Dongliang Luo
TokBench: Evaluating Your Visual Tokenizer before Visual Generation
May 26, 2025Abstract:In this work, we reveal the limitations of visual tokenizers and VAEs in preserving fine-grained features, and propose a benchmark to evaluate reconstruction performance for two challenging visual contents: text and face. Visual tokenizers and VAEs have significantly advanced visual generation and multimodal modeling by providing more efficient compressed or quantized image representations. However, while helping production models reduce computational burdens, the information loss from image compression fundamentally limits the upper bound of visual generation quality. To evaluate this upper bound, we focus on assessing reconstructed text and facial features since they typically: 1) exist at smaller scales, 2) contain dense and rich textures, 3) are prone to collapse, and 4) are highly sensitive to human vision. We first collect and curate a diverse set of clear text and face images from existing datasets. Unlike approaches using VLM models, we employ established OCR and face recognition models for evaluation, ensuring accuracy while maintaining an exceptionally lightweight assessment process <span style="font-weight: bold; color: rgb(214, 21, 21);">requiring just 2GB memory and 4 minutes</span> to complete. Using our benchmark, we analyze text and face reconstruction quality across various scales for different image tokenizers and VAEs. Our results show modern visual tokenizers still struggle to preserve fine-grained features, especially at smaller scales. We further extend this evaluation framework to video, conducting comprehensive analysis of video tokenizers. Additionally, we demonstrate that traditional metrics fail to accurately reflect reconstruction performance for faces and text, while our proposed metrics serve as an effective complement.
SemiETS: Integrating Spatial and Content Consistencies for Semi-Supervised End-to-end Text Spotting
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:Most previous scene text spotting methods rely on high-quality manual annotations to achieve promising performance. To reduce their expensive costs, we study semi-supervised text spotting (SSTS) to exploit useful information from unlabeled images. However, directly applying existing semi-supervised methods of general scenes to SSTS will face new challenges: 1) inconsistent pseudo labels between detection and recognition tasks, and 2) sub-optimal supervisions caused by inconsistency between teacher/student. Thus, we propose a new Semi-supervised framework for End-to-end Text Spotting, namely SemiETS that leverages the complementarity of text detection and recognition. Specifically, it gradually generates reliable hierarchical pseudo labels for each task, thereby reducing noisy labels. Meanwhile, it extracts important information in locations and transcriptions from bidirectional flows to improve consistency. Extensive experiments on three datasets under various settings demonstrate the effectiveness of SemiETS on arbitrary-shaped text. For example, it outperforms previous state-of-the-art SSL methods by a large margin on end-to-end spotting (+8.7%, +5.6%, and +2.6% H-mean under 0.5%, 1%, and 2% labeled data settings on Total-Text, respectively). More importantly, it still improves upon a strongly supervised text spotter trained with plenty of labeled data by 2.0%. Compelling domain adaptation ability shows practical potential. Moreover, our method demonstrates consistent improvement on different text spotters.
R-CoT: Reverse Chain-of-Thought Problem Generation for Geometric Reasoning in Large Multimodal Models
Oct 23, 2024



Abstract:Existing Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) struggle with mathematical geometric reasoning due to a lack of high-quality image-text paired data. Current geometric data generation approaches, which apply preset templates to generate geometric data or use Large Language Models (LLMs) to rephrase questions and answers (Q&A), unavoidably limit data accuracy and diversity. To synthesize higher-quality data, we propose a two-stage Reverse Chain-of-Thought (R-CoT) geometry problem generation pipeline. First, we introduce GeoChain to produce high-fidelity geometric images and corresponding descriptions highlighting relations among geometric elements. We then design a Reverse A&Q method that reasons step-by-step based on the descriptions and generates questions in reverse from the reasoning results. Experiments demonstrate that the proposed method brings significant and consistent improvements on multiple LMM baselines, achieving new performance records in the 2B, 7B, and 8B settings. Notably, R-CoT-8B significantly outperforms previous state-of-the-art open-source mathematical models by 16.6% on MathVista and 9.2% on GeoQA, while also surpassing the closed-source model GPT-4o by an average of 13% across both datasets. The code is available at https://github.com/dle666/R-CoT.
Toward Real Text Manipulation Detection: New Dataset and New Solution
Dec 12, 2023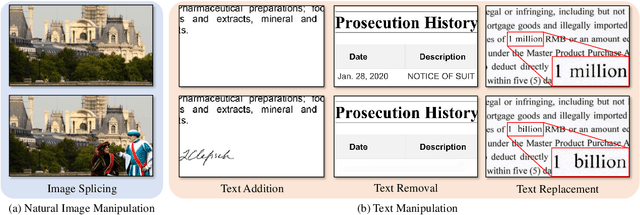
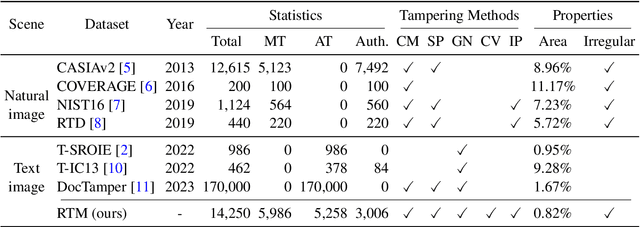

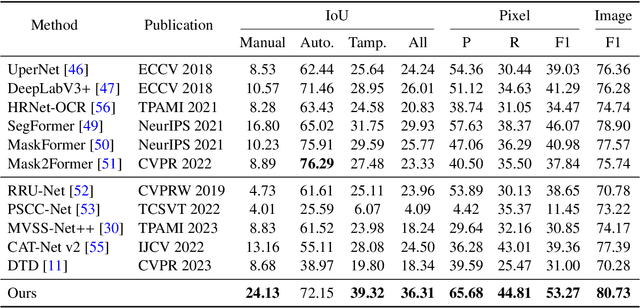
Abstract:With the surge in realistic text tampering, detecting fraudulent text in images has gained prominence for maintaining information security. However, the high costs associated with professional text manipulation and annotation limit the availability of real-world datasets, with most relying on synthetic tampering, which inadequately replicates real-world tampering attributes. To address this issue, we present the Real Text Manipulation (RTM) dataset, encompassing 14,250 text images, which include 5,986 manually and 5,258 automatically tampered images, created using a variety of techniques, alongside 3,006 unaltered text images for evaluating solution stability. Our evaluations indicate that existing methods falter in text forgery detection on the RTM dataset. We propose a robust baseline solution featuring a Consistency-aware Aggregation Hub and a Gated Cross Neighborhood-attention Fusion module for efficient multi-modal information fusion, supplemented by a Tampered-Authentic Contrastive Learning module during training, enriching feature representation distinction. This framework, extendable to other dual-stream architectures, demonstrated notable localization performance improvements of 7.33% and 6.38% on manual and overall manipulations, respectively. Our contributions aim to propel advancements in real-world text tampering detection. Code and dataset will be made available at https://github.com/DrLuo/RTM
A Discrepancy Aware Framework for Robust Anomaly Detection
Oct 11, 2023Abstract:Defect detection is a critical research area in artificial intelligence. Recently, synthetic data-based self-supervised learning has shown great potential on this task. Although many sophisticated synthesizing strategies exist, little research has been done to investigate the robustness of models when faced with different strategies. In this paper, we focus on this issue and find that existing methods are highly sensitive to them. To alleviate this issue, we present a Discrepancy Aware Framework (DAF), which demonstrates robust performance consistently with simple and cheap strategies across different anomaly detection benchmarks. We hypothesize that the high sensitivity to synthetic data of existing self-supervised methods arises from their heavy reliance on the visual appearance of synthetic data during decoding. In contrast, our method leverages an appearance-agnostic cue to guide the decoder in identifying defects, thereby alleviating its reliance on synthetic appearance. To this end, inspired by existing knowledge distillation methods, we employ a teacher-student network, which is trained based on synthesized outliers, to compute the discrepancy map as the cue. Extensive experiments on two challenging datasets prove the robustness of our method. Under the simple synthesis strategies, it outperforms existing methods by a large margin. Furthermore, it also achieves the state-of-the-art localization performance. Code is available at: https://github.com/caiyuxuan1120/DAF.
Run Away From your Teacher: Understanding BYOL by a Novel Self-Supervised Approach
Nov 22, 2020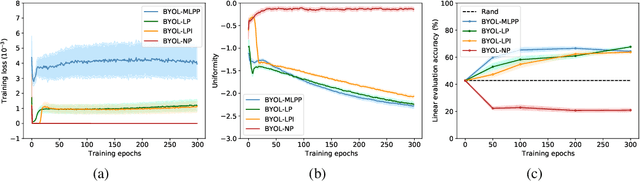
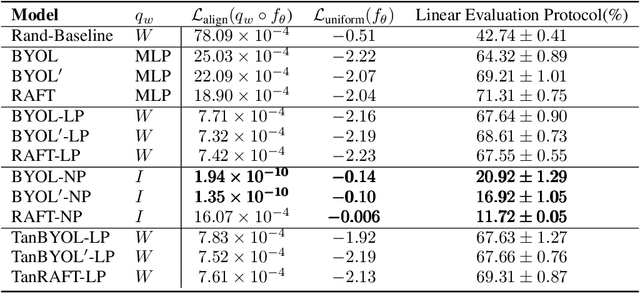
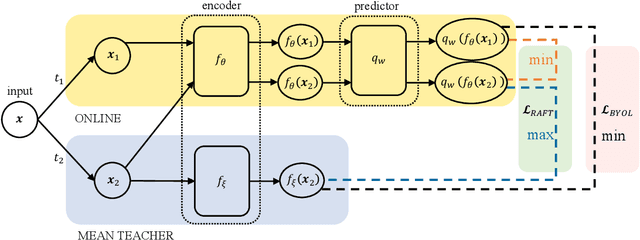
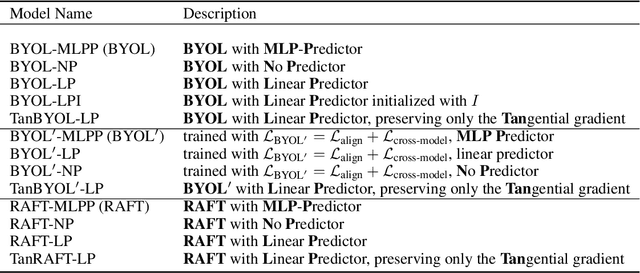
Abstract:Recently, a newly proposed self-supervised framework Bootstrap Your Own Latent (BYOL) seriously challenges the necessity of negative samples in contrastive learning frameworks. BYOL works like a charm despite the fact that it discards the negative samples completely and there is no measure to prevent collapse in its training objective. In this paper, we suggest understanding BYOL from the view of our proposed interpretable self-supervised learning framework, Run Away From your Teacher (RAFT). RAFT optimizes two objectives at the same time: (i) aligning two views of the same data to similar representations and (ii) running away from the model's Mean Teacher (MT, the exponential moving average of the history models) instead of BYOL's running towards it. The second term of RAFT explicitly prevents the representation collapse and thus makes RAFT a more conceptually reliable framework. We provide basic benchmarks of RAFT on CIFAR10 to validate the effectiveness of our method. Furthermore, we prove that BYOL is equivalent to RAFT under certain conditions, providing solid reasoning for BYOL's counter-intuitive success.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge