Peter Nabende
MasakhaPOS: Part-of-Speech Tagging for Typologically Diverse African Languages
May 23, 2023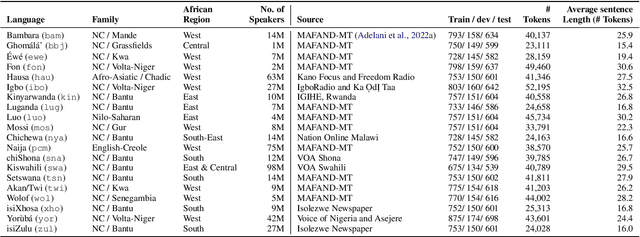
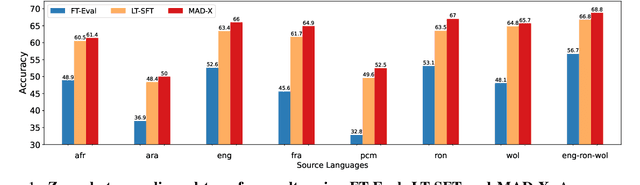
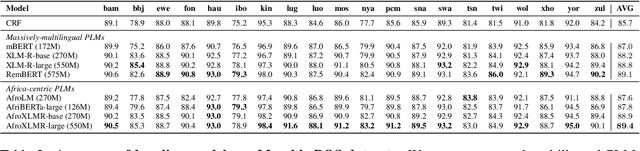
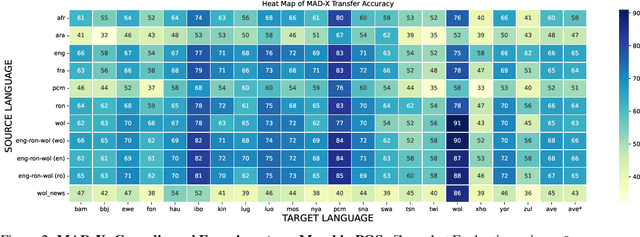
Abstract:In this paper, we present MasakhaPOS, the largest part-of-speech (POS) dataset for 20 typologically diverse African languages. We discuss the challenges in annotating POS for these languages using the UD (universal dependencies) guidelines. We conducted extensive POS baseline experiments using conditional random field and several multilingual pre-trained language models. We applied various cross-lingual transfer models trained with data available in UD. Evaluating on the MasakhaPOS dataset, we show that choosing the best transfer language(s) in both single-source and multi-source setups greatly improves the POS tagging performance of the target languages, in particular when combined with cross-lingual parameter-efficient fine-tuning methods. Crucially, transferring knowledge from a language that matches the language family and morphosyntactic properties seems more effective for POS tagging in unseen languages.
A Few Thousand Translations Go a Long Way! Leveraging Pre-trained Models for African News Translation
May 04, 2022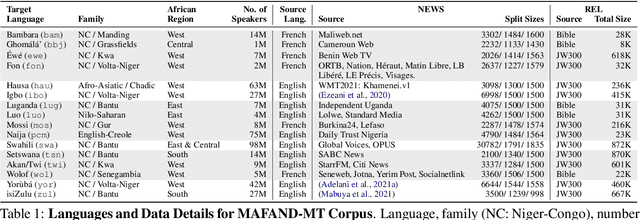
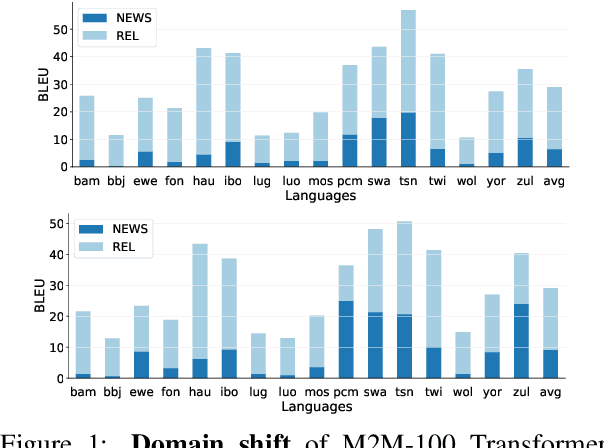
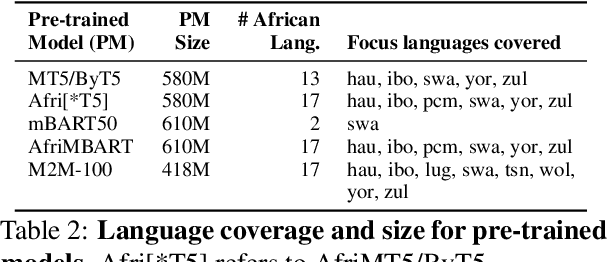
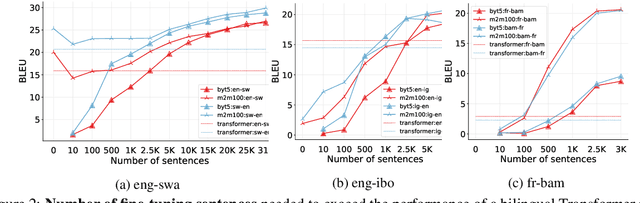
Abstract:Recent advances in the pre-training of language models leverage large-scale datasets to create multilingual models. However, low-resource languages are mostly left out in these datasets. This is primarily because many widely spoken languages are not well represented on the web and therefore excluded from the large-scale crawls used to create datasets. Furthermore, downstream users of these models are restricted to the selection of languages originally chosen for pre-training. This work investigates how to optimally leverage existing pre-trained models to create low-resource translation systems for 16 African languages. We focus on two questions: 1) How can pre-trained models be used for languages not included in the initial pre-training? and 2) How can the resulting translation models effectively transfer to new domains? To answer these questions, we create a new African news corpus covering 16 languages, of which eight languages are not part of any existing evaluation dataset. We demonstrate that the most effective strategy for transferring both to additional languages and to additional domains is to fine-tune large pre-trained models on small quantities of high-quality translation data.
Misinformation detection in Luganda-English code-mixed social media text
Apr 03, 2021



Abstract:The increasing occurrence, forms, and negative effects of misinformation on social media platforms has necessitated more misinformation detection tools. Currently, work is being done addressing COVID-19 misinformation however, there are no misinformation detection tools for any of the 40 distinct indigenous Ugandan languages. This paper addresses this gap by presenting basic language resources and a misinformation detection data set based on code-mixed Luganda-English messages sourced from the Facebook and Twitter social media platforms. Several machine learning methods are applied on the misinformation detection data set to develop classification models for detecting whether a code-mixed Luganda-English message contains misinformation or not. A 10-fold cross validation evaluation of the classification methods in an experimental misinformation detection task shows that a Discriminative Multinomial Naive Bayes (DMNB) method achieves the highest accuracy and F-measure of 78.19% and 77.90% respectively. Also, Support Vector Machine and Bagging ensemble classification models achieve comparable results. These results are promising since the machine learning models are based on n-gram features from only the misinformation detection dataset.
Ontology Driven Disease Incidence Detection on Twitter
Nov 21, 2016



Abstract:In this work we address the issue of generic automated disease incidence monitoring on twitter. We employ an ontology of disease related concepts and use it to obtain a conceptual representation of tweets. Unlike previous key word based systems and topic modeling approaches, our ontological approach allows us to apply more stringent criteria for determining which messages are relevant such as spatial and temporal characteristics whilst giving a stronger guarantee that the resulting models will perform well on new data that may be lexically divergent. We achieve this by training learners on concepts rather than individual words. For training we use a dataset containing mentions of influenza and Listeria and use the learned models to classify datasets containing mentions of an arbitrary selection of other diseases. We show that our ontological approach achieves good performance on this task using a variety of Natural Language Processing Techniques. We also show that word vectors can be learned directly from our concepts to achieve even better results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge