Colorado J Reed
Refine and Represent: Region-to-Object Representation Learning
Aug 25, 2022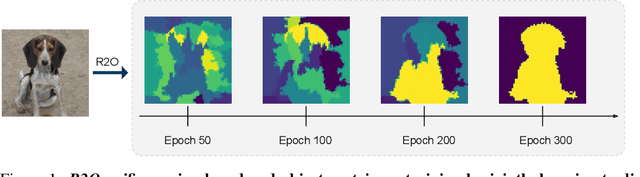
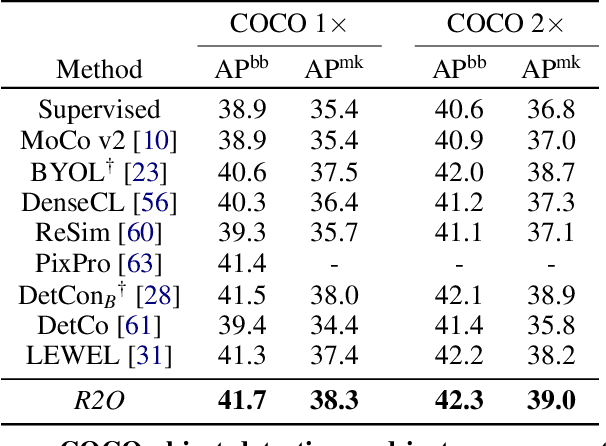
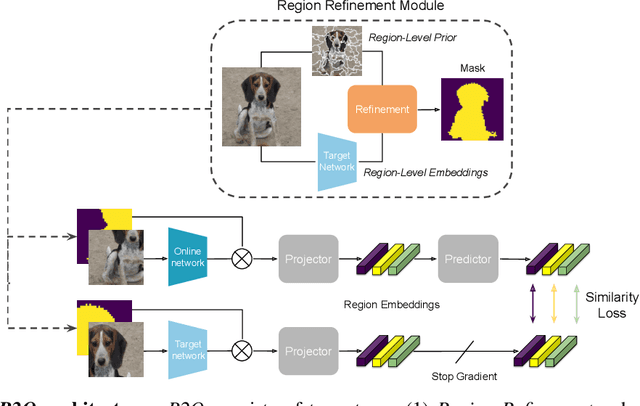
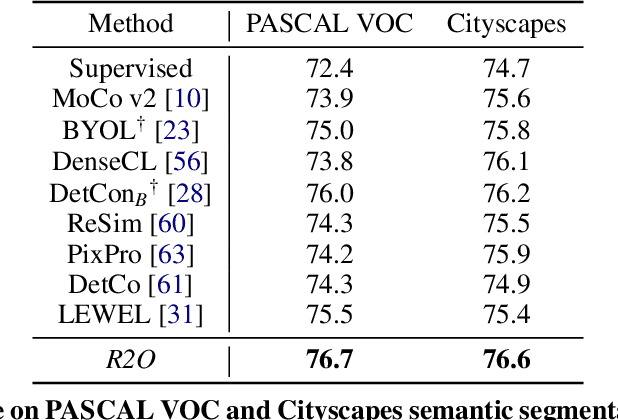
Abstract:Recent works in self-supervised learning have demonstrated strong performance on scene-level dense prediction tasks by pretraining with object-centric or region-based correspondence objectives. In this paper, we present Region-to-Object Representation Learning (R2O) which unifies region-based and object-centric pretraining. R2O operates by training an encoder to dynamically refine region-based segments into object-centric masks and then jointly learns representations of the contents within the mask. R2O uses a "region refinement module" to group small image regions, generated using a region-level prior, into larger regions which tend to correspond to objects by clustering region-level features. As pretraining progresses, R2O follows a region-to-object curriculum which encourages learning region-level features early on and gradually progresses to train object-centric representations. Representations learned using R2O lead to state-of-the art performance in semantic segmentation for PASCAL VOC (+0.7 mIOU) and Cityscapes (+0.4 mIOU) and instance segmentation on MS COCO (+0.3 mask AP). Further, after pretraining on ImageNet, R2O pretrained models are able to surpass existing state-of-the-art in unsupervised object segmentation on the Caltech-UCSD Birds 200-2011 dataset (+2.9 mIoU) without any further training. We provide the code/models from this work at https://github.com/KKallidromitis/r2o.
Snowpack Estimation in Key Mountainous Water Basins from Openly-Available, Multimodal Data Sources
Aug 08, 2022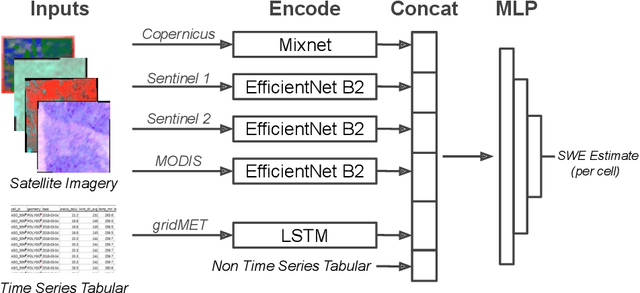
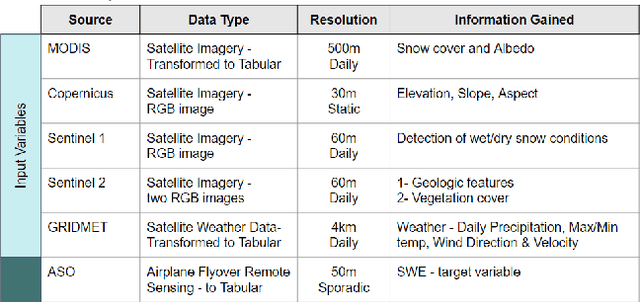
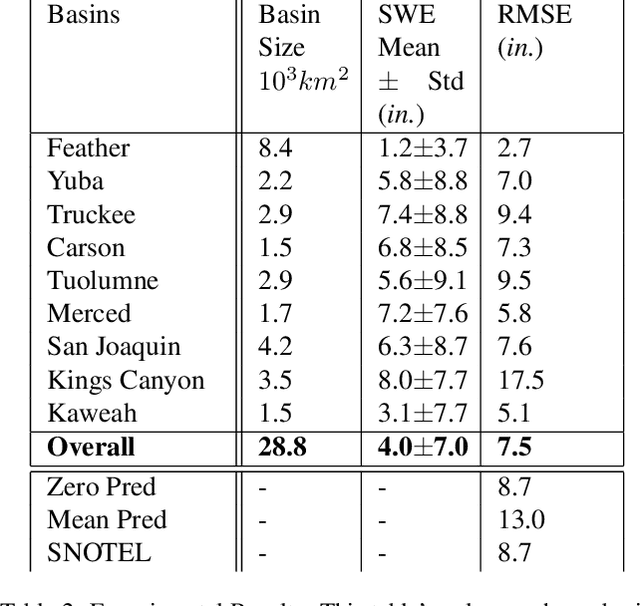
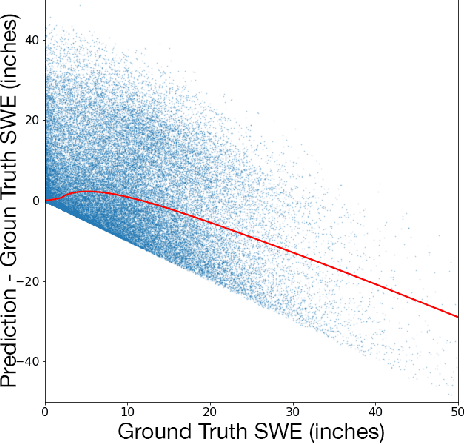
Abstract:Accurately estimating the snowpack in key mountainous basins is critical for water resource managers to make decisions that impact local and global economies, wildlife, and public policy. Currently, this estimation requires multiple LiDAR-equipped plane flights or in situ measurements, both of which are expensive, sparse, and biased towards accessible regions. In this paper, we demonstrate that fusing spatial and temporal information from multiple, openly-available satellite and weather data sources enables estimation of snowpack in key mountainous regions. Our multisource model outperforms single-source estimation by 5.0 inches RMSE, as well as outperforms sparse in situ measurements by 1.2 inches RMSE.
SunCast: Solar Irradiance Nowcasting from Geosynchronous Satellite Data
Jan 17, 2022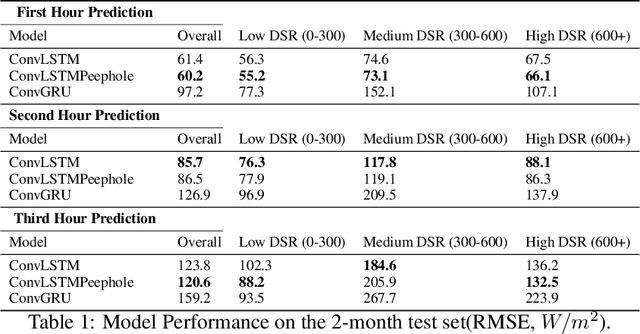
Abstract:When cloud layers cover photovoltaic (PV) panels, the amount of power the panels produce fluctuates rapidly. Therefore, to maintain enough energy on a power grid to match demand, utilities companies rely on reserve power sources that typically come from fossil fuels and therefore pollute the environment. Accurate short-term PV power prediction enables operators to maximize the amount of power obtained from PV panels and safely reduce the reserve energy needed from fossil fuel sources. While several studies have developed machine learning models to predict solar irradiance at specific PV generation facilities, little work has been done to model short-term solar irradiance on a global scale. Furthermore, models that have been developed are proprietary and have architectures that are not publicly available or rely on computationally demanding Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP) models. Here, we propose a Convolutional Long Short-Term Memory Network model that treats solar nowcasting as a next frame prediction problem, is more efficient than NWP models and has a straightforward, reproducible architecture. Our models can predict solar irradiance for entire North America for up to 3 hours in under 60 seconds on a single machine without a GPU and has a RMSE of 120 W/m2 when evaluated on 2 months of data.
DETReg: Unsupervised Pretraining with Region Priors for Object Detection
Jun 08, 2021



Abstract:Unsupervised pretraining has recently proven beneficial for computer vision tasks, including object detection. However, previous self-supervised approaches are not designed to handle a key aspect of detection: localizing objects. Here, we present DETReg, an unsupervised pretraining approach for object DEtection with TRansformers using Region priors. Motivated by the two tasks underlying object detection: localization and categorization, we combine two complementary signals for self-supervision. For an object localization signal, we use pseudo ground truth object bounding boxes from an off-the-shelf unsupervised region proposal method, Selective Search, which does not require training data and can detect objects at a high recall rate and very low precision. The categorization signal comes from an object embedding loss that encourages invariant object representations, from which the object category can be inferred. We show how to combine these two signals to train the Deformable DETR detection architecture from large amounts of unlabeled data. DETReg improves the performance over competitive baselines and previous self-supervised methods on standard benchmarks like MS COCO and PASCAL VOC. DETReg also outperforms previous supervised and unsupervised baseline approaches on low-data regime when trained with only 1%, 2%, 5%, and 10% of the labeled data on MS COCO. For code and pretrained models, visit the project page at https://amirbar.net/detreg
Region Similarity Representation Learning
Mar 24, 2021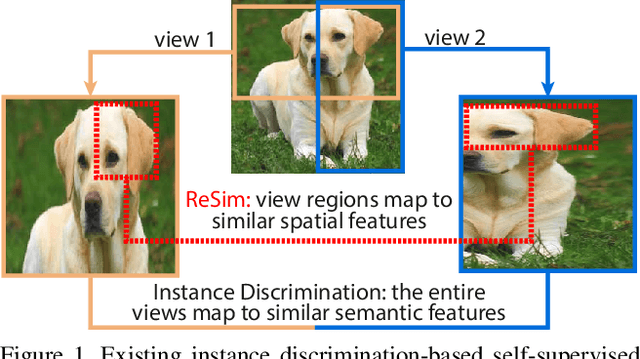
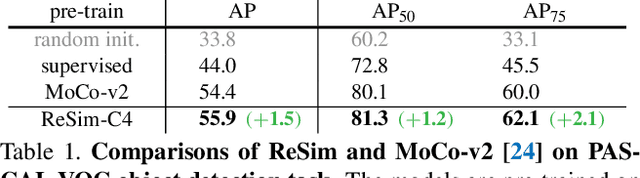
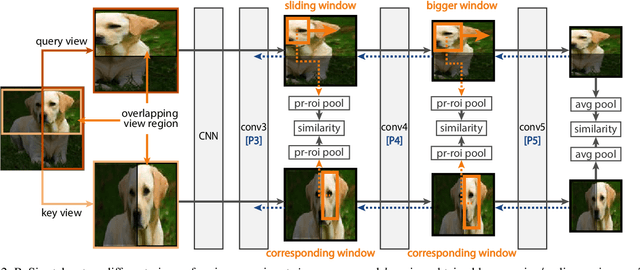
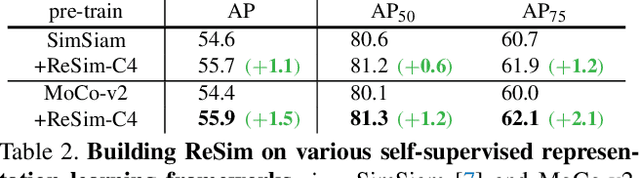
Abstract:We present Region Similarity Representation Learning (ReSim), a new approach to self-supervised representation learning for localization-based tasks such as object detection and segmentation. While existing work has largely focused on solely learning global representations for an entire image, ReSim learns both regional representations for localization as well as semantic image-level representations. ReSim operates by sliding a fixed-sized window across the overlapping area between two views (e.g., image crops), aligning these areas with their corresponding convolutional feature map regions, and then maximizing the feature similarity across views. As a result, ReSim learns spatially and semantically consistent feature representation throughout the convolutional feature maps of a neural network. A shift or scale of an image region, e.g., a shift or scale of an object, has a corresponding change in the feature maps; this allows downstream tasks to leverage these representations for localization. Through object detection, instance segmentation, and dense pose estimation experiments, we illustrate how ReSim learns representations which significantly improve the localization and classification performance compared to a competitive MoCo-v2 baseline: $+2.7$ AP$^{\text{bb}}_{75}$ VOC, $+1.1$ AP$^{\text{bb}}_{75}$ COCO, and $+1.9$ AP$^{\text{mk}}$ Cityscapes. Code and pre-trained models are released at: \url{https://github.com/Tete-Xiao/ReSim}
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge