Elmira Yadollahi
Adapting Robot's Explanation for Failures Based on Observed Human Behavior in Human-Robot Collaboration
Apr 13, 2025

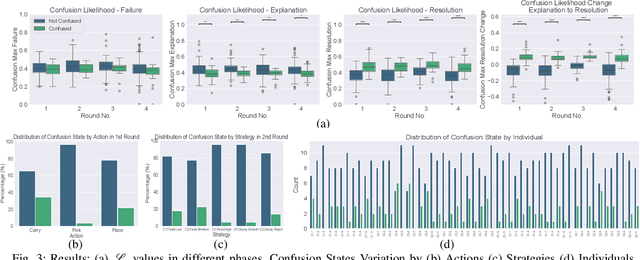
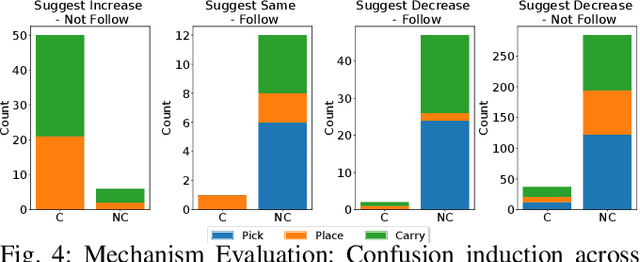
Abstract:This work aims to interpret human behavior to anticipate potential user confusion when a robot provides explanations for failure, allowing the robot to adapt its explanations for more natural and efficient collaboration. Using a dataset that included facial emotion detection, eye gaze estimation, and gestures from 55 participants in a user study, we analyzed how human behavior changed in response to different types of failures and varying explanation levels. Our goal is to assess whether human collaborators are ready to accept less detailed explanations without inducing confusion. We formulate a data-driven predictor to predict human confusion during robot failure explanations. We also propose and evaluate a mechanism, based on the predictor, to adapt the explanation level according to observed human behavior. The promising results from this evaluation indicate the potential of this research in adapting a robot's explanations for failures to enhance the collaborative experience.
Expectations, Explanations, and Embodiment: Attempts at Robot Failure Recovery
Apr 09, 2025
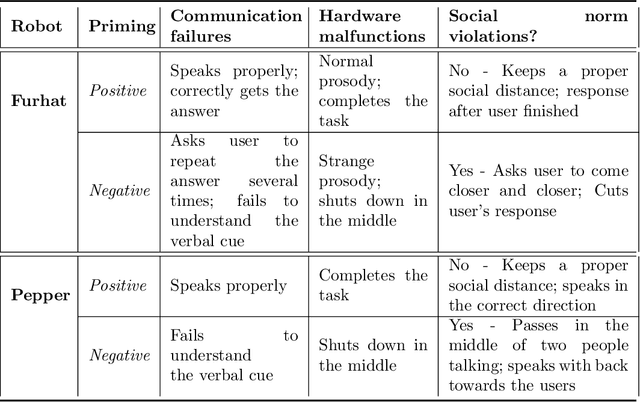
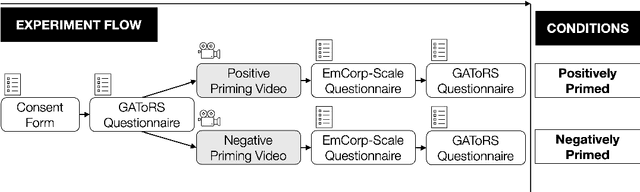
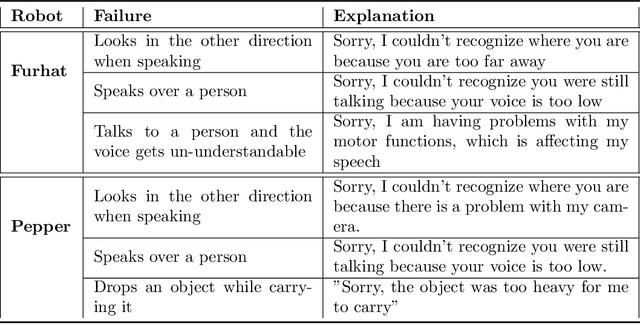
Abstract:Expectations critically shape how people form judgments about robots, influencing whether they view failures as minor technical glitches or deal-breaking flaws. This work explores how high and low expectations, induced through brief video priming, affect user perceptions of robot failures and the utility of explanations in HRI. We conducted two online studies ($N=600$ total participants); each replicated two robots with different embodiments, Furhat and Pepper. In our first study, grounded in expectation theory, participants were divided into two groups, one primed with positive and the other with negative expectations regarding the robot's performance, establishing distinct expectation frameworks. This validation study aimed to verify whether the videos could reliably establish low and high-expectation profiles. In the second study, participants were primed using the validated videos and then viewed a new scenario in which the robot failed at a task. Half viewed a version where the robot explained its failure, while the other half received no explanation. We found that explanations significantly improved user perceptions of Furhat, especially when participants were primed to have lower expectations. Explanations boosted satisfaction and enhanced the robot's perceived expressiveness, indicating that effectively communicating the cause of errors can help repair user trust. By contrast, Pepper's explanations produced minimal impact on user attitudes, suggesting that a robot's embodiment and style of interaction could determine whether explanations can successfully offset negative impressions. Together, these findings underscore the need to consider users' expectations when tailoring explanation strategies in HRI. When expectations are initially low, a cogent explanation can make the difference between dismissing a failure and appreciating the robot's transparency and effort to communicate.
REFLEX Dataset: A Multimodal Dataset of Human Reactions to Robot Failures and Explanations
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:This work presents REFLEX: Robotic Explanations to FaiLures and Human EXpressions, a comprehensive multimodal dataset capturing human reactions to robot failures and subsequent explanations in collaborative settings. It aims to facilitate research into human-robot interaction dynamics, addressing the need to study reactions to both initial failures and explanations, as well as the evolution of these reactions in long-term interactions. By providing rich, annotated data on human responses to different types of failures, explanation levels, and explanation varying strategies, the dataset contributes to the development of more robust, adaptive, and satisfying robotic systems capable of maintaining positive relationships with human collaborators, even during challenges like repeated failures.
How do Humans take an Object from a Robot: Behavior changes observed in a User Study
Jan 03, 2025


Abstract:To facilitate human-robot interaction and gain human trust, a robot should recognize and adapt to changes in human behavior. This work documents different human behaviors observed while taking objects from an interactive robot in an experimental study, categorized across two dimensions: pull force applied and handedness. We also present the changes observed in human behavior upon repeated interaction with the robot to take various objects.
The 1st InterAI Workshop: Interactive AI for Human-centered Robotics
Sep 17, 2024Abstract:The workshop is affiliated with 33nd IEEE International Conference on Robot and Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN 2024) August 26~30, 2023 / Pasadena, CA, USA. It is designed as a half-day event, extending over four hours from 9:00 to 12:30 PST time. It accommodates both in-person and virtual attendees (via Zoom), ensuring a flexible participation mode. The agenda is thoughtfully crafted to include a diverse range of sessions: two keynote speeches that promise to provide insightful perspectives, two dedicated paper presentation sessions, an interactive panel discussion to foster dialogue among experts which facilitates deeper dives into specific topics, and a 15-minute coffee break. The workshop website: https://sites.google.com/view/interaiworkshops/home.
Effects of Explanation Strategies to Resolve Failures in Human-Robot Collaboration
Sep 18, 2023Abstract:Despite significant improvements in robot capabilities, they are likely to fail in human-robot collaborative tasks due to high unpredictability in human environments and varying human expectations. In this work, we explore the role of explanation of failures by a robot in a human-robot collaborative task. We present a user study incorporating common failures in collaborative tasks with human assistance to resolve the failure. In the study, a robot and a human work together to fill a shelf with objects. Upon encountering a failure, the robot explains the failure and the resolution to overcome the failure, either through handovers or humans completing the task. The study is conducted using different levels of robotic explanation based on the failure action, failure cause, and action history, and different strategies in providing the explanation over the course of repeated interaction. Our results show that the success in resolving the failures is not only a function of the level of explanation but also the type of failures. Furthermore, while novice users rate the robot higher overall in terms of their satisfaction with the explanation, their satisfaction is not only a function of the robot's explanation level at a certain round but also the prior information they received from the robot.
A Systematic Review on Reproducibility in Child-Robot Interaction
Sep 04, 2023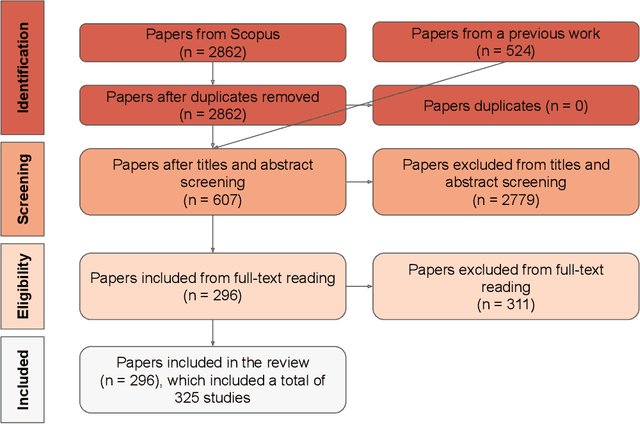
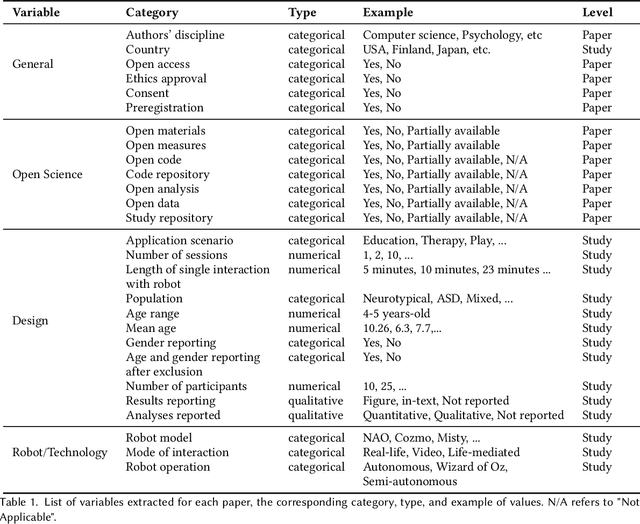
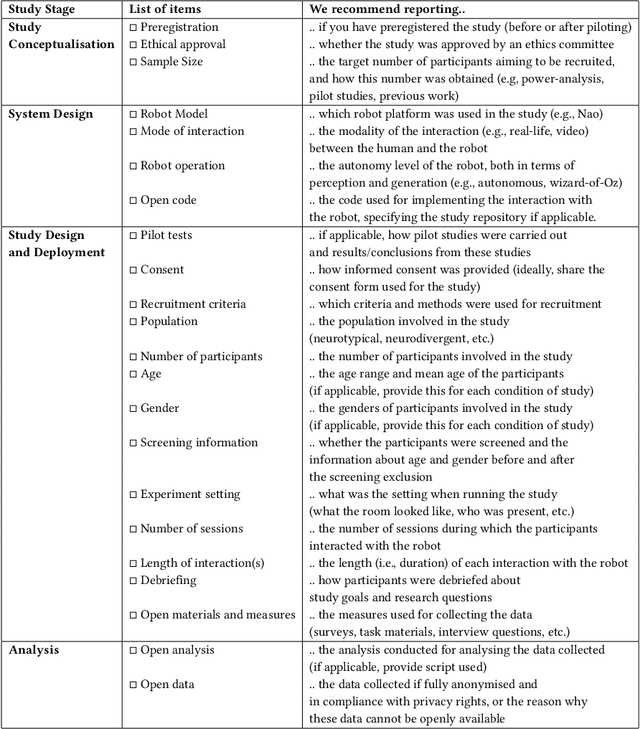
Abstract:Research reproducibility - i.e., rerunning analyses on original data to replicate the results - is paramount for guaranteeing scientific validity. However, reproducibility is often very challenging, especially in research fields where multi-disciplinary teams are involved, such as child-robot interaction (CRI). This paper presents a systematic review of the last three years (2020-2022) of research in CRI under the lens of reproducibility, by analysing the field for transparency in reporting. Across a total of 325 studies, we found deficiencies in reporting demographics (e.g. age of participants), study design and implementation (e.g. length of interactions), and open data (e.g. maintaining an active code repository). From this analysis, we distill a set of guidelines and provide a checklist to systematically report CRI studies to help and guide research to improve reproducibility in CRI and beyond.
Participatory Design of AI with Children: Reflections on IDC Design Challenge
Apr 18, 2023
Abstract:Children growing up in the era of Artificial Intelligence (AI) will be most impacted by the technology across their life span. Participatory Design (PD) is widely adopted by the Interaction Design and Children (IDC) community, which empowers children to bring their interests, needs, and creativity to the design process of future technologies. While PD has drawn increasing attention to human-centered AI design, it remains largely untapped in facilitating the design process of AI technologies relevant to children and their community. In this paper, we report intriguing children's design ideas on AI technologies resulting from the "Research and Design Challenge" of the 22nd ACM Interaction Design and Children (IDC 2023) conference. The diversity of design problems, AI applications and capabilities revealed by the children's design ideas shed light on the potential of engaging children in PD activities for future AI technologies. We discuss opportunities and challenges for accessible and inclusive PD experiences with children in shaping the future of AI-powered society.
User Study Exploring the Role of Explanation of Failures by Robots in Human Robot Collaboration Tasks
Mar 28, 2023



Abstract:Despite great advances in what robots can do, they still experience failures in human-robot collaborative tasks due to high randomness in unstructured human environments. Moreover, a human's unfamiliarity with a robot and its abilities can cause such failures to repeat. This makes the ability to failure explanation very important for a robot. In this work, we describe a user study that incorporated different robotic failures in a human-robot collaboration (HRC) task aimed at filling a shelf. We included different types of failures and repeated occurrences of such failures in a prolonged interaction between humans and robots. The failure resolution involved human intervention in form of human-robot bidirectional handovers. Through such studies, we aim to test different explanation types and explanation progression in the interaction and record humans.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge