Charlene Wu
Learning to Represent Individual Differences for Choice Decision Making
Mar 27, 2025Abstract:Human decision making can be challenging to predict because decisions are affected by a number of complex factors. Adding to this complexity, decision-making processes can differ considerably between individuals, and methods aimed at predicting human decisions need to take individual differences into account. Behavioral science offers methods by which to measure individual differences (e.g., questionnaires, behavioral models), but these are often narrowed down to low dimensions and not tailored to specific prediction tasks. This paper investigates the use of representation learning to measure individual differences from behavioral experiment data. Representation learning offers a flexible approach to create individual embeddings from data that are both structured (e.g., demographic information) and unstructured (e.g., free text), where the flexibility provides more options for individual difference measures for personalization, e.g., free text responses may allow for open-ended questions that are less privacy-sensitive. In the current paper we use representation learning to characterize individual differences in human performance on an economic decision-making task. We demonstrate that models using representation learning to capture individual differences consistently improve decision predictions over models without representation learning, and even outperform well-known theory-based behavioral models used in these environments. Our results propose that representation learning offers a useful and flexible tool to capture individual differences.
Stylish and Functional: Guided Interpolation Subject to Physical Constraints
Dec 20, 2024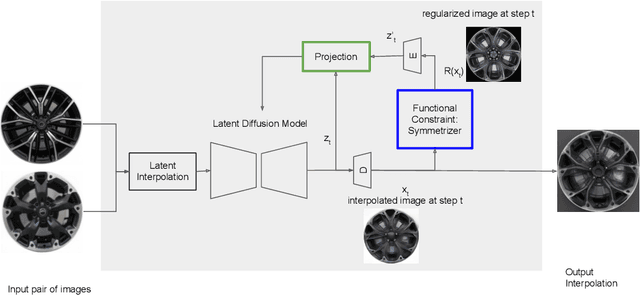
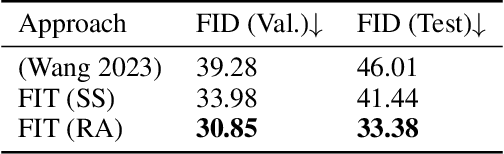

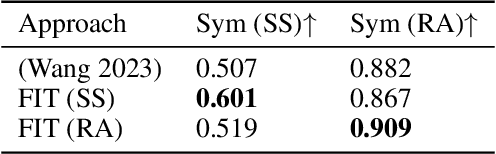
Abstract:Generative AI is revolutionizing engineering design practices by enabling rapid prototyping and manipulation of designs. One example of design manipulation involves taking two reference design images and using them as prompts to generate a design image that combines aspects of both. Real engineering designs have physical constraints and functional requirements in addition to aesthetic design considerations. Internet-scale foundation models commonly used for image generation, however, are unable to take these physical constraints and functional requirements into consideration as part of the generation process. We consider the problem of generating a design inspired by two input designs, and propose a zero-shot framework toward enforcing physical, functional requirements over the generation process by leveraging a pretrained diffusion model as the backbone. As a case study, we consider the example of rotational symmetry in generation of wheel designs. Automotive wheels are required to be rotationally symmetric for physical stability. We formulate the requirement of rotational symmetry by the use of a symmetrizer, and we use this symmetrizer to guide the diffusion process towards symmetric wheel generations. Our experimental results find that the proposed approach makes generated interpolations with higher realism than methods in related work, as evaluated by Fr\'echet inception distance (FID). We also find that our approach generates designs that more closely satisfy physical and functional requirements than generating without the symmetry guidance.
Leveraging Language Models and Bandit Algorithms to Drive Adoption of Battery-Electric Vehicles
Oct 30, 2024



Abstract:Behavior change interventions are important to coordinate societal action across a wide array of important applications, including the adoption of electrified vehicles to reduce emissions. Prior work has demonstrated that interventions for behavior must be personalized, and that the intervention that is most effective on average across a large group can result in a backlash effect that strengthens opposition among some subgroups. Thus, it is important to target interventions to different audiences, and to present them in a natural, conversational style. In this context, an important emerging application domain for large language models (LLMs) is conversational interventions for behavior change. In this work, we leverage prior work on understanding values motivating the adoption of battery electric vehicles. We leverage new advances in LLMs, combined with a contextual bandit, to develop conversational interventions that are personalized to the values of each study participant. We use a contextual bandit algorithm to learn to target values based on the demographics of each participant. To train our bandit algorithm in an offline manner, we leverage LLMs to play the role of study participants. We benchmark the persuasive effectiveness of our bandit-enhanced LLM against an unaided LLM generating conversational interventions without demographic-targeted values.
Understanding the Cognitive Complexity in Language Elicited by Product Images
Sep 25, 2024Abstract:Product images (e.g., a phone) can be used to elicit a diverse set of consumer-reported features expressed through language, including surface-level perceptual attributes (e.g., "white") and more complex ones, like perceived utility (e.g., "battery"). The cognitive complexity of elicited language reveals the nature of cognitive processes and the context required to understand them; cognitive complexity also predicts consumers' subsequent choices. This work offers an approach for measuring and validating the cognitive complexity of human language elicited by product images, providing a tool for understanding the cognitive processes of human as well as virtual respondents simulated by Large Language Models (LLMs). We also introduce a large dataset that includes diverse descriptive labels for product images, including human-rated complexity. We demonstrate that human-rated cognitive complexity can be approximated using a set of natural language models that, combined, roughly capture the complexity construct. Moreover, this approach is minimally supervised and scalable, even in use cases with limited human assessment of complexity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge