Ahmet Enis Cetin
Knowledge Distillation Approach for SOS Fusion Staging: Towards Fully Automated Skeletal Maturity Assessment
May 27, 2025



Abstract:We introduce a novel deep learning framework for the automated staging of spheno-occipital synchondrosis (SOS) fusion, a critical diagnostic marker in both orthodontics and forensic anthropology. Our approach leverages a dual-model architecture wherein a teacher model, trained on manually cropped images, transfers its precise spatial understanding to a student model that operates on full, uncropped images. This knowledge distillation is facilitated by a newly formulated loss function that aligns spatial logits as well as incorporates gradient-based attention spatial mapping, ensuring that the student model internalizes the anatomically relevant features without relying on external cropping or YOLO-based segmentation. By leveraging expert-curated data and feedback at each step, our framework attains robust diagnostic accuracy, culminating in a clinically viable end-to-end pipeline. This streamlined approach obviates the need for additional pre-processing tools and accelerates deployment, thereby enhancing both the efficiency and consistency of skeletal maturation assessment in diverse clinical settings.
Intelligent Incident Hypertension Prediction in Obstructive Sleep Apnea
May 27, 2025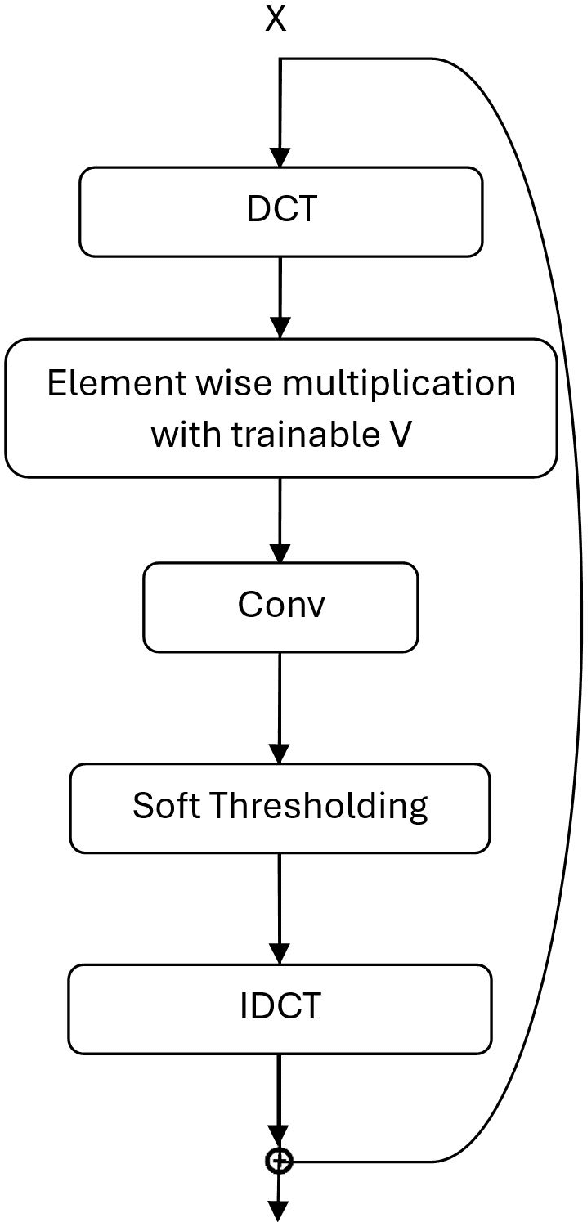



Abstract:Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a significant risk factor for hypertension, primarily due to intermittent hypoxia and sleep fragmentation. Predicting whether individuals with OSA will develop hypertension within five years remains a complex challenge. This study introduces a novel deep learning approach that integrates Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT)-based transfer learning to enhance prediction accuracy. We are the first to incorporate all polysomnography signals together for hypertension prediction, leveraging their collective information to improve model performance. Features were extracted from these signals and transformed into a 2D representation to utilize pre-trained 2D neural networks such as MobileNet, EfficientNet, and ResNet variants. To further improve feature learning, we introduced a DCT layer, which transforms input features into a frequency-based representation, preserving essential spectral information, decorrelating features, and enhancing robustness to noise. This frequency-domain approach, coupled with transfer learning, is especially beneficial for limited medical datasets, as it leverages rich representations from pre-trained networks to improve generalization. By strategically placing the DCT layer at deeper truncation depths within EfficientNet, our model achieved a best area under the curve (AUC) of 72.88%, demonstrating the effectiveness of frequency-domain feature extraction and transfer learning in predicting hypertension risk in OSA patients over a five-year period.
Gradient Attention Map Based Verification of Deep Convolutional Neural Networks with Application to X-ray Image Datasets
Apr 29, 2025



Abstract:Deep learning models have great potential in medical imaging, including orthodontics and skeletal maturity assessment. However, applying a model to data different from its training set can lead to unreliable predictions that may impact patient care. To address this, we propose a comprehensive verification framework that evaluates model suitability through multiple complementary strategies. First, we introduce a Gradient Attention Map (GAM)-based approach that analyzes attention patterns using Grad-CAM and compares them via similarity metrics such as IoU, Dice Similarity, SSIM, Cosine Similarity, Pearson Correlation, KL Divergence, and Wasserstein Distance. Second, we extend verification to early convolutional feature maps, capturing structural mis-alignments missed by attention alone. Finally, we incorporate an additional garbage class into the classification model to explicitly reject out-of-distribution inputs. Experimental results demonstrate that these combined methods effectively identify unsuitable models and inputs, promoting safer and more reliable deployment of deep learning in medical imaging.
Shifts in Doctors' Eye Movements Between Real and AI-Generated Medical Images
Apr 21, 2025Abstract:Eye-tracking analysis plays a vital role in medical imaging, providing key insights into how radiologists visually interpret and diagnose clinical cases. In this work, we first analyze radiologists' attention and agreement by measuring the distribution of various eye-movement patterns, including saccades direction, amplitude, and their joint distribution. These metrics help uncover patterns in attention allocation and diagnostic strategies. Furthermore, we investigate whether and how doctors' gaze behavior shifts when viewing authentic (Real) versus deep-learning-generated (Fake) images. To achieve this, we examine fixation bias maps, focusing on first, last, short, and longest fixations independently, along with detailed saccades patterns, to quantify differences in gaze distribution and visual saliency between authentic and synthetic images.
Eyes Tell the Truth: GazeVal Highlights Shortcomings of Generative AI in Medical Imaging
Mar 26, 2025



Abstract:The demand for high-quality synthetic data for model training and augmentation has never been greater in medical imaging. However, current evaluations predominantly rely on computational metrics that fail to align with human expert recognition. This leads to synthetic images that may appear realistic numerically but lack clinical authenticity, posing significant challenges in ensuring the reliability and effectiveness of AI-driven medical tools. To address this gap, we introduce GazeVal, a practical framework that synergizes expert eye-tracking data with direct radiological evaluations to assess the quality of synthetic medical images. GazeVal leverages gaze patterns of radiologists as they provide a deeper understanding of how experts perceive and interact with synthetic data in different tasks (i.e., diagnostic or Turing tests). Experiments with sixteen radiologists revealed that 96.6% of the generated images (by the most recent state-of-the-art AI algorithm) were identified as fake, demonstrating the limitations of generative AI in producing clinically accurate images.
Edge-Fog Computing-Enabled EEG Data Compression via Asymmetrical Variational Discrete Cosine Transform Network
Mar 13, 2025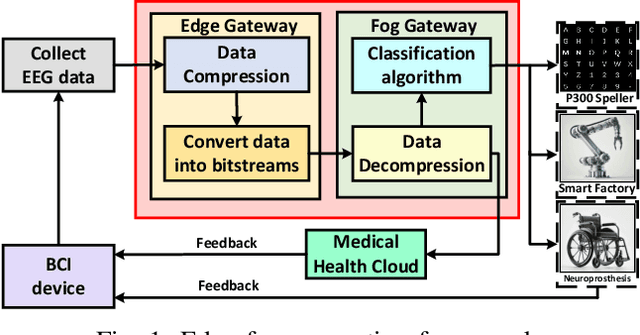
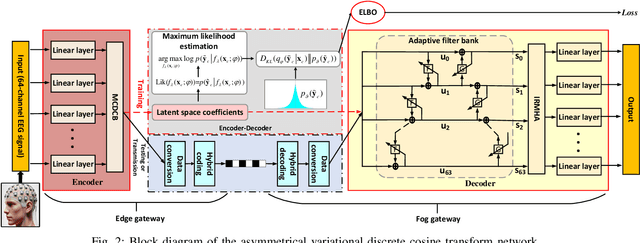
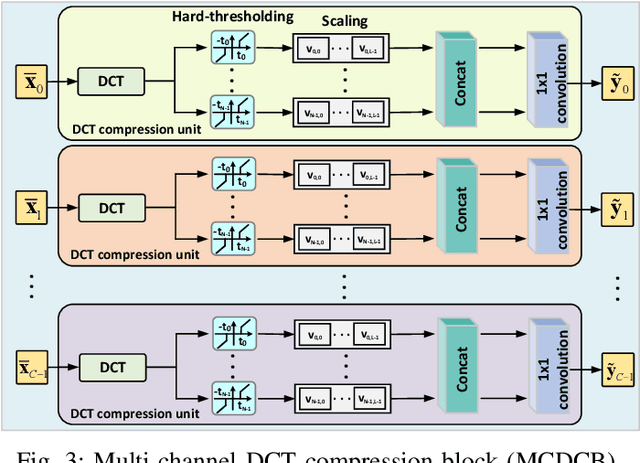
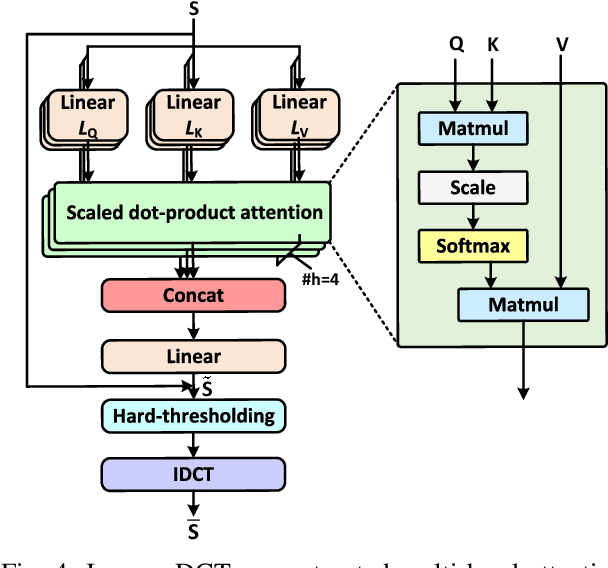
Abstract:The large volume of electroencephalograph (EEG) data produced by brain-computer interface (BCI) systems presents challenges for rapid transmission over bandwidth-limited channels in Internet of Things (IoT) networks. To address the issue, we propose a novel multi-channel asymmetrical variational discrete cosine transform (DCT) network for EEG data compression within an edge-fog computing framework. At the edge level, low-complexity DCT compression units are designed using parallel trainable hard-thresholding and scaling operators to remove redundant data and extract the effective latent space representation. At the fog level, an adaptive filter bank is applied to merge important features from adjacent channels into each individual channel by leveraging inter-channel correlations. Then, the inverse DCT reconstructed multi-head attention is developed to capture both local and global dependencies and reconstruct the original signals. Furthermore, by applying the principles of variational inference, a new evidence lower bound is formulated as the loss function, driving the model to balance compression efficiency and reconstruction accuracy. Experimental results on two public datasets demonstrate that the proposed method achieves superior compression performance without sacrificing any useful information for BCI detection compared with state-of-the-art techniques, indicating a feasible solution for EEG data compression.
Efficient Bearing Sensor Data Compression via an Asymmetrical Autoencoder with a Lifting Wavelet Transform Layer
Jan 20, 2025Abstract:Bearing data compression is vital to manage the large volumes of data generated during condition monitoring. In this paper, a novel asymmetrical autoencoder with a lifting wavelet transform (LWT) layer is developed to compress bearing sensor data. The encoder part of the network consists of a convolutional layer followed by a wavelet filterbank layer. Specifically, a dual-channel convolutional block with diverse convolutional kernel sizes and varying processing depths is integrated into the wavelet filterbank layer to enable comprehensive feature extraction from the wavelet domain. Additionally, the adaptive hard-thresholding nonlinearity is applied to remove redundant components while denoising the primary wavelet coefficients. On the decoder side, inverse LWT, along with multiple linear layers and activation functions, is employed to reconstruct the original signals. Furthermore, to enhance compression efficiency, a sparsity constraint is introduced during training to impose sparsity on the latent representations. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed approach achieves superior data compression performance compared to state-of-the-art methods.
Sparse Mamba: Reinforcing Controllability In Structural State Space Models
Aug 31, 2024

Abstract:In this article, we introduce the concept of controllability and observability to the M amba architecture in our Sparse-Mamba (S-Mamba) for natural language processing (NLP) applications. The structured state space model (SSM) development in recent studies, such as Mamba and Mamba2, outperformed and solved the computational inefficiency of transformers and large language models (LLMs) on longer sequences in small to medium NLP tasks. The Mamba SSMs architecture drops the need for attention layer or MLB blocks in transformers. However, the current Mamba models do not reinforce the controllability on state space equations in the calculation of A, B, C, and D matrices at each time step, which increase the complexity and the computational cost needed. In this article we show that the number of parameters can be significantly decreased by reinforcing controllability in the state space equations in the proposed Sparse-Mamba (S-Mamba), while maintaining the performance. The controllable n x n state matrix A is sparse and it has only n free parameters. Our novel approach will ensure a controllable system and could be the gate key for Mamba 3.
A Probabilistic Hadamard U-Net for MRI Bias Field Correction
Mar 08, 2024Abstract:Magnetic field inhomogeneity correction remains a challenging task in MRI analysis. Most established techniques are designed for brain MRI by supposing that image intensities in the identical tissue follow a uniform distribution. Such an assumption cannot be easily applied to other organs, especially those that are small in size and heterogeneous in texture (large variations in intensity), such as the prostate. To address this problem, this paper proposes a probabilistic Hadamard U-Net (PHU-Net) for prostate MRI bias field correction. First, a novel Hadamard U-Net (HU-Net) is introduced to extract the low-frequency scalar field, multiplied by the original input to obtain the prototypical corrected image. HU-Net converts the input image from the time domain into the frequency domain via Hadamard transform. In the frequency domain, high-frequency components are eliminated using the trainable filter (scaling layer), hard-thresholding layer, and sparsity penalty. Next, a conditional variational autoencoder is used to encode possible bias field-corrected variants into a low-dimensional latent space. Random samples drawn from latent space are then incorporated with a prototypical corrected image to generate multiple plausible images. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of PHU-Net in correcting bias-field in prostate MRI with a fast inference speed. It has also been shown that prostate MRI segmentation accuracy improves with the high-quality corrected images from PHU-Net. The code will be available in the final version of this manuscript.
A novel asymmetrical autoencoder with a sparsifying discrete cosine Stockwell transform layer for gearbox sensor data compression
Oct 04, 2023



Abstract:The lack of an efficient compression model remains a challenge for the wireless transmission of gearbox data in non-contact gear fault diagnosis problems. In this paper, we present a signal-adaptive asymmetrical autoencoder with a transform domain layer to compress sensor signals. First, a new discrete cosine Stockwell transform (DCST) layer is introduced to replace linear layers in a multi-layer autoencoder. A trainable filter is implemented in the DCST domain by utilizing the multiplication property of the convolution. A trainable hard-thresholding layer is applied to reduce redundant data in the DCST layer to make the feature map sparse. In comparison to the linear layer, the DCST layer reduces the number of trainable parameters and improves the accuracy of data reconstruction. Second, training the autoencoder with a sparsifying DCST layer only requires a small number of datasets. The proposed method is superior to other autoencoder-based methods on the University of Connecticut (UoC) and Southeast University (SEU) gearbox datasets, as the average quality score is improved by 2.00% at the lowest and 32.35% at the highest with a limited number of training samples
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge