David Menotti
Advancing Multinational License Plate Recognition Through Synthetic and Real Data Fusion: A Comprehensive Evaluation
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Automatic License Plate Recognition is a frequent research topic due to its wide-ranging practical applications. While recent studies use synthetic images to improve License Plate Recognition (LPR) results, there remain several limitations in these efforts. This work addresses these constraints by comprehensively exploring the integration of real and synthetic data to enhance LPR performance. We subject 16 Optical Character Recognition (OCR) models to a benchmarking process involving 12 public datasets acquired from various regions. Several key findings emerge from our investigation. Primarily, the massive incorporation of synthetic data substantially boosts model performance in both intra- and cross-dataset scenarios. We examine three distinct methodologies for generating synthetic data: template-based generation, character permutation, and utilizing a Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) model, each contributing significantly to performance enhancement. The combined use of these methodologies demonstrates a notable synergistic effect, leading to end-to-end results that surpass those reached by state-of-the-art methods and established commercial systems. Our experiments also underscore the efficacy of synthetic data in mitigating challenges posed by limited training data, enabling remarkable results to be achieved even with small fractions of the original training data. Finally, we investigate the trade-off between accuracy and speed among different models, identifying those that strike the optimal balance in each intra-dataset and cross-dataset settings.
Toward Advancing License Plate Super-Resolution in Real-World Scenarios: A Dataset and Benchmark
May 09, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in super-resolution for License Plate Recognition (LPR) have sought to address challenges posed by low-resolution (LR) and degraded images in surveillance, traffic monitoring, and forensic applications. However, existing studies have relied on private datasets and simplistic degradation models. To address this gap, we introduce UFPR-SR-Plates, a novel dataset containing 10,000 tracks with 100,000 paired low and high-resolution license plate images captured under real-world conditions. We establish a benchmark using multiple sequential LR and high-resolution (HR) images per vehicle -- five of each -- and two state-of-the-art models for super-resolution of license plates. We also investigate three fusion strategies to evaluate how combining predictions from a leading Optical Character Recognition (OCR) model for multiple super-resolved license plates enhances overall performance. Our findings demonstrate that super-resolution significantly boosts LPR performance, with further improvements observed when applying majority vote-based fusion techniques. Specifically, the Layout-Aware and Character-Driven Network (LCDNet) model combined with the Majority Vote by Character Position (MVCP) strategy led to the highest recognition rates, increasing from 1.7% with low-resolution images to 31.1% with super-resolution, and up to 44.7% when combining OCR outputs from five super-resolved images. These findings underscore the critical role of super-resolution and temporal information in enhancing LPR accuracy under real-world, adverse conditions. The proposed dataset is publicly available to support further research and can be accessed at: https://valfride.github.io/nascimento2024toward/
Improving Small Drone Detection Through Multi-Scale Processing and Data Augmentation
Apr 27, 2025



Abstract:Detecting small drones, often indistinguishable from birds, is crucial for modern surveillance. This work introduces a drone detection methodology built upon the medium-sized YOLOv11 object detection model. To enhance its performance on small targets, we implemented a multi-scale approach in which the input image is processed both as a whole and in segmented parts, with subsequent prediction aggregation. We also utilized a copy-paste data augmentation technique to enrich the training dataset with diverse drone and bird examples. Finally, we implemented a post-processing technique that leverages frame-to-frame consistency to mitigate missed detections. The proposed approach attained a top-3 ranking in the 8th WOSDETC Drone-vsBird Detection Grand Challenge, held at the 2025 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), showcasing its capability to detect drones in complex environments effectively.
Second FRCSyn-onGoing: Winning Solutions and Post-Challenge Analysis to Improve Face Recognition with Synthetic Data
Dec 02, 2024Abstract:Synthetic data is gaining increasing popularity for face recognition technologies, mainly due to the privacy concerns and challenges associated with obtaining real data, including diverse scenarios, quality, and demographic groups, among others. It also offers some advantages over real data, such as the large amount of data that can be generated or the ability to customize it to adapt to specific problem-solving needs. To effectively use such data, face recognition models should also be specifically designed to exploit synthetic data to its fullest potential. In order to promote the proposal of novel Generative AI methods and synthetic data, and investigate the application of synthetic data to better train face recognition systems, we introduce the 2nd FRCSyn-onGoing challenge, based on the 2nd Face Recognition Challenge in the Era of Synthetic Data (FRCSyn), originally launched at CVPR 2024. This is an ongoing challenge that provides researchers with an accessible platform to benchmark i) the proposal of novel Generative AI methods and synthetic data, and ii) novel face recognition systems that are specifically proposed to take advantage of synthetic data. We focus on exploring the use of synthetic data both individually and in combination with real data to solve current challenges in face recognition such as demographic bias, domain adaptation, and performance constraints in demanding situations, such as age disparities between training and testing, changes in the pose, or occlusions. Very interesting findings are obtained in this second edition, including a direct comparison with the first one, in which synthetic databases were restricted to DCFace and GANDiffFace.
Watchlist Challenge: 3rd Open-set Face Detection and Identification
Sep 11, 2024Abstract:In the current landscape of biometrics and surveillance, the ability to accurately recognize faces in uncontrolled settings is paramount. The Watchlist Challenge addresses this critical need by focusing on face detection and open-set identification in real-world surveillance scenarios. This paper presents a comprehensive evaluation of participating algorithms, using the enhanced UnConstrained College Students (UCCS) dataset with new evaluation protocols. In total, four participants submitted four face detection and nine open-set face recognition systems. The evaluation demonstrates that while detection capabilities are generally robust, closed-set identification performance varies significantly, with models pre-trained on large-scale datasets showing superior performance. However, open-set scenarios require further improvement, especially at higher true positive identification rates, i.e., lower thresholds.
Less is more: concatenating videos for Sign Language Translation from a small set of signs
Sep 03, 2024Abstract:The limited amount of labeled data for training the Brazilian Sign Language (Libras) to Portuguese Translation models is a challenging problem due to video collection and annotation costs. This paper proposes generating sign language content by concatenating short clips containing isolated signals for training Sign Language Translation models. We employ the V-LIBRASIL dataset, composed of 4,089 sign videos for 1,364 signs, interpreted by at least three persons, to create hundreds of thousands of sentences with their respective Libras translation, and then, to feed the model. More specifically, we propose several experiments varying the vocabulary size and sentence structure, generating datasets with approximately 170K, 300K, and 500K videos. Our results achieve meaningful scores of 9.2% and 26.2% for BLEU-4 and METEOR, respectively. Our technique enables the creation or extension of existing datasets at a much lower cost than the collection and annotation of thousands of sentences providing clear directions for future works.
Enhancing License Plate Super-Resolution: A Layout-Aware and Character-Driven Approach
Aug 27, 2024



Abstract:Despite significant advancements in License Plate Recognition (LPR) through deep learning, most improvements rely on high-resolution images with clear characters. This scenario does not reflect real-world conditions where traffic surveillance often captures low-resolution and blurry images. Under these conditions, characters tend to blend with the background or neighboring characters, making accurate LPR challenging. To address this issue, we introduce a novel loss function, Layout and Character Oriented Focal Loss (LCOFL), which considers factors such as resolution, texture, and structural details, as well as the performance of the LPR task itself. We enhance character feature learning using deformable convolutions and shared weights in an attention module and employ a GAN-based training approach with an Optical Character Recognition (OCR) model as the discriminator to guide the super-resolution process. Our experimental results show significant improvements in character reconstruction quality, outperforming two state-of-the-art methods in both quantitative and qualitative measures. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/valfride/lpsr-lacd
Multi-Feature Aggregation in Diffusion Models for Enhanced Face Super-Resolution
Aug 27, 2024

Abstract:Super-resolution algorithms often struggle with images from surveillance environments due to adverse conditions such as unknown degradation, variations in pose, irregular illumination, and occlusions. However, acquiring multiple images, even of low quality, is possible with surveillance cameras. In this work, we develop an algorithm based on diffusion models that utilize a low-resolution image combined with features extracted from multiple low-quality images to generate a super-resolved image while minimizing distortions in the individual's identity. Unlike other algorithms, our approach recovers facial features without explicitly providing attribute information or without the need to calculate a gradient of a function during the reconstruction process. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time multi-features combined with low-resolution images are used as conditioners to generate more reliable super-resolution images using stochastic differential equations. The FFHQ dataset was employed for training, resulting in state-of-the-art performance in facial recognition and verification metrics when evaluated on the CelebA and Quis-Campi datasets. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/marcelowds/fasr
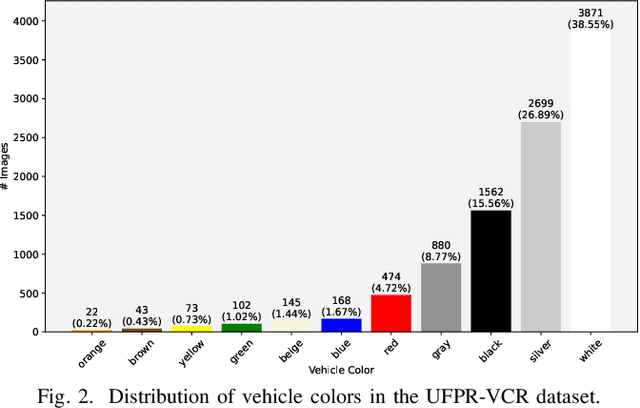
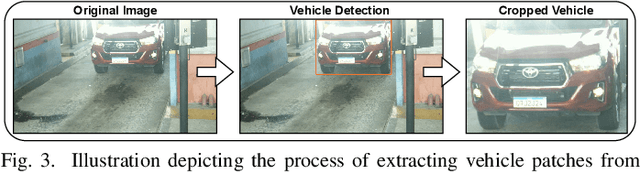
Toward Enhancing Vehicle Color Recognition in Adverse Conditions: A Dataset and Benchmark
Aug 21, 2024



Abstract:Vehicle information recognition is crucial in various practical domains, particularly in criminal investigations. Vehicle Color Recognition (VCR) has garnered significant research interest because color is a visually distinguishable attribute of vehicles and is less affected by partial occlusion and changes in viewpoint. Despite the success of existing methods for this task, the relatively low complexity of the datasets used in the literature has been largely overlooked. This research addresses this gap by compiling a new dataset representing a more challenging VCR scenario. The images - sourced from six license plate recognition datasets - are categorized into eleven colors, and their annotations were validated using official vehicle registration information. We evaluate the performance of four deep learning models on a widely adopted dataset and our proposed dataset to establish a benchmark. The results demonstrate that our dataset poses greater difficulty for the tested models and highlights scenarios that require further exploration in VCR. Remarkably, nighttime scenes account for a significant portion of the errors made by the best-performing model. This research provides a foundation for future studies on VCR, while also offering valuable insights for the field of fine-grained vehicle classification.
A Multilevel Strategy to Improve People Tracking in a Real-World Scenario
Apr 29, 2024



Abstract:The Pal\'acio do Planalto, office of the President of Brazil, was invaded by protesters on January 8, 2023. Surveillance videos taken from inside the building were subsequently released by the Brazilian Supreme Court for public scrutiny. We used segments of such footage to create the UFPR-Planalto801 dataset for people tracking and re-identification in a real-world scenario. This dataset consists of more than 500,000 images. This paper presents a tracking approach targeting this dataset. The method proposed in this paper relies on the use of known state-of-the-art trackers combined in a multilevel hierarchy to correct the ID association over the trajectories. We evaluated our method using IDF1, MOTA, MOTP and HOTA metrics. The results show improvements for every tracker used in the experiments, with IDF1 score increasing by a margin up to 9.5%.
* Accepted for presentation at the International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications (VISAPP) 2024
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge