Frank H. Miller
Cyst-X: AI-Powered Pancreatic Cancer Risk Prediction from Multicenter MRI in Centralized and Federated Learning
Jul 29, 2025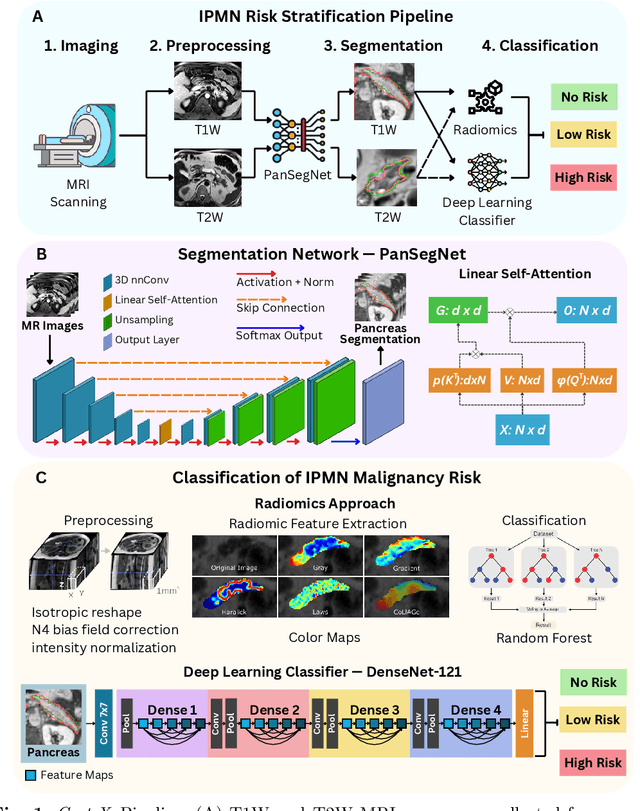

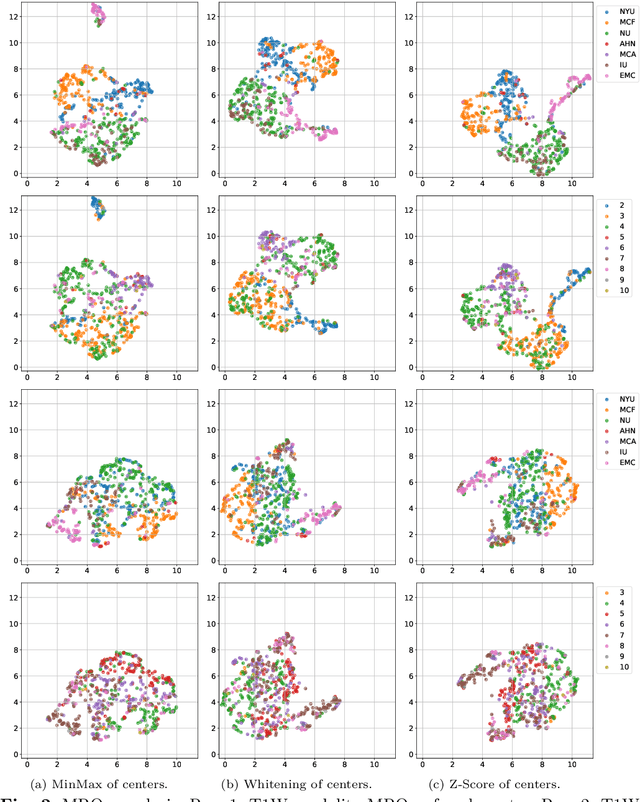
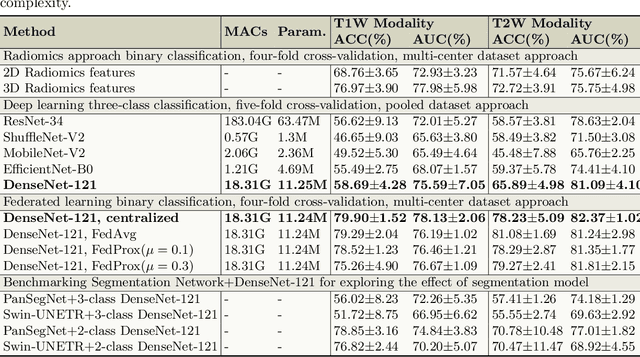
Abstract:Pancreatic cancer is projected to become the second-deadliest malignancy in Western countries by 2030, highlighting the urgent need for better early detection. Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs), key precursors to pancreatic cancer, are challenging to assess with current guidelines, often leading to unnecessary surgeries or missed malignancies. We present Cyst-X, an AI framework that predicts IPMN malignancy using multicenter MRI data, leveraging MRI's superior soft tissue contrast over CT. Trained on 723 T1- and 738 T2-weighted scans from 764 patients across seven institutions, our models (AUC=0.82) significantly outperform both Kyoto guidelines (AUC=0.75) and expert radiologists. The AI-derived imaging features align with known clinical markers and offer biologically meaningful insights. We also demonstrate strong performance in a federated learning setting, enabling collaborative training without sharing patient data. To promote privacy-preserving AI development and improve IPMN risk stratification, the Cyst-X dataset is released as the first large-scale, multi-center pancreatic cysts MRI dataset.
Eyes Tell the Truth: GazeVal Highlights Shortcomings of Generative AI in Medical Imaging
Mar 26, 2025



Abstract:The demand for high-quality synthetic data for model training and augmentation has never been greater in medical imaging. However, current evaluations predominantly rely on computational metrics that fail to align with human expert recognition. This leads to synthetic images that may appear realistic numerically but lack clinical authenticity, posing significant challenges in ensuring the reliability and effectiveness of AI-driven medical tools. To address this gap, we introduce GazeVal, a practical framework that synergizes expert eye-tracking data with direct radiological evaluations to assess the quality of synthetic medical images. GazeVal leverages gaze patterns of radiologists as they provide a deeper understanding of how experts perceive and interact with synthetic data in different tasks (i.e., diagnostic or Turing tests). Experiments with sixteen radiologists revealed that 96.6% of the generated images (by the most recent state-of-the-art AI algorithm) were identified as fake, demonstrating the limitations of generative AI in producing clinically accurate images.
Optimizing Synthetic Data for Enhanced Pancreatic Tumor Segmentation
Jul 27, 2024



Abstract:Pancreatic cancer remains one of the leading causes of cancer-related mortality worldwide. Precise segmentation of pancreatic tumors from medical images is a bottleneck for effective clinical decision-making. However, achieving a high accuracy is often limited by the small size and availability of real patient data for training deep learning models. Recent approaches have employed synthetic data generation to augment training datasets. While promising, these methods may not yet meet the performance benchmarks required for real-world clinical use. This study critically evaluates the limitations of existing generative-AI based frameworks for pancreatic tumor segmentation. We conduct a series of experiments to investigate the impact of synthetic \textit{tumor size} and \textit{boundary definition} precision on model performance. Our findings demonstrate that: (1) strategically selecting a combination of synthetic tumor sizes is crucial for optimal segmentation outcomes, and (2) generating synthetic tumors with precise boundaries significantly improves model accuracy. These insights highlight the importance of utilizing refined synthetic data augmentation for enhancing the clinical utility of segmentation models in pancreatic cancer decision making including diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment plans. Our code will be available at https://github.com/lkpengcs/SynTumorAnalyzer.
Large-Scale Multi-Center CT and MRI Segmentation of Pancreas with Deep Learning
May 20, 2024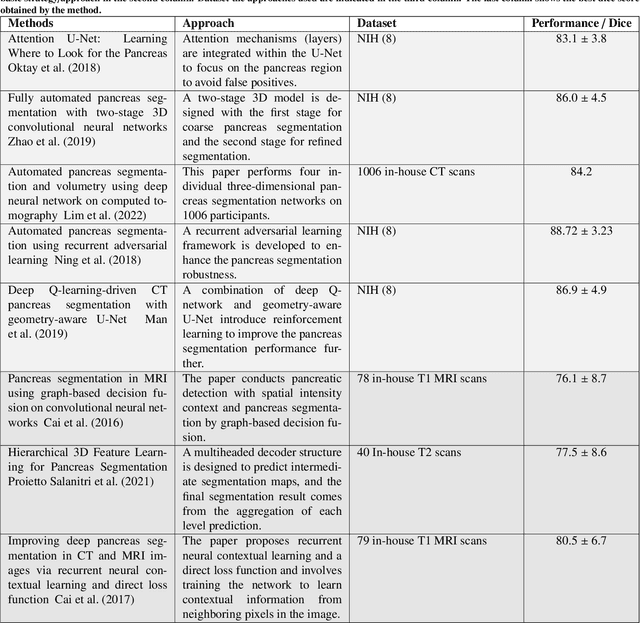
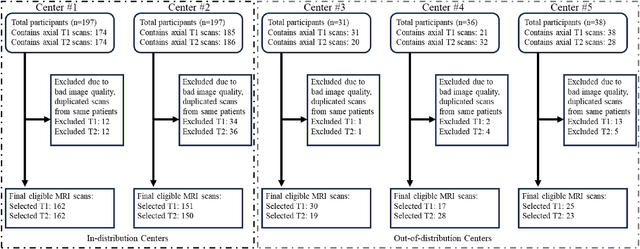
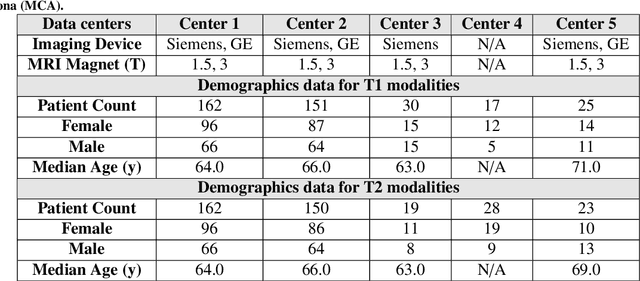
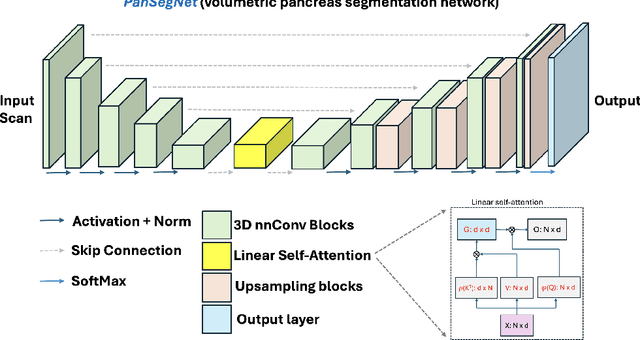
Abstract:Automated volumetric segmentation of the pancreas on cross-sectional imaging is needed for diagnosis and follow-up of pancreatic diseases. While CT-based pancreatic segmentation is more established, MRI-based segmentation methods are understudied, largely due to a lack of publicly available datasets, benchmarking research efforts, and domain-specific deep learning methods. In this retrospective study, we collected a large dataset (767 scans from 499 participants) of T1-weighted (T1W) and T2-weighted (T2W) abdominal MRI series from five centers between March 2004 and November 2022. We also collected CT scans of 1,350 patients from publicly available sources for benchmarking purposes. We developed a new pancreas segmentation method, called PanSegNet, combining the strengths of nnUNet and a Transformer network with a new linear attention module enabling volumetric computation. We tested PanSegNet's accuracy in cross-modality (a total of 2,117 scans) and cross-center settings with Dice and Hausdorff distance (HD95) evaluation metrics. We used Cohen's kappa statistics for intra and inter-rater agreement evaluation and paired t-tests for volume and Dice comparisons, respectively. For segmentation accuracy, we achieved Dice coefficients of 88.3% (std: 7.2%, at case level) with CT, 85.0% (std: 7.9%) with T1W MRI, and 86.3% (std: 6.4%) with T2W MRI. There was a high correlation for pancreas volume prediction with R^2 of 0.91, 0.84, and 0.85 for CT, T1W, and T2W, respectively. We found moderate inter-observer (0.624 and 0.638 for T1W and T2W MRI, respectively) and high intra-observer agreement scores. All MRI data is made available at https://osf.io/kysnj/. Our source code is available at https://github.com/NUBagciLab/PaNSegNet.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge