed with the Sacrebleu (Post, 2018) package for reproducibility, we show that English2Gbe outperforms bilingual models (English to Ewe and English to Fon) and gives state-of-the-art results on the JW300 benchmark for Fon established by Nekoto et al. (2020). We hope this work will contribute to the massive adoption of Multilingual models inside the community. Our code is made accessible from Github.
Neural Fashion Image Captioning : Accounting for Data Diversity
Jun 24, 2021



Abstract:Image captioning has increasingly large domains of application, and fashion is not an exception. Having automatic item descriptions is of great interest for fashion web platforms hosting sometimes hundreds of thousands of images. This paper is one of the first tackling image captioning for fashion images. To contribute addressing dataset diversity issues, we introduced the InFashAIv1 dataset containing almost 16.000 African fashion item images with their titles, prices and general descriptions. We also used the well known DeepFashion dataset in addition to InFashAIv1. Captions are generated using the Show and Tell model made of CNN encoder and RNN Decoder. We showed that jointly training the model on both datasets improves captions quality for African style fashion images, suggesting a transfer learning from Western style data. The InFashAIv1 dataset is released on Github to encourage works with more diversity inclusion.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge