Emanuel Tewolde
What Does It Take to Be a Good AI Research Agent? Studying the Role of Ideation Diversity
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:AI research agents offer the promise to accelerate scientific progress by automating the design, implementation, and training of machine learning models. However, the field is still in its infancy, and the key factors driving the success or failure of agent trajectories are not fully understood. We examine the role that ideation diversity plays in agent performance. First, we analyse agent trajectories on MLE-bench, a well-known benchmark to evaluate AI research agents, across different models and agent scaffolds. Our analysis reveals that different models and agent scaffolds yield varying degrees of ideation diversity, and that higher-performing agents tend to have increased ideation diversity. Further, we run a controlled experiment where we modify the degree of ideation diversity, demonstrating that higher ideation diversity results in stronger performance. Finally, we strengthen our results by examining additional evaluation metrics beyond the standard medal-based scoring of MLE-bench, showing that our findings still hold across other agent performance metrics.
When Ethics and Payoffs Diverge: LLM Agents in Morally Charged Social Dilemmas
May 25, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have enabled their use in complex agentic roles, involving decision-making with humans or other agents, making ethical alignment a key AI safety concern. While prior work has examined both LLMs' moral judgment and strategic behavior in social dilemmas, there is limited understanding of how they act when moral imperatives directly conflict with rewards or incentives. To investigate this, we introduce Moral Behavior in Social Dilemma Simulation (MoralSim) and evaluate how LLMs behave in the prisoner's dilemma and public goods game with morally charged contexts. In MoralSim, we test a range of frontier models across both game structures and three distinct moral framings, enabling a systematic examination of how LLMs navigate social dilemmas in which ethical norms conflict with payoff-maximizing strategies. Our results show substantial variation across models in both their general tendency to act morally and the consistency of their behavior across game types, the specific moral framing, and situational factors such as opponent behavior and survival risks. Crucially, no model exhibits consistently moral behavior in MoralSim, highlighting the need for caution when deploying LLMs in agentic roles where the agent's "self-interest" may conflict with ethical expectations. Our code is available at https://github.com/sbackmann/moralsim.
Learning and Computation of $Φ$-Equilibria at the Frontier of Tractability
Feb 25, 2025Abstract:$\Phi$-equilibria -- and the associated notion of $\Phi$-regret -- are a powerful and flexible framework at the heart of online learning and game theory, whereby enriching the set of deviations $\Phi$ begets stronger notions of rationality. Recently, Daskalakis, Farina, Fishelson, Pipis, and Schneider (STOC '24) -- abbreviated as DFFPS -- settled the existence of efficient algorithms when $\Phi$ contains only linear maps under a general, $d$-dimensional convex constraint set $\mathcal{X}$. In this paper, we significantly extend their work by resolving the case where $\Phi$ is $k$-dimensional; degree-$\ell$ polynomials constitute a canonical such example with $k = d^{O(\ell)}$. In particular, positing only oracle access to $\mathcal{X}$, we obtain two main positive results: i) a $\text{poly}(n, d, k, \text{log}(1/\epsilon))$-time algorithm for computing $\epsilon$-approximate $\Phi$-equilibria in $n$-player multilinear games, and ii) an efficient online algorithm that incurs average $\Phi$-regret at most $\epsilon$ using $\text{poly}(d, k)/\epsilon^2$ rounds. We also show nearly matching lower bounds in the online learning setting, thereby obtaining for the first time a family of deviations that captures the learnability of $\Phi$-regret. From a technical standpoint, we extend the framework of DFFPS from linear maps to the more challenging case of maps with polynomial dimension. At the heart of our approach is a polynomial-time algorithm for computing an expected fixed point of any $\phi : \mathcal{X} \to \mathcal{X}$ based on the ellipsoid against hope (EAH) algorithm of Papadimitriou and Roughgarden (JACM '08). In particular, our algorithm for computing $\Phi$-equilibria is based on executing EAH in a nested fashion -- each step of EAH itself being implemented by invoking a separate call to EAH.
Expected Variational Inequalities
Feb 25, 2025Abstract:Variational inequalities (VIs) encompass many fundamental problems in diverse areas ranging from engineering to economics and machine learning. However, their considerable expressivity comes at the cost of computational intractability. In this paper, we introduce and analyze a natural relaxation -- which we refer to as expected variational inequalities (EVIs) -- where the goal is to find a distribution that satisfies the VI constraint in expectation. By adapting recent techniques from game theory, we show that, unlike VIs, EVIs can be solved in polynomial time under general (nonmonotone) operators. EVIs capture the seminal notion of correlated equilibria, but enjoy a greater reach beyond games. We also employ our framework to capture and generalize several existing disparate results, including from settings such as smooth games, and games with coupled constraints or nonconcave utilities.
Computing Game Symmetries and Equilibria That Respect Them
Jan 15, 2025Abstract:Strategic interactions can be represented more concisely, and analyzed and solved more efficiently, if we are aware of the symmetries within the multiagent system. Symmetries also have conceptual implications, for example for equilibrium selection. We study the computational complexity of identifying and using symmetries. Using the classical framework of normal-form games, we consider game symmetries that can be across some or all players and/or actions. We find a strong connection between game symmetries and graph automorphisms, yielding graph automorphism and graph isomorphism completeness results for characterizing the symmetries present in a game. On the other hand, we also show that the problem becomes polynomial-time solvable when we restrict the consideration of actions in one of two ways. Next, we investigate when exactly game symmetries can be successfully leveraged for Nash equilibrium computation. We show that finding a Nash equilibrium that respects a given set of symmetries is PPAD- and CLS-complete in general-sum and team games respectively -- that is, exactly as hard as Brouwer fixed point and gradient descent problems. Finally, we present polynomial-time methods for the special cases where we are aware of a vast number of symmetries, or where the game is two-player zero-sum and we do not even know the symmetries.
Imperfect-Recall Games: Equilibrium Concepts and Their Complexity
Jun 23, 2024Abstract:We investigate optimal decision making under imperfect recall, that is, when an agent forgets information it once held before. An example is the absentminded driver game, as well as team games in which the members have limited communication capabilities. In the framework of extensive-form games with imperfect recall, we analyze the computational complexities of finding equilibria in multiplayer settings across three different solution concepts: Nash, multiselves based on evidential decision theory (EDT), and multiselves based on causal decision theory (CDT). We are interested in both exact and approximate solution computation. As special cases, we consider (1) single-player games, (2) two-player zero-sum games and relationships to maximin values, and (3) games without exogenous stochasticity (chance nodes). We relate these problems to the complexity classes P, PPAD, PLS, $\Sigma_2^P$ , $\exists$R, and $\exists \forall$R.
Social Choice for AI Alignment: Dealing with Diverse Human Feedback
Apr 16, 2024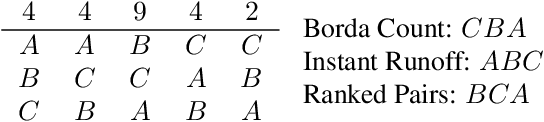
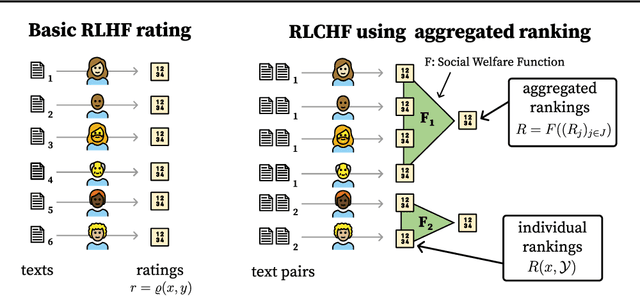
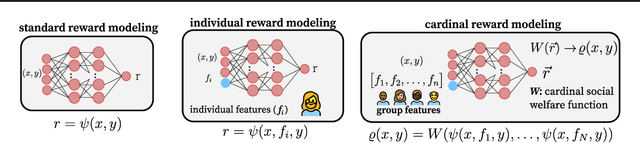
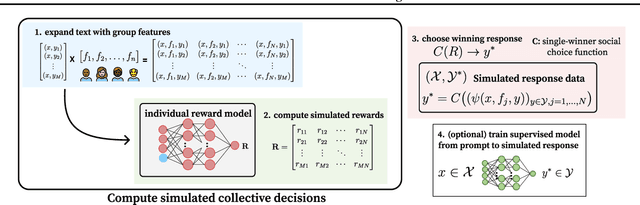
Abstract:Foundation models such as GPT-4 are fine-tuned to avoid unsafe or otherwise problematic behavior, so that, for example, they refuse to comply with requests for help with committing crimes or with producing racist text. One approach to fine-tuning, called reinforcement learning from human feedback, learns from humans' expressed preferences over multiple outputs. Another approach is constitutional AI, in which the input from humans is a list of high-level principles. But how do we deal with potentially diverging input from humans? How can we aggregate the input into consistent data about ''collective'' preferences or otherwise use it to make collective choices about model behavior? In this paper, we argue that the field of social choice is well positioned to address these questions, and we discuss ways forward for this agenda, drawing on discussions in a recent workshop on Social Choice for AI Ethics and Safety held in Berkeley, CA, USA in December 2023.
The Computational Complexity of Single-Player Imperfect-Recall Games
May 28, 2023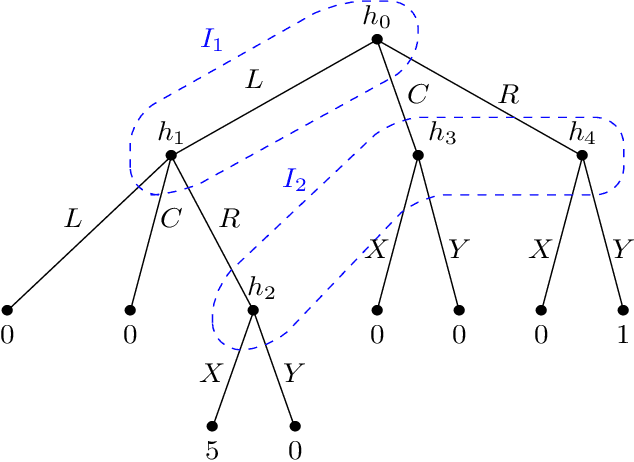
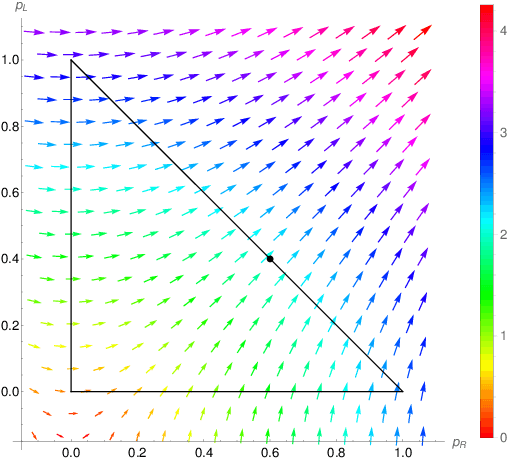
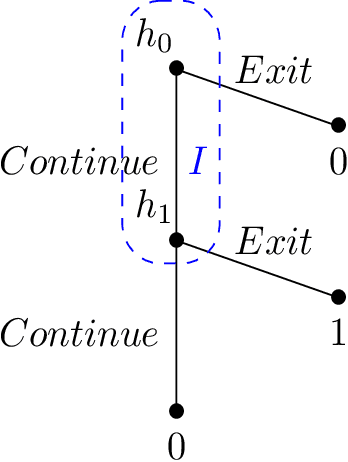
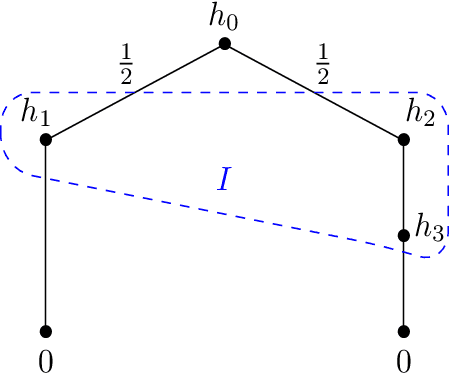
Abstract:We study single-player extensive-form games with imperfect recall, such as the Sleeping Beauty problem or the Absentminded Driver game. For such games, two natural equilibrium concepts have been proposed as alternative solution concepts to ex-ante optimality. One equilibrium concept uses generalized double halving (GDH) as a belief system and evidential decision theory (EDT), and another one uses generalized thirding (GT) as a belief system and causal decision theory (CDT). Our findings relate those three solution concepts of a game to solution concepts of a polynomial maximization problem: global optima, optimal points with respect to subsets of variables and Karush-Kuhn-Tucker (KKT) points. Based on these correspondences, we are able to settle various complexity-theoretic questions on the computation of such strategies. For ex-ante optimality and (EDT,GDH)-equilibria, we obtain NP-hardness and inapproximability, and for (CDT,GT)-equilibria we obtain CLS-completeness results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge