David A. Shamma
Leveraging Language Models and Bandit Algorithms to Drive Adoption of Battery-Electric Vehicles
Oct 30, 2024



Abstract:Behavior change interventions are important to coordinate societal action across a wide array of important applications, including the adoption of electrified vehicles to reduce emissions. Prior work has demonstrated that interventions for behavior must be personalized, and that the intervention that is most effective on average across a large group can result in a backlash effect that strengthens opposition among some subgroups. Thus, it is important to target interventions to different audiences, and to present them in a natural, conversational style. In this context, an important emerging application domain for large language models (LLMs) is conversational interventions for behavior change. In this work, we leverage prior work on understanding values motivating the adoption of battery electric vehicles. We leverage new advances in LLMs, combined with a contextual bandit, to develop conversational interventions that are personalized to the values of each study participant. We use a contextual bandit algorithm to learn to target values based on the demographics of each participant. To train our bandit algorithm in an offline manner, we leverage LLMs to play the role of study participants. We benchmark the persuasive effectiveness of our bandit-enhanced LLM against an unaided LLM generating conversational interventions without demographic-targeted values.
On LLM Wizards: Identifying Large Language Models' Behaviors for Wizard of Oz Experiments
Jul 10, 2024Abstract:The Wizard of Oz (WoZ) method is a widely adopted research approach where a human Wizard ``role-plays'' a not readily available technology and interacts with participants to elicit user behaviors and probe the design space. With the growing ability for modern large language models (LLMs) to role-play, one can apply LLMs as Wizards in WoZ experiments with better scalability and lower cost than the traditional approach. However, methodological guidance on responsibly applying LLMs in WoZ experiments and a systematic evaluation of LLMs' role-playing ability are lacking. Through two LLM-powered WoZ studies, we take the first step towards identifying an experiment lifecycle for researchers to safely integrate LLMs into WoZ experiments and interpret data generated from settings that involve Wizards role-played by LLMs. We also contribute a heuristic-based evaluation framework that allows the estimation of LLMs' role-playing ability in WoZ experiments and reveals LLMs' behavior patterns at scale.
* To be published in ACM IVA 2024
Using LLMs to Model the Beliefs and Preferences of Targeted Populations
Mar 29, 2024Abstract:We consider the problem of aligning a large language model (LLM) to model the preferences of a human population. Modeling the beliefs, preferences, and behaviors of a specific population can be useful for a variety of different applications, such as conducting simulated focus groups for new products, conducting virtual surveys, and testing behavioral interventions, especially for interventions that are expensive, impractical, or unethical. Existing work has had mixed success using LLMs to accurately model human behavior in different contexts. We benchmark and evaluate two well-known fine-tuning approaches and evaluate the resulting populations on their ability to match the preferences of real human respondents on a survey of preferences for battery electric vehicles (BEVs). We evaluate our models against their ability to match population-wide statistics as well as their ability to match individual responses, and we investigate the role of temperature in controlling the trade-offs between these two. Additionally, we propose and evaluate a novel loss term to improve model performance on responses that require a numeric response.
LOH and behold: Web-scale visual search, recommendation and clustering using Locally Optimized Hashing
Jul 30, 2016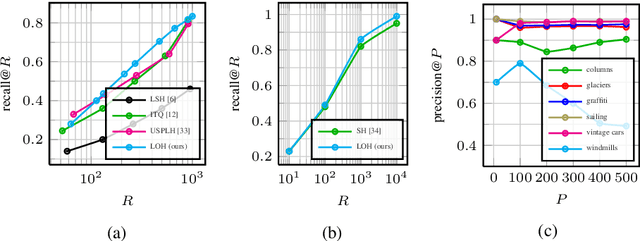



Abstract:We propose a novel hashing-based matching scheme, called Locally Optimized Hashing (LOH), based on a state-of-the-art quantization algorithm that can be used for efficient, large-scale search, recommendation, clustering, and deduplication. We show that matching with LOH only requires set intersections and summations to compute and so is easily implemented in generic distributed computing systems. We further show application of LOH to: a) large-scale search tasks where performance is on par with other state-of-the-art hashing approaches; b) large-scale recommendation where queries consisting of thousands of images can be used to generate accurate recommendations from collections of hundreds of millions of images; and c) efficient clustering with a graph-based algorithm that can be scaled to massive collections in a distributed environment or can be used for deduplication for small collections, like search results, performing better than traditional hashing approaches while only requiring a few milliseconds to run. In this paper we experiment on datasets of up to 100 million images, but in practice our system can scale to larger collections and can be used for other types of data that have a vector representation in a Euclidean space.
Visual Congruent Ads for Image Search
Apr 21, 2016
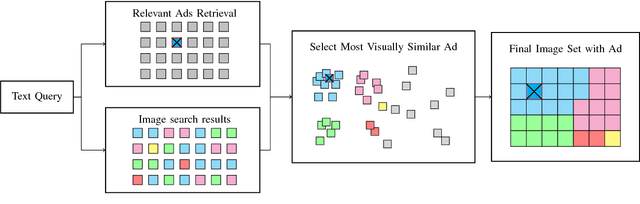
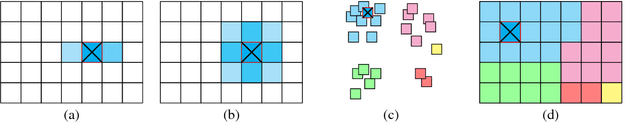

Abstract:The quality of user experience online is affected by the relevance and placement of advertisements. We propose a new system for selecting and displaying visual advertisements in image search result sets. Our method compares the visual similarity of candidate ads to the image search results and selects the most visually similar ad to be displayed. The method further selects an appropriate location in the displayed image grid to minimize the perceptual visual differences between the ad and its neighbors. We conduct an experiment with about 900 users and find that our proposed method provides significant improvement in the users' overall satisfaction with the image search experience, without diminishing the users' ability to see the ad or recall the advertised brand.
Visual Genome: Connecting Language and Vision Using Crowdsourced Dense Image Annotations
Feb 23, 2016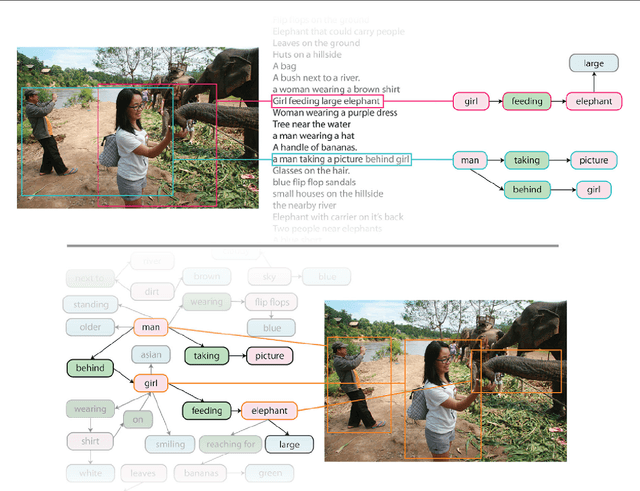
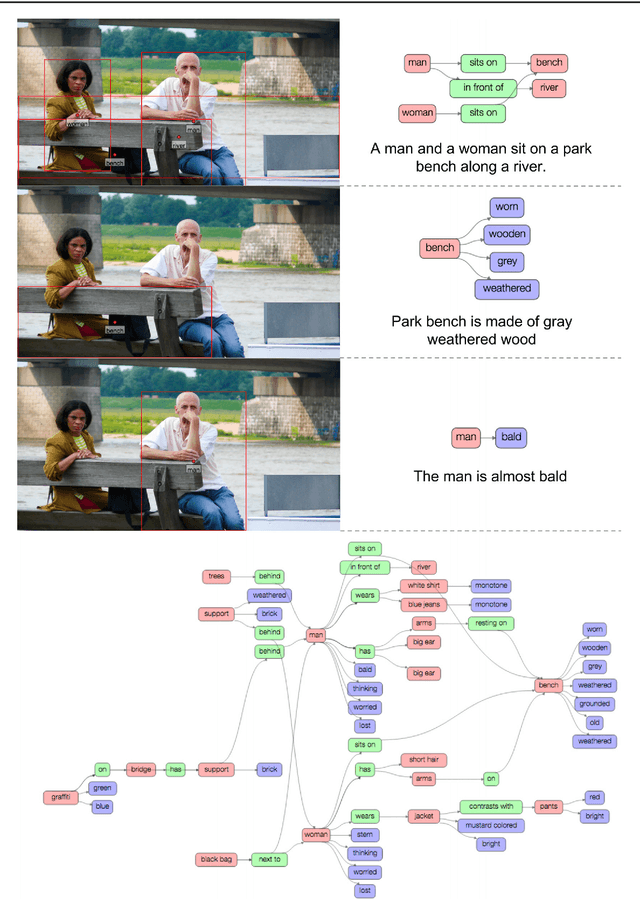

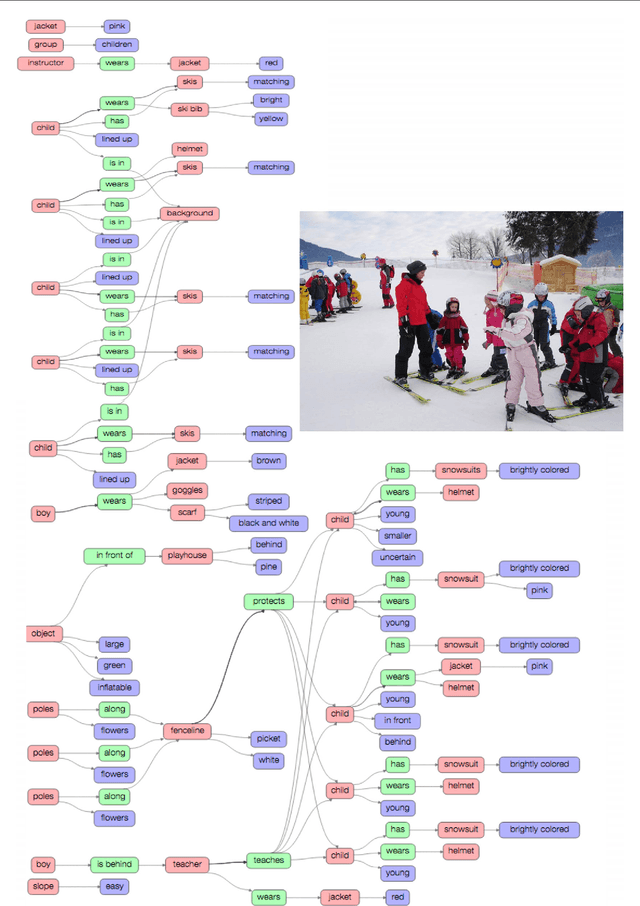
Abstract:Despite progress in perceptual tasks such as image classification, computers still perform poorly on cognitive tasks such as image description and question answering. Cognition is core to tasks that involve not just recognizing, but reasoning about our visual world. However, models used to tackle the rich content in images for cognitive tasks are still being trained using the same datasets designed for perceptual tasks. To achieve success at cognitive tasks, models need to understand the interactions and relationships between objects in an image. When asked "What vehicle is the person riding?", computers will need to identify the objects in an image as well as the relationships riding(man, carriage) and pulling(horse, carriage) in order to answer correctly that "the person is riding a horse-drawn carriage". In this paper, we present the Visual Genome dataset to enable the modeling of such relationships. We collect dense annotations of objects, attributes, and relationships within each image to learn these models. Specifically, our dataset contains over 100K images where each image has an average of 21 objects, 18 attributes, and 18 pairwise relationships between objects. We canonicalize the objects, attributes, relationships, and noun phrases in region descriptions and questions answer pairs to WordNet synsets. Together, these annotations represent the densest and largest dataset of image descriptions, objects, attributes, relationships, and question answers.
Embracing Error to Enable Rapid Crowdsourcing
Feb 14, 2016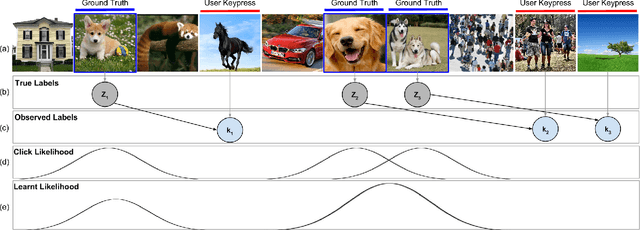

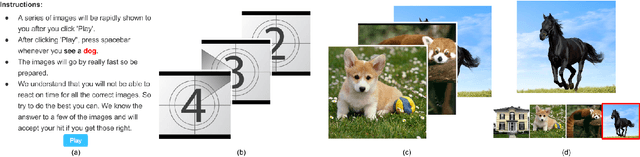

Abstract:Microtask crowdsourcing has enabled dataset advances in social science and machine learning, but existing crowdsourcing schemes are too expensive to scale up with the expanding volume of data. To scale and widen the applicability of crowdsourcing, we present a technique that produces extremely rapid judgments for binary and categorical labels. Rather than punishing all errors, which causes workers to proceed slowly and deliberately, our technique speeds up workers' judgments to the point where errors are acceptable and even expected. We demonstrate that it is possible to rectify these errors by randomizing task order and modeling response latency. We evaluate our technique on a breadth of common labeling tasks such as image verification, word similarity, sentiment analysis and topic classification. Where prior work typically achieves a 0.25x to 1x speedup over fixed majority vote, our approach often achieves an order of magnitude (10x) speedup.
Describing and Understanding Neighborhood Characteristics through Online Social Media
Mar 11, 2015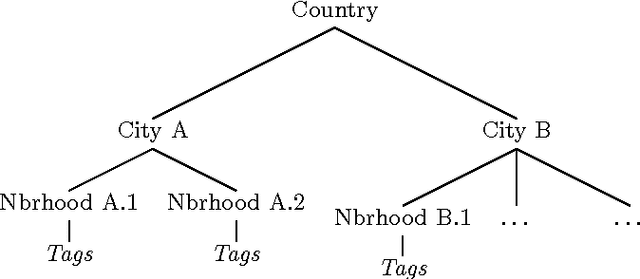
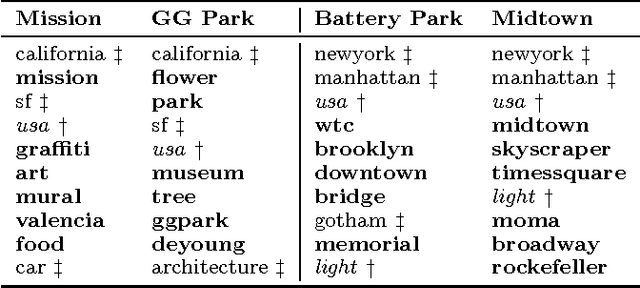
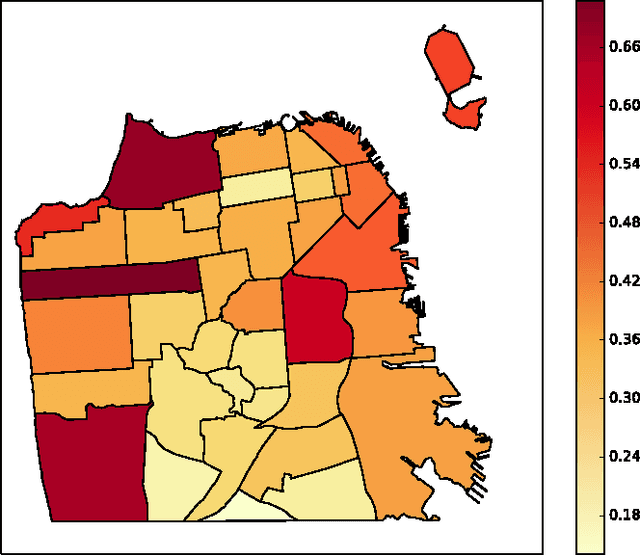

Abstract:Geotagged data can be used to describe regions in the world and discover local themes. However, not all data produced within a region is necessarily specifically descriptive of that area. To surface the content that is characteristic for a region, we present the geographical hierarchy model (GHM), a probabilistic model based on the assumption that data observed in a region is a random mixture of content that pertains to different levels of a hierarchy. We apply the GHM to a dataset of 8 million Flickr photos in order to discriminate between content (i.e., tags) that specifically characterizes a region (e.g., neighborhood) and content that characterizes surrounding areas or more general themes. Knowledge of the discriminative and non-discriminative terms used throughout the hierarchy enables us to quantify the uniqueness of a given region and to compare similar but distant regions. Our evaluation demonstrates that our model improves upon traditional Naive Bayes classification by 47% and hierarchical TF-IDF by 27%. We further highlight the differences and commonalities with human reasoning about what is locally characteristic for a neighborhood, distilled from ten interviews and a survey that covered themes such as time, events, and prior regional knowledge
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge