Fuling Wang
Sign Language Translation using Frame and Event Stream: Benchmark Dataset and Algorithms
Mar 09, 2025Abstract:Accurate sign language understanding serves as a crucial communication channel for individuals with disabilities. Current sign language translation algorithms predominantly rely on RGB frames, which may be limited by fixed frame rates, variable lighting conditions, and motion blur caused by rapid hand movements. Inspired by the recent successful application of event cameras in other fields, we propose to leverage event streams to assist RGB cameras in capturing gesture data, addressing the various challenges mentioned above. Specifically, we first collect a large-scale RGB-Event sign language translation dataset using the DVS346 camera, termed VECSL, which contains 15,676 RGB-Event samples, 15,191 glosses, and covers 2,568 Chinese characters. These samples were gathered across a diverse range of indoor and outdoor environments, capturing multiple viewing angles, varying light intensities, and different camera motions. Due to the absence of benchmark algorithms for comparison in this new task, we retrained and evaluated multiple state-of-the-art SLT algorithms, and believe that this benchmark can effectively support subsequent related research. Additionally, we propose a novel RGB-Event sign language translation framework (i.e., M$^2$-SLT) that incorporates fine-grained micro-sign and coarse-grained macro-sign retrieval, achieving state-of-the-art results on the proposed dataset. Both the source code and dataset will be released on https://github.com/Event-AHU/OpenESL.
XiHeFusion: Harnessing Large Language Models for Science Communication in Nuclear Fusion
Feb 08, 2025



Abstract:Nuclear fusion is one of the most promising ways for humans to obtain infinite energy. Currently, with the rapid development of artificial intelligence, the mission of nuclear fusion has also entered a critical period of its development. How to let more people to understand nuclear fusion and join in its research is one of the effective means to accelerate the implementation of fusion. This paper proposes the first large model in the field of nuclear fusion, XiHeFusion, which is obtained through supervised fine-tuning based on the open-source large model Qwen2.5-14B. We have collected multi-source knowledge about nuclear fusion tasks to support the training of this model, including the common crawl, eBooks, arXiv, dissertation, etc. After the model has mastered the knowledge of the nuclear fusion field, we further used the chain of thought to enhance its logical reasoning ability, making XiHeFusion able to provide more accurate and logical answers. In addition, we propose a test questionnaire containing 180+ questions to assess the conversational ability of this science popularization large model. Extensive experimental results show that our nuclear fusion dialogue model, XiHeFusion, can perform well in answering science popularization knowledge. The pre-trained XiHeFusion model is released on https://github.com/Event-AHU/XiHeFusion.
Activating Associative Disease-Aware Vision Token Memory for LLM-Based X-ray Report Generation
Jan 07, 2025Abstract:X-ray image based medical report generation achieves significant progress in recent years with the help of the large language model, however, these models have not fully exploited the effective information in visual image regions, resulting in reports that are linguistically sound but insufficient in describing key diseases. In this paper, we propose a novel associative memory-enhanced X-ray report generation model that effectively mimics the process of professional doctors writing medical reports. It considers both the mining of global and local visual information and associates historical report information to better complete the writing of the current report. Specifically, given an X-ray image, we first utilize a classification model along with its activation maps to accomplish the mining of visual regions highly associated with diseases and the learning of disease query tokens. Then, we employ a visual Hopfield network to establish memory associations for disease-related tokens, and a report Hopfield network to retrieve report memory information. This process facilitates the generation of high-quality reports based on a large language model and achieves state-of-the-art performance on multiple benchmark datasets, including the IU X-ray, MIMIC-CXR, and Chexpert Plus. The source code of this work is released on \url{https://github.com/Event-AHU/Medical_Image_Analysis}.
CXPMRG-Bench: Pre-training and Benchmarking for X-ray Medical Report Generation on CheXpert Plus Dataset
Oct 01, 2024
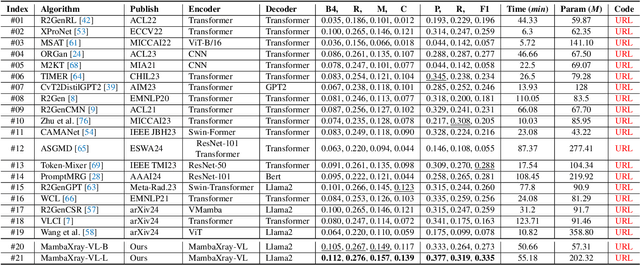
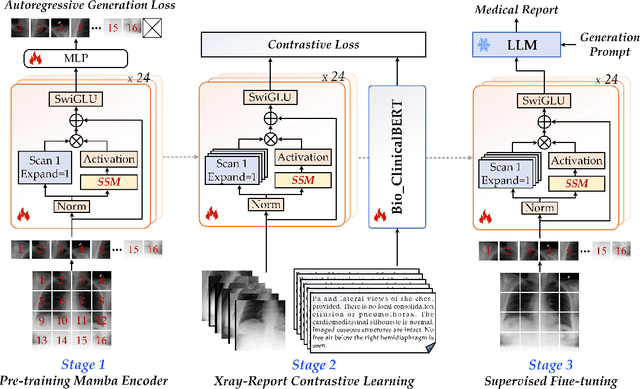
Abstract:X-ray image-based medical report generation (MRG) is a pivotal area in artificial intelligence which can significantly reduce diagnostic burdens and patient wait times. Despite significant progress, we believe that the task has reached a bottleneck due to the limited benchmark datasets and the existing large models' insufficient capability enhancements in this specialized domain. Specifically, the recently released CheXpert Plus dataset lacks comparative evaluation algorithms and their results, providing only the dataset itself. This situation makes the training, evaluation, and comparison of subsequent algorithms challenging. Thus, we conduct a comprehensive benchmarking of existing mainstream X-ray report generation models and large language models (LLMs), on the CheXpert Plus dataset. We believe that the proposed benchmark can provide a solid comparative basis for subsequent algorithms and serve as a guide for researchers to quickly grasp the state-of-the-art models in this field. More importantly, we propose a large model for the X-ray image report generation using a multi-stage pre-training strategy, including self-supervised autoregressive generation and Xray-report contrastive learning, and supervised fine-tuning. Extensive experimental results indicate that the autoregressive pre-training based on Mamba effectively encodes X-ray images, and the image-text contrastive pre-training further aligns the feature spaces, achieving better experimental results. Source code can be found on \url{https://github.com/Event-AHU/Medical_Image_Analysis}.
Event Stream based Sign Language Translation: A High-Definition Benchmark Dataset and A New Algorithm
Aug 20, 2024



Abstract:Sign Language Translation (SLT) is a core task in the field of AI-assisted disability. Unlike traditional SLT based on visible light videos, which is easily affected by factors such as lighting, rapid hand movements, and privacy breaches, this paper proposes the use of high-definition Event streams for SLT, effectively mitigating the aforementioned issues. This is primarily because Event streams have a high dynamic range and dense temporal signals, which can withstand low illumination and motion blur well. Additionally, due to their sparsity in space, they effectively protect the privacy of the target person. More specifically, we propose a new high-resolution Event stream sign language dataset, termed Event-CSL, which effectively fills the data gap in this area of research. It contains 14,827 videos, 14,821 glosses, and 2,544 Chinese words in the text vocabulary. These samples are collected in a variety of indoor and outdoor scenes, encompassing multiple angles, light intensities, and camera movements. We have benchmarked existing mainstream SLT works to enable fair comparison for future efforts. Based on this dataset and several other large-scale datasets, we propose a novel baseline method that fully leverages the Mamba model's ability to integrate temporal information of CNN features, resulting in improved sign language translation outcomes. Both the benchmark dataset and source code will be released on https://github.com/Event-AHU/OpenESL
R2GenCSR: Retrieving Context Samples for Large Language Model based X-ray Medical Report Generation
Aug 19, 2024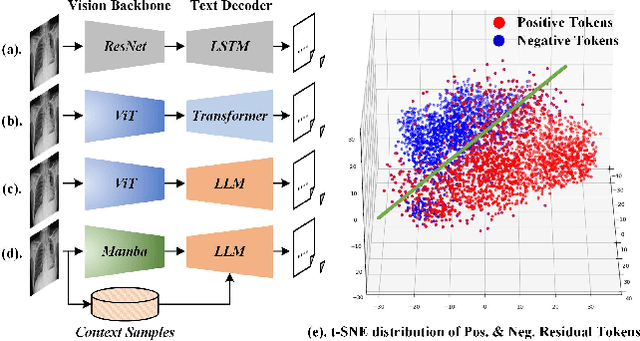
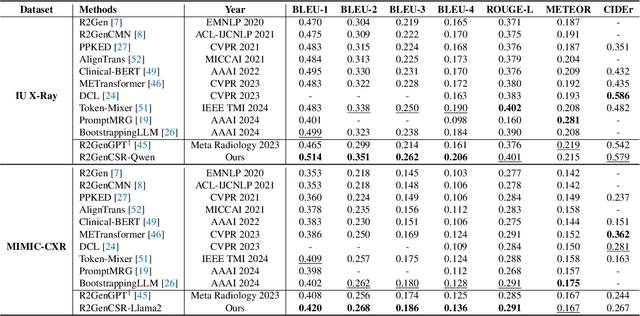
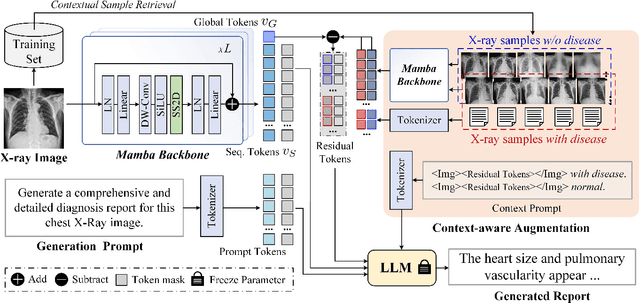
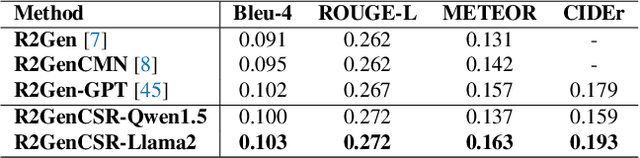
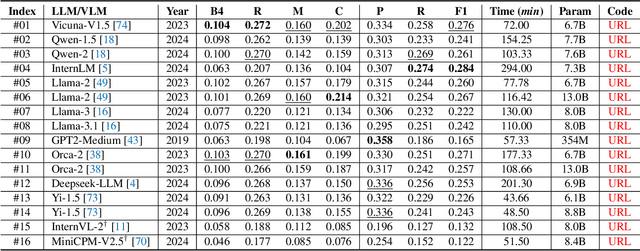
Abstract:Inspired by the tremendous success of Large Language Models (LLMs), existing X-ray medical report generation methods attempt to leverage large models to achieve better performance. They usually adopt a Transformer to extract the visual features of a given X-ray image, and then, feed them into the LLM for text generation. How to extract more effective information for the LLMs to help them improve final results is an urgent problem that needs to be solved. Additionally, the use of visual Transformer models also brings high computational complexity. To address these issues, this paper proposes a novel context-guided efficient X-ray medical report generation framework. Specifically, we introduce the Mamba as the vision backbone with linear complexity, and the performance obtained is comparable to that of the strong Transformer model. More importantly, we perform context retrieval from the training set for samples within each mini-batch during the training phase, utilizing both positively and negatively related samples to enhance feature representation and discriminative learning. Subsequently, we feed the vision tokens, context information, and prompt statements to invoke the LLM for generating high-quality medical reports. Extensive experiments on three X-ray report generation datasets (i.e., IU-Xray, MIMIC-CXR, CheXpert Plus) fully validated the effectiveness of our proposed model. The source code of this work will be released on \url{https://github.com/Event-AHU/Medical_Image_Analysis}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge