Demi Guo
Leveraging Deepfakes to Close the Domain Gap between Real and Synthetic Images in Facial Capture Pipelines
Apr 27, 2022



Abstract:We propose an end-to-end pipeline for both building and tracking 3D facial models from personalized in-the-wild (cellphone, webcam, youtube clips, etc.) video data. First, we present a method for automatic data curation and retrieval based on a hierarchical clustering framework typical of collision detection algorithms in traditional computer graphics pipelines. Subsequently, we utilize synthetic turntables and leverage deepfake technology in order to build a synthetic multi-view stereo pipeline for appearance capture that is robust to imperfect synthetic geometry and image misalignment. The resulting model is fit with an animation rig, which is then used to track facial performances. Notably, our novel use of deepfake technology enables us to perform robust tracking of in-the-wild data using differentiable renderers despite a significant synthetic-to-real domain gap. Finally, we outline how we train a motion capture regressor, leveraging the aforementioned techniques to avoid the need for real-world ground truth data and/or a high-end calibrated camera capture setup.
Parameter-Efficient Transfer Learning with Diff Pruning
Dec 14, 2020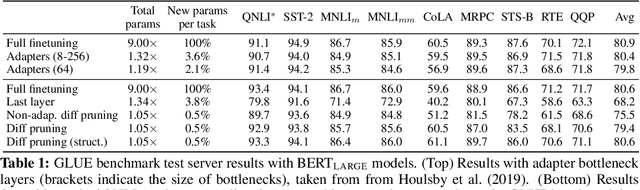

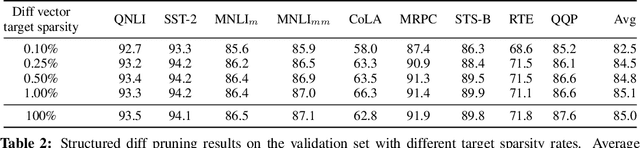

Abstract:While task-specific finetuning of pretrained networks has led to significant empirical advances in NLP, the large size of networks makes finetuning difficult to deploy in multi-task, memory-constrained settings. We propose diff pruning as a simple approach to enable parameter-efficient transfer learning within the pretrain-finetune framework. This approach views finetuning as learning a task-specific diff vector that is applied on top of the pretrained parameter vector, which remains fixed and is shared across different tasks. The diff vector is adaptively pruned during training with a differentiable approximation to the L0-norm penalty to encourage sparsity. Diff pruning becomes parameter-efficient as the number of tasks increases, as it requires storing only the nonzero positions and weights of the diff vector for each task, while the cost of storing the shared pretrained model remains constant. It further does not require access to all tasks during training, which makes it attractive in settings where tasks arrive in stream or the set of tasks is unknown. We find that models finetuned with diff pruning can match the performance of fully finetuned baselines on the GLUE benchmark while only modifying 0.5% of the pretrained model's parameters per task.
Sequence-Level Mixed Sample Data Augmentation
Nov 18, 2020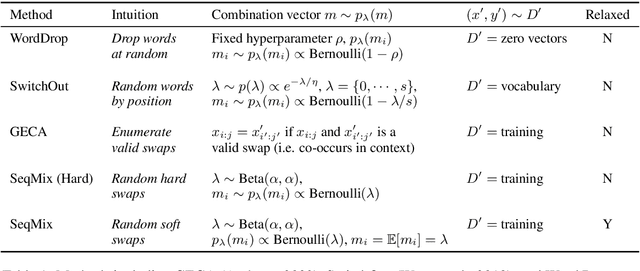
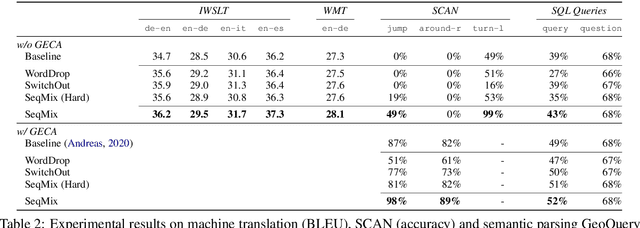
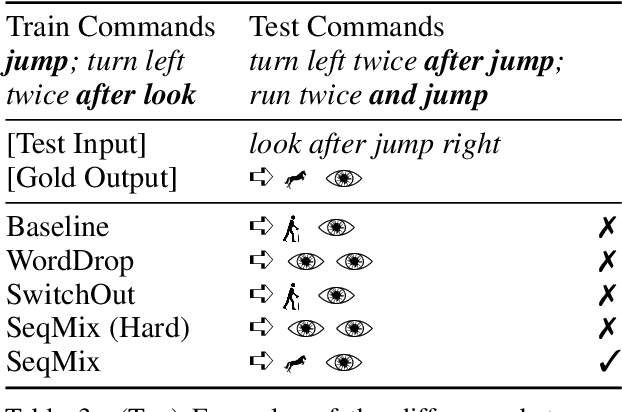
Abstract:Despite their empirical success, neural networks still have difficulty capturing compositional aspects of natural language. This work proposes a simple data augmentation approach to encourage compositional behavior in neural models for sequence-to-sequence problems. Our approach, SeqMix, creates new synthetic examples by softly combining input/output sequences from the training set. We connect this approach to existing techniques such as SwitchOut and word dropout, and show that these techniques are all approximating variants of a single objective. SeqMix consistently yields approximately 1.0 BLEU improvement on five different translation datasets over strong Transformer baselines. On tasks that require strong compositional generalization such as SCAN and semantic parsing, SeqMix also offers further improvements.
PointContrast: Unsupervised Pre-training for 3D Point Cloud Understanding
Jul 22, 2020

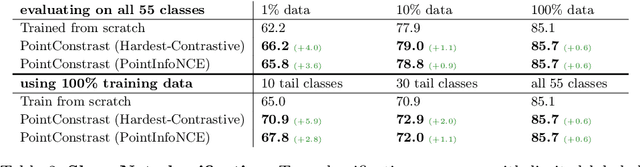

Abstract:Arguably one of the top success stories of deep learning is transfer learning. The finding that pre-training a network on a rich source set (eg., ImageNet) can help boost performance once fine-tuned on a usually much smaller target set, has been instrumental to many applications in language and vision. Yet, very little is known about its usefulness in 3D point cloud understanding. We see this as an opportunity considering the effort required for annotating data in 3D. In this work, we aim at facilitating research on 3D representation learning. Different from previous works, we focus on high-level scene understanding tasks. To this end, we select a suite of diverse datasets and tasks to measure the effect of unsupervised pre-training on a large source set of 3D scenes. Our findings are extremely encouraging: using a unified triplet of architecture, source dataset, and contrastive loss for pre-training, we achieve improvement over recent best results in segmentation and detection across 6 different benchmarks for indoor and outdoor, real and synthetic datasets -- demonstrating that the learned representation can generalize across domains. Furthermore, the improvement was similar to supervised pre-training, suggesting that future efforts should favor scaling data collection over more detailed annotation. We hope these findings will encourage more research on unsupervised pretext task design for 3D deep learning.
MicroNet for Efficient Language Modeling
May 16, 2020
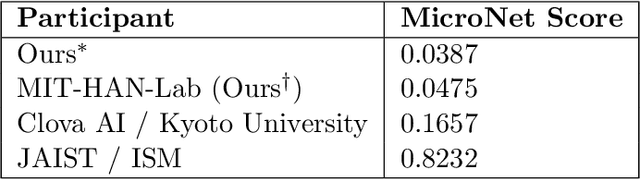
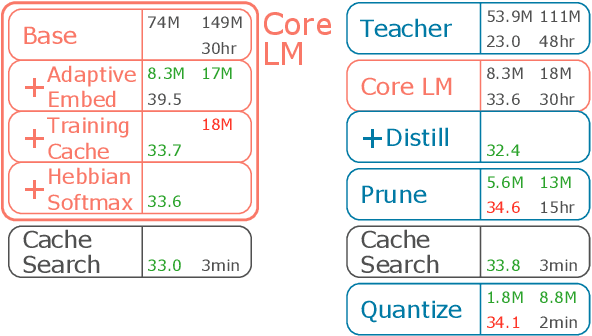
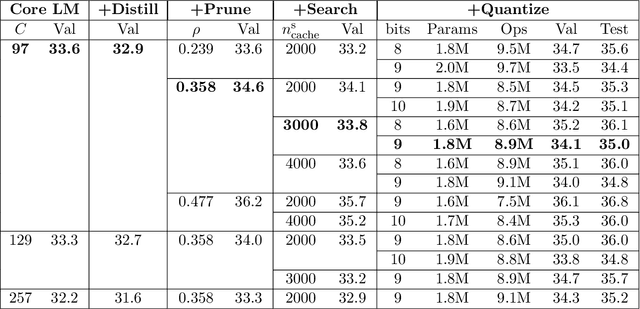
Abstract:It is important to design compact language models for efficient deployment. We improve upon recent advances in both the language modeling domain and the model-compression domain to construct parameter and computation efficient language models. We use an efficient transformer-based architecture with adaptive embedding and softmax, differentiable non-parametric cache, Hebbian softmax, knowledge distillation, network pruning, and low-bit quantization. In this paper, we provide the winning solution to the NeurIPS 2019 MicroNet Challenge in the language modeling track. Compared to the baseline language model provided by the MicroNet Challenge, our model is 90 times more parameter-efficient and 36 times more computation-efficient while achieving the required test perplexity of 35 on the Wikitext-103 dataset. We hope that this work will aid future research into efficient language models, and we have released our full source code at https://github.com/mit-han-lab/neurips-micronet.
Analyzing machine-learned representations: A natural language case study
Sep 12, 2019


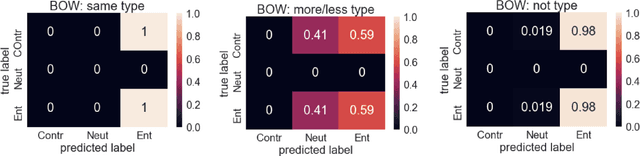
Abstract:As modern deep networks become more complex, and get closer to human-like capabilities in certain domains, the question arises of how the representations and decision rules they learn compare to the ones in humans. In this work, we study representations of sentences in one such artificial system for natural language processing. We first present a diagnostic test dataset to examine the degree of abstract composable structure represented. Analyzing performance on these diagnostic tests indicates a lack of systematicity in the representations and decision rules, and reveals a set of heuristic strategies. We then investigate the effect of the training distribution on learning these heuristic strategies, and study changes in these representations with various augmentations to the training set. Our results reveal parallels to the analogous representations in people. We find that these systems can learn abstract rules and generalize them to new contexts under certain circumstances -- similar to human zero-shot reasoning. However, we also note some shortcomings in this generalization behavior -- similar to human judgment errors like belief bias. Studying these parallels suggests new ways to understand psychological phenomena in humans as well as informs best strategies for building artificial intelligence with human-like language understanding.
Why Build an Assistant in Minecraft?
Jul 25, 2019Abstract:In this document we describe a rationale for a research program aimed at building an open "assistant" in the game Minecraft, in order to make progress on the problems of natural language understanding and learning from dialogue.
CraftAssist: A Framework for Dialogue-enabled Interactive Agents
Jul 19, 2019
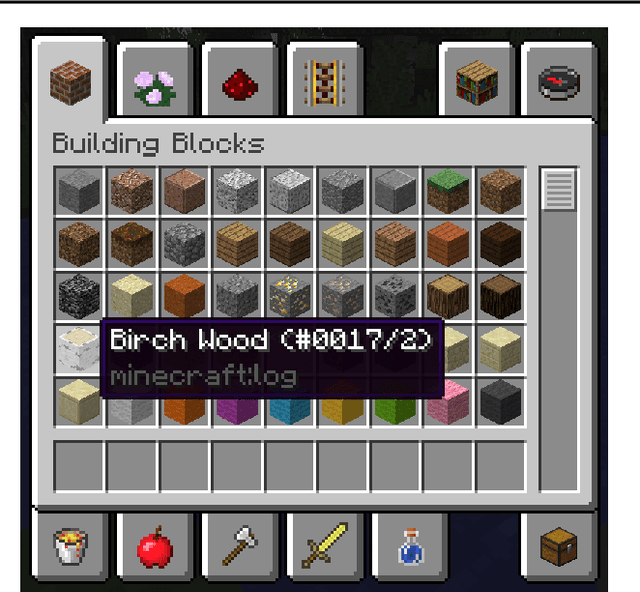
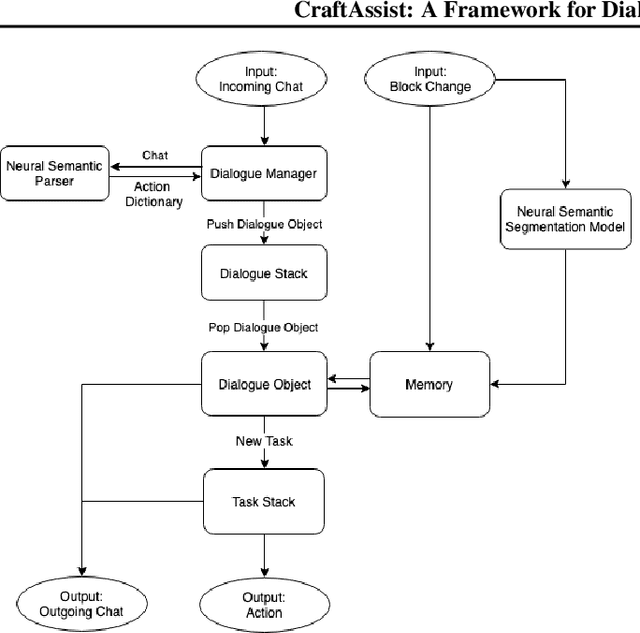

Abstract:This paper describes an implementation of a bot assistant in Minecraft, and the tools and platform allowing players to interact with the bot and to record those interactions. The purpose of building such an assistant is to facilitate the study of agents that can complete tasks specified by dialogue, and eventually, to learn from dialogue interactions.
Latent Alignment and Variational Attention
Jul 10, 2018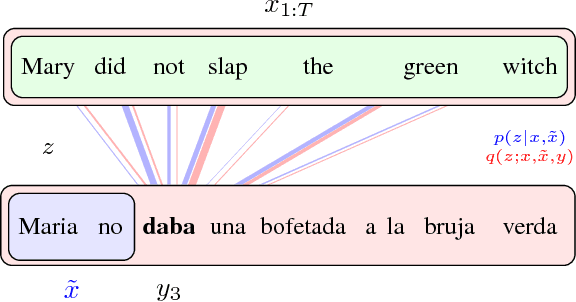
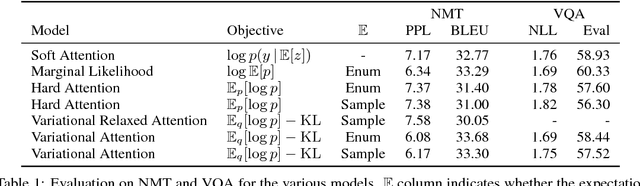
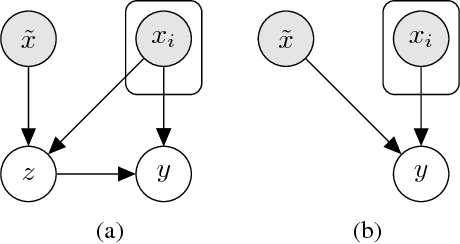
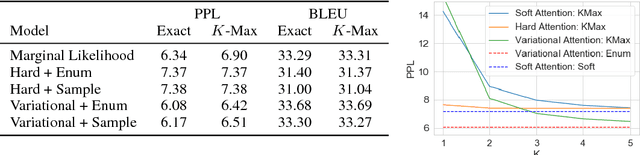
Abstract:Neural attention has become central to many state-of-the-art models in natural language processing and related domains. Attention networks are an easy-to-train and effective method for softly simulating alignment; however, the approach does not marginalize over latent alignments in a probabilistic sense. This property makes it difficult to compare attention to other alignment approaches, to compose it with probabilistic models, and to perform posterior inference conditioned on observed data. A related latent approach, hard attention, fixes these issues, but is generally harder to train and less accurate. This work considers variational attention networks, alternatives to soft and hard attention for learning latent variable alignment models, with tighter approximation bounds based on amortized variational inference. We further propose methods for reducing the variance of gradients to make these approaches computationally feasible. Experiments show that for machine translation and visual question answering, inefficient exact latent variable models outperform standard neural attention, but these gains go away when using hard attention based training. On the other hand, variational attention retains most of the performance gain but with training speed comparable to neural attention.
Evaluating Compositionality in Sentence Embeddings
May 17, 2018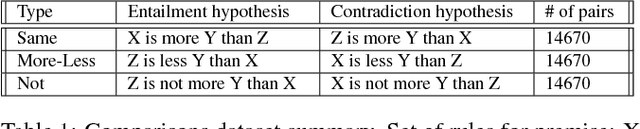
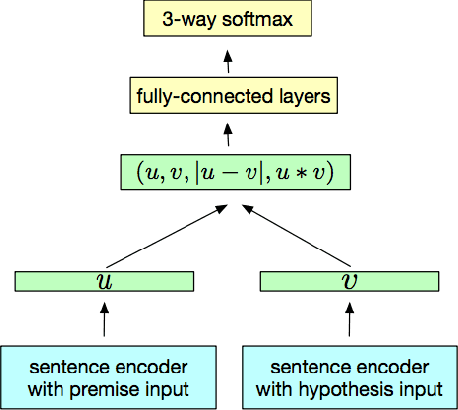
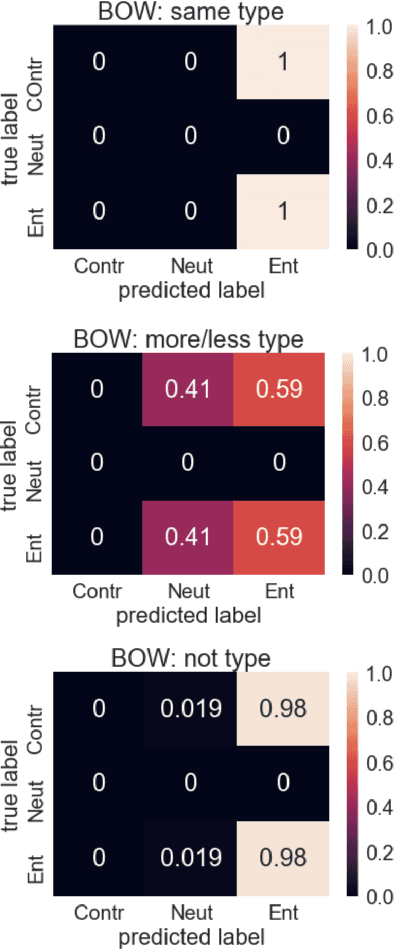
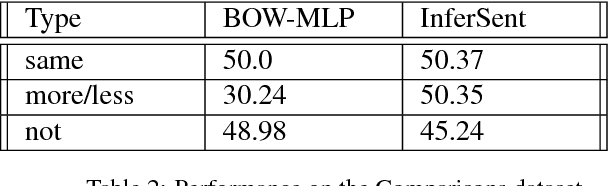
Abstract:An important challenge for human-like AI is compositional semantics. Recent research has attempted to address this by using deep neural networks to learn vector space embeddings of sentences, which then serve as input to other tasks. We present a new dataset for one such task, `natural language inference' (NLI), that cannot be solved using only word-level knowledge and requires some compositionality. We find that the performance of state of the art sentence embeddings (InferSent; Conneau et al., 2017) on our new dataset is poor. We analyze the decision rules learned by InferSent and find that they are consistent with simple heuristics that are ecologically valid in its training dataset. Further, we find that augmenting training with our dataset improves test performance on our dataset without loss of performance on the original training dataset. This highlights the importance of structured datasets in better understanding and improving AI systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge