Dan Lin
DAOS: A Multimodal In-cabin Behavior Monitoring with Driver Action-Object Synergy Dataset
Jan 17, 2026Abstract:In driver activity monitoring, movements are mostly limited to the upper body, which makes many actions look similar. To tell these actions apart, human often rely on the objects the driver is using, such as holding a phone compared with gripping the steering wheel. However, most existing driver-monitoring datasets lack accurate object-location annotations or do not link objects to their associated actions, leaving a critical gap for reliable action recognition. To address this, we introduce the Driver Action with Object Synergy (DAOS) dataset, comprising 9,787 video clips annotated with 36 fine-grained driver actions and 15 object classes, totaling more than 2.5 million corresponding object instances. DAOS offers multi-modal, multi-view data (RGB, IR, and depth) from front, face, left, and right perspectives. Although DAOS captures a wide range of cabin objects, only a few are directly relevant to each action for prediction, so focusing on task-specific human-object relations is essential. To tackle this challenge, we propose the Action-Object-Relation Network (AOR-Net). AOR-Net comprehends complex driver actions through multi-level reasoning and a chain-of-action prompting mechanism that models the logical relationships among actions, objects, and their relations. Additionally, the Mixture of Thoughts module is introduced to dynamically select essential knowledge at each stage, enhancing robustness in object-rich and object-scarce conditions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our model outperforms other state-of-the-art methods on various datasets.
A Generative Foundation Model for Chest Radiography
Sep 04, 2025Abstract:The scarcity of well-annotated diverse medical images is a major hurdle for developing reliable AI models in healthcare. Substantial technical advances have been made in generative foundation models for natural images. Here we develop `ChexGen', a generative vision-language foundation model that introduces a unified framework for text-, mask-, and bounding box-guided synthesis of chest radiographs. Built upon the latent diffusion transformer architecture, ChexGen was pretrained on the largest curated chest X-ray dataset to date, consisting of 960,000 radiograph-report pairs. ChexGen achieves accurate synthesis of radiographs through expert evaluations and quantitative metrics. We demonstrate the utility of ChexGen for training data augmentation and supervised pretraining, which led to performance improvements across disease classification, detection, and segmentation tasks using a small fraction of training data. Further, our model enables the creation of diverse patient cohorts that enhance model fairness by detecting and mitigating demographic biases. Our study supports the transformative role of generative foundation models in building more accurate, data-efficient, and equitable medical AI systems.
Open World Object Detection: A Survey
Oct 15, 2024



Abstract:Exploring new knowledge is a fundamental human ability that can be mirrored in the development of deep neural networks, especially in the field of object detection. Open world object detection (OWOD) is an emerging area of research that adapts this principle to explore new knowledge. It focuses on recognizing and learning from objects absent from initial training sets, thereby incrementally expanding its knowledge base when new class labels are introduced. This survey paper offers a thorough review of the OWOD domain, covering essential aspects, including problem definitions, benchmark datasets, source codes, evaluation metrics, and a comparative study of existing methods. Additionally, we investigate related areas like open set recognition (OSR) and incremental learning (IL), underlining their relevance to OWOD. Finally, the paper concludes by addressing the limitations and challenges faced by current OWOD algorithms and proposes directions for future research. To our knowledge, this is the first comprehensive survey of the emerging OWOD field with over one hundred references, marking a significant step forward for object detection technology. A comprehensive source code and benchmarks are archived and concluded at https://github.com/ArminLee/OWOD Review.
MultiFuser: Multimodal Fusion Transformer for Enhanced Driver Action Recognition
Aug 03, 2024Abstract:Driver action recognition, aiming to accurately identify drivers' behaviours, is crucial for enhancing driver-vehicle interactions and ensuring driving safety. Unlike general action recognition, drivers' environments are often challenging, being gloomy and dark, and with the development of sensors, various cameras such as IR and depth cameras have emerged for analyzing drivers' behaviors. Therefore, in this paper, we propose a novel multimodal fusion transformer, named MultiFuser, which identifies cross-modal interrelations and interactions among multimodal car cabin videos and adaptively integrates different modalities for improved representations. Specifically, MultiFuser comprises layers of Bi-decomposed Modules to model spatiotemporal features, with a modality synthesizer for multimodal features integration. Each Bi-decomposed Module includes a Modal Expertise ViT block for extracting modality-specific features and a Patch-wise Adaptive Fusion block for efficient cross-modal fusion. Extensive experiments are conducted on Drive&Act dataset and the results demonstrate the efficacy of our proposed approach.
CM2-Net: Continual Cross-Modal Mapping Network for Driver Action Recognition
Jun 18, 2024Abstract:Driver action recognition has significantly advanced in enhancing driver-vehicle interactions and ensuring driving safety by integrating multiple modalities, such as infrared and depth. Nevertheless, compared to RGB modality only, it is always laborious and costly to collect extensive data for all types of non-RGB modalities in car cabin environments. Therefore, previous works have suggested independently learning each non-RGB modality by fine-tuning a model pre-trained on RGB videos, but these methods are less effective in extracting informative features when faced with newly-incoming modalities due to large domain gaps. In contrast, we propose a Continual Cross-Modal Mapping Network (CM2-Net) to continually learn each newly-incoming modality with instructive prompts from the previously-learned modalities. Specifically, we have developed Accumulative Cross-modal Mapping Prompting (ACMP), to map the discriminative and informative features learned from previous modalities into the feature space of newly-incoming modalities. Then, when faced with newly-incoming modalities, these mapped features are able to provide effective prompts for which features should be extracted and prioritized. These prompts are accumulating throughout the continual learning process, thereby boosting further recognition performances. Extensive experiments conducted on the Drive&Act dataset demonstrate the performance superiority of CM2-Net on both uni- and multi-modal driver action recognition.
Multi-modality action recognition based on dual feature shift in vehicle cabin monitoring
Jan 26, 2024Abstract:Driver Action Recognition (DAR) is crucial in vehicle cabin monitoring systems. In real-world applications, it is common for vehicle cabins to be equipped with cameras featuring different modalities. However, multi-modality fusion strategies for the DAR task within car cabins have rarely been studied. In this paper, we propose a novel yet efficient multi-modality driver action recognition method based on dual feature shift, named DFS. DFS first integrates complementary features across modalities by performing modality feature interaction. Meanwhile, DFS achieves the neighbour feature propagation within single modalities, by feature shifting among temporal frames. To learn common patterns and improve model efficiency, DFS shares feature extracting stages among multiple modalities. Extensive experiments have been carried out to verify the effectiveness of the proposed DFS model on the Drive\&Act dataset. The results demonstrate that DFS achieves good performance and improves the efficiency of multi-modality driver action recognition.
River of No Return: Graph Percolation Embeddings for Efficient Knowledge Graph Reasoning
May 17, 2023Abstract:We study Graph Neural Networks (GNNs)-based embedding techniques for knowledge graph (KG) reasoning. For the first time, we link the path redundancy issue in the state-of-the-art KG reasoning models based on path encoding and message passing to the transformation error in model training, which brings us new theoretical insights into KG reasoning, as well as high efficacy in practice. On the theoretical side, we analyze the entropy of transformation error in KG paths and point out query-specific redundant paths causing entropy increases. These findings guide us to maintain the shortest paths and remove redundant paths for minimized-entropy message passing. To achieve this goal, on the practical side, we propose an efficient Graph Percolation Process motivated by the percolation model in Fluid Mechanics, and design a lightweight GNN-based KG reasoning framework called Graph Percolation Embeddings (GraPE). GraPE outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods in both transductive and inductive reasoning tasks while requiring fewer training parameters and less inference time.
An EEG Channel Selection Framework for Driver Drowsiness Detection via Interpretability Guidance
Apr 26, 2023



Abstract:Drowsy driving has a crucial influence on driving safety, creating an urgent demand for driver drowsiness detection. Electroencephalogram (EEG) signal can accurately reflect the mental fatigue state and thus has been widely studied in drowsiness monitoring. However, the raw EEG data is inherently noisy and redundant, which is neglected by existing works that just use single-channel EEG data or full-head channel EEG data for model training, resulting in limited performance of driver drowsiness detection. In this paper, we are the first to propose an Interpretability-guided Channel Selection (ICS) framework for the driver drowsiness detection task. Specifically, we design a two-stage training strategy to progressively select the key contributing channels with the guidance of interpretability. We first train a teacher network in the first stage using full-head channel EEG data. Then we apply the class activation mapping (CAM) to the trained teacher model to highlight the high-contributing EEG channels and further propose a channel voting scheme to select the top N contributing EEG channels. Finally, we train a student network with the selected channels of EEG data in the second stage for driver drowsiness detection. Experiments are designed on a public dataset, and the results demonstrate that our method is highly applicable and can significantly improve the performance of cross-subject driver drowsiness detection.
Defend Data Poisoning Attacks on Voice Authentication
Sep 09, 2022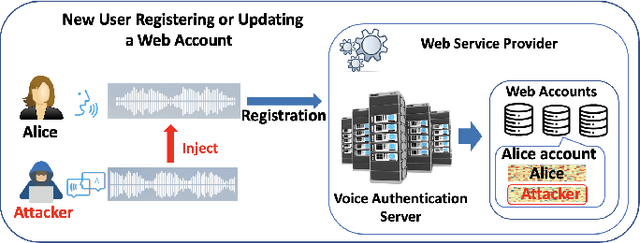
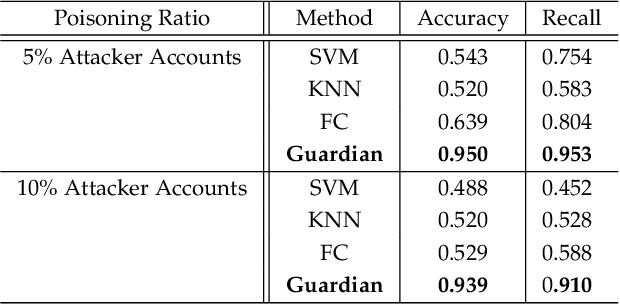
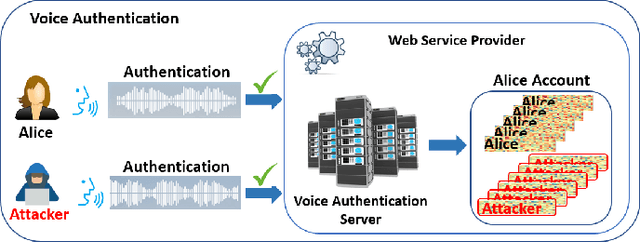
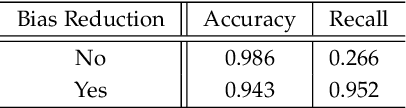
Abstract:With the advances in deep learning, speaker verification has achieved very high accuracy and is gaining popularity as a type of biometric authentication option in many scenes of our daily life, especially the growing market of web services. Compared to traditional passwords, "vocal passwords" are much more convenient as they relieve people from memorizing different passwords. However, new machine learning attacks are putting these voice authentication systems at risk. Without a strong security guarantee, attackers could access legitimate users' web accounts by fooling the deep neural network (DNN) based voice recognition models. In this paper, we demonstrate an easy-to-implement data poisoning attack to the voice authentication system, which can hardly be captured by existing defense mechanisms. Thus, we propose a more robust defense method, called Guardian, which is a convolutional neural network-based discriminator. The Guardian discriminator integrates a series of novel techniques including bias reduction, input augmentation, and ensemble learning. Our approach is able to distinguish about 95% of attacked accounts from normal accounts, which is much more effective than existing approaches with only 60% accuracy.
PRSNet: Part Relation and Selection Network for Bone Age Assessment
Sep 05, 2019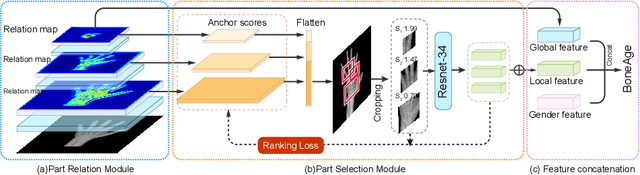
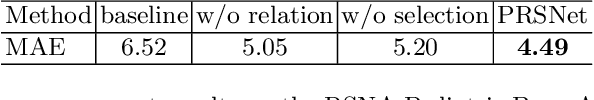
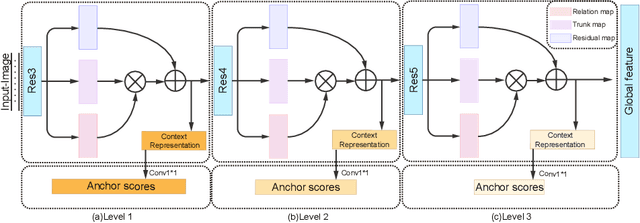
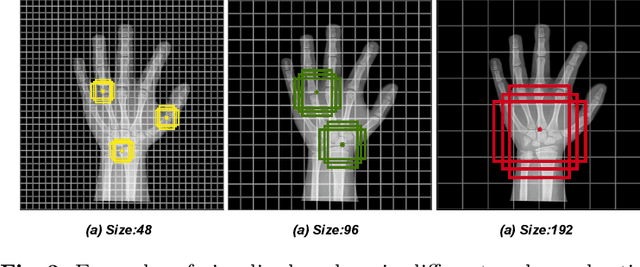
Abstract:Bone age is one of the most important indicators for assessing bone's maturity, which can help to interpret human's growth development level and potential progress. In the clinical practice, bone age assessment (BAA) of X-ray images requires the joint consideration of the appearance and location information of hand bones. These kinds of information can be effectively captured by the relation of different anatomical parts of hand bone. Recently developed methods differ mostly in how they model the part relation and choose useful parts for BAA. However, these methods neglect the mining of relationship among different parts, which can help to improve the assessment accuracy. In this paper, we propose a novel part relation module, which accurately discovers the underlying concurrency of parts by using multi-scale context information of deep learning feature representation. Furthermore, based on the part relation, we explore a new part selection module, which comprehensively measures the importance of parts and select the top ranking parts for assisting BAA. We jointly train our part relation and selection modules in an end-to-end way, achieving state-of-the-art performance on the public RSNA 2017 Pediatric Bone Age benchmark dataset and outperforming other competitive methods by a significant margin.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge