Danail Stoyanov
*: shared first/last authors
A multi-centre, multi-device benchmark dataset for landmark-based comprehensive fetal biometry
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:Accurate fetal growth assessment from ultrasound (US) relies on precise biometry measured by manually identifying anatomical landmarks in standard planes. Manual landmarking is time-consuming, operator-dependent, and sensitive to variability across scanners and sites, limiting the reproducibility of automated approaches. There is a need for multi-source annotated datasets to develop artificial intelligence-assisted fetal growth assessment methods. To address this bottleneck, we present an open, multi-centre, multi-device benchmark dataset of fetal US images with expert anatomical landmark annotations for clinically used fetal biometric measurements. These measurements include head bi-parietal and occipito-frontal diameters, abdominal transverse and antero-posterior diameters, and femoral length. The dataset comprises 4,513 de-identified US images from 1,904 subjects acquired at three clinical sites using seven different US devices. We provide standardised, subject-disjoint train/test splits, evaluation code, and baseline results to enable fair and reproducible comparison of methods. Using an automatic biometry model, we quantify domain shift and demonstrate that training and evaluation confined to a single centre substantially overestimate performance relative to multi-centre testing. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first publicly available multi-centre, multi-device, landmark-annotated dataset that covers all primary fetal biometry measures, providing a robust benchmark for domain adaptation and multi-centre generalisation in fetal biometry and enabling more reliable AI-assisted fetal growth assessment across centres. All data, annotations, training code, and evaluation pipelines are made publicly available.
Learning from Single Timestamps: Complexity Estimation in Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:Purpose: Accurate assessment of surgical complexity is essential in Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy (LC), where severe inflammation is associated with longer operative times and increased risk of postoperative complications. The Parkland Grading Scale (PGS) provides a clinically validated framework for stratifying inflammation severity; however, its automation in surgical videos remains largely unexplored, particularly in realistic scenarios where complete videos must be analyzed without prior manual curation. Methods: In this work, we introduce STC-Net, a novel framework for SingleTimestamp-based Complexity estimation in LC via the PGS, designed to operate under weak temporal supervision. Unlike prior methods limited to static images or manually trimmed clips, STC-Net operates directly on full videos. It jointly performs temporal localization and grading through a localization, window proposal, and grading module. We introduce a novel loss formulation combining hard and soft localization objectives and background-aware grading supervision. Results: Evaluated on a private dataset of 1,859 LC videos, STC-Net achieves an accuracy of 62.11% and an F1-score of 61.42%, outperforming non-localized baselines by over 10% in both metrics and highlighting the effectiveness of weak supervision for surgical complexity assessment. Conclusion: STC-Net demonstrates a scalable and effective approach for automated PGS-based surgical complexity estimation from full LC videos, making it promising for post-operative analysis and surgical training.
Federated Learning for Surgical Vision in Appendicitis Classification: Results of the FedSurg EndoVis 2024 Challenge
Oct 06, 2025Abstract:Purpose: The FedSurg challenge was designed to benchmark the state of the art in federated learning for surgical video classification. Its goal was to assess how well current methods generalize to unseen clinical centers and adapt through local fine-tuning while enabling collaborative model development without sharing patient data. Methods: Participants developed strategies to classify inflammation stages in appendicitis using a preliminary version of the multi-center Appendix300 video dataset. The challenge evaluated two tasks: generalization to an unseen center and center-specific adaptation after fine-tuning. Submitted approaches included foundation models with linear probing, metric learning with triplet loss, and various FL aggregation schemes (FedAvg, FedMedian, FedSAM). Performance was assessed using F1-score and Expected Cost, with ranking robustness evaluated via bootstrapping and statistical testing. Results: In the generalization task, performance across centers was limited. In the adaptation task, all teams improved after fine-tuning, though ranking stability was low. The ViViT-based submission achieved the strongest overall performance. The challenge highlighted limitations in generalization, sensitivity to class imbalance, and difficulties in hyperparameter tuning in decentralized training, while spatiotemporal modeling and context-aware preprocessing emerged as promising strategies. Conclusion: The FedSurg Challenge establishes the first benchmark for evaluating FL strategies in surgical video classification. Findings highlight the trade-off between local personalization and global robustness, and underscore the importance of architecture choice, preprocessing, and loss design. This benchmarking offers a reference point for future development of imbalance-aware, adaptive, and robust FL methods in clinical surgical AI.
Exploring Pre-training Across Domains for Few-Shot Surgical Skill Assessment
Sep 11, 2025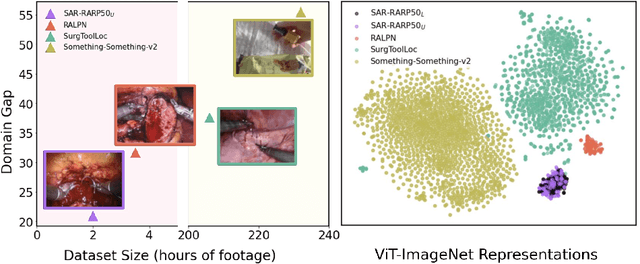

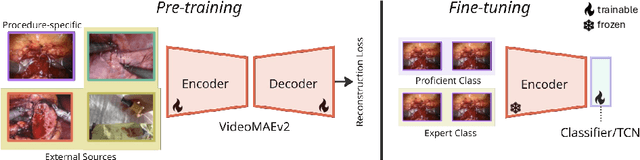
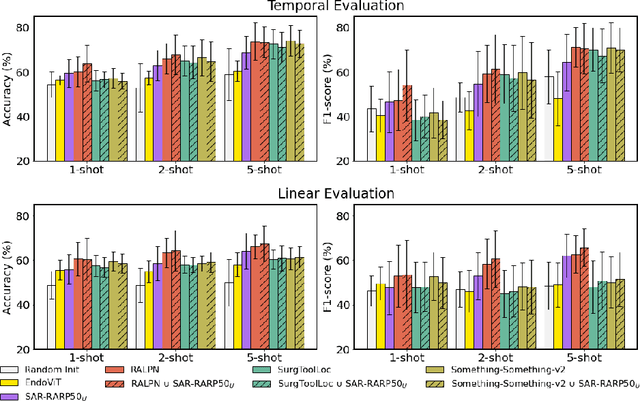
Abstract:Automated surgical skill assessment (SSA) is a central task in surgical computer vision. Developing robust SSA models is challenging due to the scarcity of skill annotations, which are time-consuming to produce and require expert consensus. Few-shot learning (FSL) offers a scalable alternative enabling model development with minimal supervision, though its success critically depends on effective pre-training. While widely studied for several surgical downstream tasks, pre-training has remained largely unexplored in SSA. In this work, we formulate SSA as a few-shot task and investigate how self-supervised pre-training strategies affect downstream few-shot SSA performance. We annotate a publicly available robotic surgery dataset with Objective Structured Assessment of Technical Skill (OSATS) scores, and evaluate various pre-training sources across three few-shot settings. We quantify domain similarity and analyze how domain gap and the inclusion of procedure-specific data into pre-training influence transferability. Our results show that small but domain-relevant datasets can outperform large scale, less aligned ones, achieving accuracies of 60.16%, 66.03%, and 73.65% in the 1-, 2-, and 5-shot settings, respectively. Moreover, incorporating procedure-specific data into pre-training with a domain-relevant external dataset significantly boosts downstream performance, with an average gain of +1.22% in accuracy and +2.28% in F1-score; however, applying the same strategy with less similar but large-scale sources can instead lead to performance degradation. Code and models are available at https://github.com/anastadimi/ssa-fsl.
Comparative validation of surgical phase recognition, instrument keypoint estimation, and instrument instance segmentation in endoscopy: Results of the PhaKIR 2024 challenge
Jul 22, 2025Abstract:Reliable recognition and localization of surgical instruments in endoscopic video recordings are foundational for a wide range of applications in computer- and robot-assisted minimally invasive surgery (RAMIS), including surgical training, skill assessment, and autonomous assistance. However, robust performance under real-world conditions remains a significant challenge. Incorporating surgical context - such as the current procedural phase - has emerged as a promising strategy to improve robustness and interpretability. To address these challenges, we organized the Surgical Procedure Phase, Keypoint, and Instrument Recognition (PhaKIR) sub-challenge as part of the Endoscopic Vision (EndoVis) challenge at MICCAI 2024. We introduced a novel, multi-center dataset comprising thirteen full-length laparoscopic cholecystectomy videos collected from three distinct medical institutions, with unified annotations for three interrelated tasks: surgical phase recognition, instrument keypoint estimation, and instrument instance segmentation. Unlike existing datasets, ours enables joint investigation of instrument localization and procedural context within the same data while supporting the integration of temporal information across entire procedures. We report results and findings in accordance with the BIAS guidelines for biomedical image analysis challenges. The PhaKIR sub-challenge advances the field by providing a unique benchmark for developing temporally aware, context-driven methods in RAMIS and offers a high-quality resource to support future research in surgical scene understanding.
StereoMamba: Real-time and Robust Intraoperative Stereo Disparity Estimation via Long-range Spatial Dependencies
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:Stereo disparity estimation is crucial for obtaining depth information in robot-assisted minimally invasive surgery (RAMIS). While current deep learning methods have made significant advancements, challenges remain in achieving an optimal balance between accuracy, robustness, and inference speed. To address these challenges, we propose the StereoMamba architecture, which is specifically designed for stereo disparity estimation in RAMIS. Our approach is based on a novel Feature Extraction Mamba (FE-Mamba) module, which enhances long-range spatial dependencies both within and across stereo images. To effectively integrate multi-scale features from FE-Mamba, we then introduce a novel Multidimensional Feature Fusion (MFF) module. Experiments against the state-of-the-art on the ex-vivo SCARED benchmark demonstrate that StereoMamba achieves superior performance on EPE of 2.64 px and depth MAE of 2.55 mm, the second-best performance on Bad2 of 41.49% and Bad3 of 26.99%, while maintaining an inference speed of 21.28 FPS for a pair of high-resolution images (1280*1024), striking the optimum balance between accuracy, robustness, and efficiency. Furthermore, by comparing synthesized right images, generated from warping left images using the generated disparity maps, with the actual right image, StereoMamba achieves the best average SSIM (0.8970) and PSNR (16.0761), exhibiting strong zero-shot generalization on the in-vivo RIS2017 and StereoMIS datasets.
Point Tracking in Surgery--The 2024 Surgical Tattoos in Infrared (STIR) Challenge
Mar 31, 2025Abstract:Understanding tissue motion in surgery is crucial to enable applications in downstream tasks such as segmentation, 3D reconstruction, virtual tissue landmarking, autonomous probe-based scanning, and subtask autonomy. Labeled data are essential to enabling algorithms in these downstream tasks since they allow us to quantify and train algorithms. This paper introduces a point tracking challenge to address this, wherein participants can submit their algorithms for quantification. The submitted algorithms are evaluated using a dataset named surgical tattoos in infrared (STIR), with the challenge aptly named the STIR Challenge 2024. The STIR Challenge 2024 comprises two quantitative components: accuracy and efficiency. The accuracy component tests the accuracy of algorithms on in vivo and ex vivo sequences. The efficiency component tests the latency of algorithm inference. The challenge was conducted as a part of MICCAI EndoVis 2024. In this challenge, we had 8 total teams, with 4 teams submitting before and 4 submitting after challenge day. This paper details the STIR Challenge 2024, which serves to move the field towards more accurate and efficient algorithms for spatial understanding in surgery. In this paper we summarize the design, submissions, and results from the challenge. The challenge dataset is available here: https://zenodo.org/records/14803158 , and the code for baseline models and metric calculation is available here: https://github.com/athaddius/STIRMetrics
EndoLRMGS: Complete Endoscopic Scene Reconstruction combining Large Reconstruction Modelling and Gaussian Splatting
Mar 28, 2025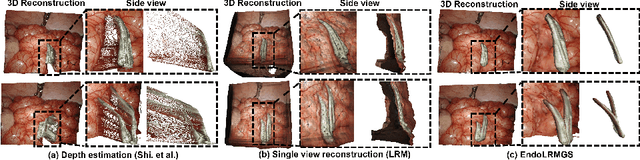
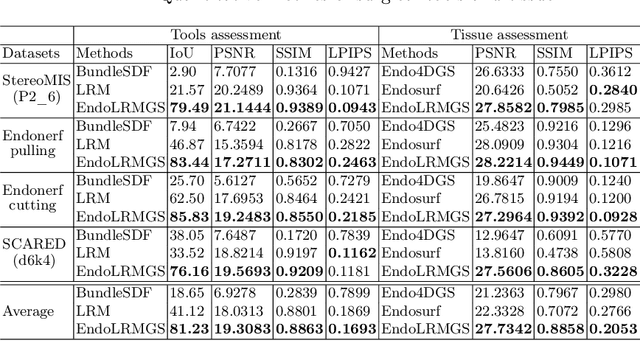
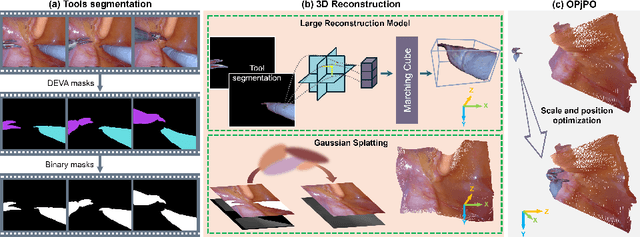
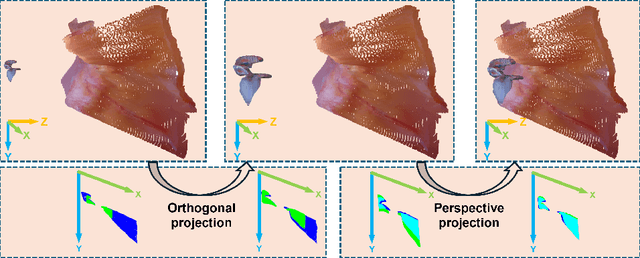
Abstract:Complete reconstruction of surgical scenes is crucial for robot-assisted surgery (RAS). Deep depth estimation is promising but existing works struggle with depth discontinuities, resulting in noisy predictions at object boundaries and do not achieve complete reconstruction omitting occluded surfaces. To address these issues we propose EndoLRMGS, that combines Large Reconstruction Modelling (LRM) and Gaussian Splatting (GS), for complete surgical scene reconstruction. GS reconstructs deformable tissues and LRM generates 3D models for surgical tools while position and scale are subsequently optimized by introducing orthogonal perspective joint projection optimization (OPjPO) to enhance accuracy. In experiments on four surgical videos from three public datasets, our method improves the Intersection-over-union (IoU) of tool 3D models in 2D projections by>40%. Additionally, EndoLRMGS improves the PSNR of the tools projection from 3.82% to 11.07%. Tissue rendering quality also improves, with PSNR increasing from 0.46% to 49.87%, and SSIM from 1.53% to 29.21% across all test videos.
3D Acetabular Surface Reconstruction from 2D Pre-operative X-ray Images using SRVF Elastic Registration and Deformation Graph
Mar 28, 2025Abstract:Accurate and reliable selection of the appropriate acetabular cup size is crucial for restoring joint biomechanics in total hip arthroplasty (THA). This paper proposes a novel framework that integrates square-root velocity function (SRVF)-based elastic shape registration technique with an embedded deformation (ED) graph approach to reconstruct the 3D articular surface of the acetabulum by fusing multiple views of 2D pre-operative pelvic X-ray images and a hemispherical surface model. The SRVF-based elastic registration establishes 2D-3D correspondences between the parametric hemispherical model and X-ray images, and the ED framework incorporates the SRVF-derived correspondences as constraints to optimize the 3D acetabular surface reconstruction using nonlinear least-squares optimization. Validations using both simulation and real patient datasets are performed to demonstrate the robustness and the potential clinical value of the proposed algorithm. The reconstruction result can assist surgeons in selecting the correct acetabular cup on the first attempt in primary THA, minimising the need for revision surgery.
SurgicalVLM-Agent: Towards an Interactive AI Co-Pilot for Pituitary Surgery
Mar 12, 2025Abstract:Image-guided surgery demands adaptive, real-time decision support, yet static AI models struggle with structured task planning and providing interactive guidance. Large vision-language models (VLMs) offer a promising solution by enabling dynamic task planning and predictive decision support. We introduce SurgicalVLM-Agent, an AI co-pilot for image-guided pituitary surgery, capable of conversation, planning, and task execution. The agent dynamically processes surgeon queries and plans the tasks such as MRI tumor segmentation, endoscope anatomy segmentation, overlaying preoperative imaging with intraoperative views, instrument tracking, and surgical visual question answering (VQA). To enable structured task planning, we develop the PitAgent dataset, a surgical context-aware dataset covering segmentation, overlaying, instrument localization, tool tracking, tool-tissue interactions, phase identification, and surgical activity recognition. Additionally, we propose FFT-GaLore, a fast Fourier transform (FFT)-based gradient projection technique for efficient low-rank adaptation, optimizing fine-tuning for LLaMA 3.2 in surgical environments. We validate SurgicalVLM-Agent by assessing task planning and prompt generation on our PitAgent dataset and evaluating zero-shot VQA using a public pituitary dataset. Results demonstrate state-of-the-art performance in task planning and query interpretation, with highly semantically meaningful VQA responses, advancing AI-driven surgical assistance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge