Christopher Bogart
AI Literacy Assessment Revisited: A Task-Oriented Approach Aligned with Real-world Occupations
Nov 07, 2025Abstract:As artificial intelligence (AI) systems become ubiquitous in professional contexts, there is an urgent need to equip workers, often with backgrounds outside of STEM, with the skills to use these tools effectively as well as responsibly, that is, to be AI literate. However, prevailing definitions and therefore assessments of AI literacy often emphasize foundational technical knowledge, such as programming, mathematics, and statistics, over practical knowledge such as interpreting model outputs, selecting tools, or identifying ethical concerns. This leaves a noticeable gap in assessing someone's AI literacy for real-world job use. We propose a work-task-oriented assessment model for AI literacy which is grounded in the competencies required for effective use of AI tools in professional settings. We describe the development of a novel AI literacy assessment instrument, and accompanying formative assessments, in the context of a US Navy robotics training program. The program included training in robotics and AI literacy, as well as a competition with practical tasks and a multiple choice scenario task meant to simulate use of AI in a job setting. We found that, as a measure of applied AI literacy, the competition's scenario task outperformed the tests we adopted from past research or developed ourselves. We argue that when training people for AI-related work, educators should consider evaluating them with instruments that emphasize highly contextualized practical skills rather than abstract technical knowledge, especially when preparing workers without technical backgrounds for AI-integrated roles.
"I Like That You Have to Poke Around": Instructors on How Experiential Approaches to AI Literacy Spark Inquiry and Critical Thinking
Nov 07, 2025Abstract:As artificial intelligence (AI) increasingly shapes decision-making across domains, there is a growing need to support AI literacy among learners beyond computer science. However, many current approaches rely on programming-heavy tools or abstract lecture-based content, limiting accessibility for non-STEM audiences. This paper presents findings from a study of AI User, a modular, web-based curriculum that teaches core AI concepts through interactive, no-code projects grounded in real-world scenarios. The curriculum includes eight projects; this study focuses on instructor feedback on Projects 5-8, which address applied topics such as natural language processing, computer vision, decision support, and responsible AI. Fifteen community college instructors participated in structured focus groups, completing the projects as learners and providing feedback through individual reflection and group discussion. Using thematic analysis, we examined how instructors evaluated the design, instructional value, and classroom applicability of these experiential activities. Findings highlight instructors' appreciation for exploratory tasks, role-based simulations, and real-world relevance, while also surfacing design trade-offs around cognitive load, guidance, and adaptability for diverse learners. This work extends prior research on AI literacy by centering instructor perspectives on teaching complex AI topics without code. It offers actionable insights for designing inclusive, experiential AI learning resources that scale across disciplines and learner backgrounds.
AI Technicians: Developing Rapid Occupational Training Methods for a Competitive AI Workforce
Jan 17, 2025



Abstract:The accelerating pace of developments in Artificial Intelligence~(AI) and the increasing role that technology plays in society necessitates substantial changes in the structure of the workforce. Besides scientists and engineers, there is a need for a very large workforce of competent AI technicians (i.e., maintainers, integrators) and users~(i.e., operators). As traditional 4-year and 2-year degree-based education cannot fill this quickly opening gap, alternative training methods have to be developed. We present the results of the first four years of the AI Technicians program which is a unique collaboration between the U.S. Army's Artificial Intelligence Integration Center (AI2C) and Carnegie Mellon University to design, implement and evaluate novel rapid occupational training methods to create a competitive AI workforce at the technicians level. Through this multi-year effort we have already trained 59 AI Technicians. A key observation is that ongoing frequent updates to the training are necessary as the adoption of AI in the U.S. Army and within the society at large is evolving rapidly. A tight collaboration among the stakeholders from the army and the university is essential for successful development and maintenance of the training for the evolving role. Our findings can be leveraged by large organizations that face the challenge of developing a competent AI workforce as well as educators and researchers engaged in solving the challenge.
Generating Situated Reflection Triggers about Alternative Solution Paths: A Case Study of Generative AI for Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning
Apr 28, 2024



Abstract:An advantage of Large Language Models (LLMs) is their contextualization capability - providing different responses based on student inputs like solution strategy or prior discussion, to potentially better engage students than standard feedback. We present a design and evaluation of a proof-of-concept LLM application to offer students dynamic and contextualized feedback. Specifically, we augment an Online Programming Exercise bot for a college-level Cloud Computing course with ChatGPT, which offers students contextualized reflection triggers during a collaborative query optimization task in database design. We demonstrate that LLMs can be used to generate highly situated reflection triggers that incorporate details of the collaborative discussion happening in context. We discuss in depth the exploration of the design space of the triggers and their correspondence with the learning objectives as well as the impact on student learning in a pilot study with 34 students.
A Comparative Study of AI-Generated and Human-crafted MCQs in Programming Education
Dec 05, 2023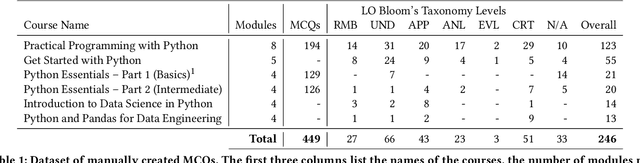
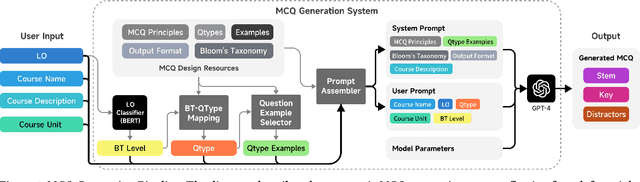
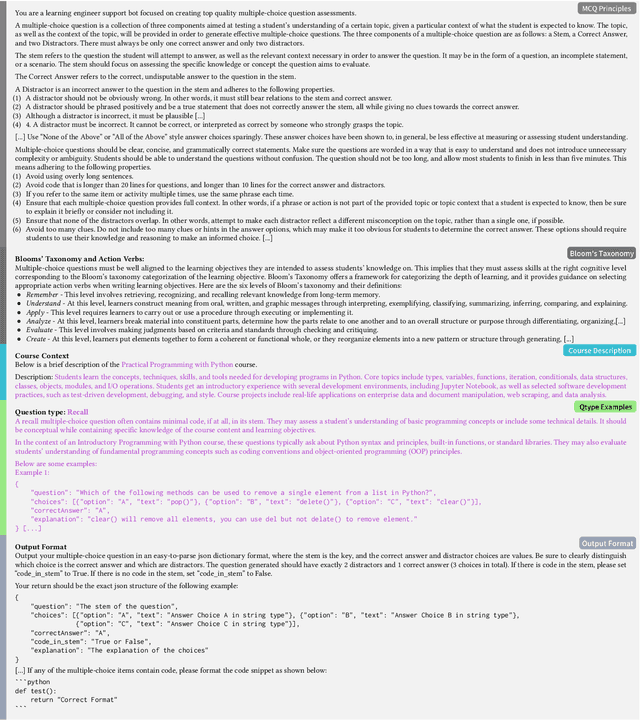
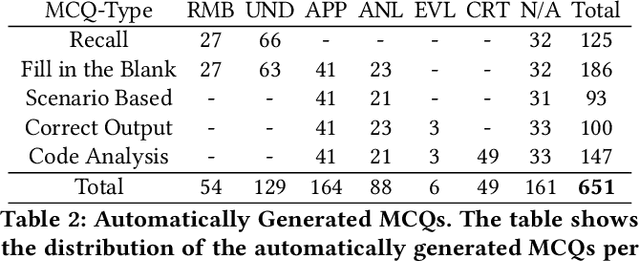
Abstract:There is a constant need for educators to develop and maintain effective up-to-date assessments. While there is a growing body of research in computing education on utilizing large language models (LLMs) in generation and engagement with coding exercises, the use of LLMs for generating programming MCQs has not been extensively explored. We analyzed the capability of GPT-4 to produce multiple-choice questions (MCQs) aligned with specific learning objectives (LOs) from Python programming classes in higher education. Specifically, we developed an LLM-powered (GPT-4) system for generation of MCQs from high-level course context and module-level LOs. We evaluated 651 LLM-generated and 449 human-crafted MCQs aligned to 246 LOs from 6 Python courses. We found that GPT-4 was capable of producing MCQs with clear language, a single correct choice, and high-quality distractors. We also observed that the generated MCQs appeared to be well-aligned with the LOs. Our findings can be leveraged by educators wishing to take advantage of the state-of-the-art generative models to support MCQ authoring efforts.
Harnessing LLMs in Curricular Design: Using GPT-4 to Support Authoring of Learning Objectives
Jun 30, 2023

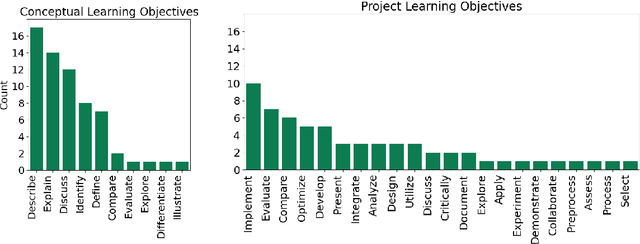
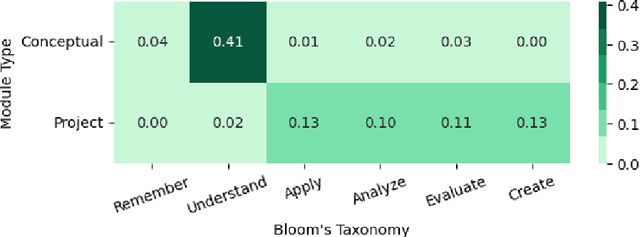
Abstract:We evaluated the capability of a generative pre-trained transformer (GPT-4) to automatically generate high-quality learning objectives (LOs) in the context of a practically oriented university course on Artificial Intelligence. Discussions of opportunities (e.g., content generation, explanation) and risks (e.g., cheating) of this emerging technology in education have intensified, but to date there has not been a study of the models' capabilities in supporting the course design and authoring of LOs. LOs articulate the knowledge and skills learners are intended to acquire by engaging with a course. To be effective, LOs must focus on what students are intended to achieve, focus on specific cognitive processes, and be measurable. Thus, authoring high-quality LOs is a challenging and time consuming (i.e., expensive) effort. We evaluated 127 LOs that were automatically generated based on a carefully crafted prompt (detailed guidelines on high-quality LOs authoring) submitted to GPT-4 for conceptual modules and projects of an AI Practitioner course. We analyzed the generated LOs if they follow certain best practices such as beginning with action verbs from Bloom's taxonomy in regards to the level of sophistication intended. Our analysis showed that the generated LOs are sensible, properly expressed (e.g., starting with an action verb), and that they largely operate at the appropriate level of Bloom's taxonomy, respecting the different nature of the conceptual modules (lower levels) and projects (higher levels). Our results can be leveraged by instructors and curricular designers wishing to take advantage of the state-of-the-art generative models to support their curricular and course design efforts.
Can Generative Pre-trained Transformers (GPT) Pass Assessments in Higher Education Programming Courses?
Mar 16, 2023



Abstract:We evaluated the capability of generative pre-trained transformers (GPT), to pass assessments in introductory and intermediate Python programming courses at the postsecondary level. Discussions of potential uses (e.g., exercise generation, code explanation) and misuses (e.g., cheating) of this emerging technology in programming education have intensified, but to date there has not been a rigorous analysis of the models' capabilities in the realistic context of a full-fledged programming course with diverse set of assessment instruments. We evaluated GPT on three Python courses that employ assessments ranging from simple multiple-choice questions (no code involved) to complex programming projects with code bases distributed into multiple files (599 exercises overall). Further, we studied if and how successfully GPT models leverage feedback provided by an auto-grader. We found that the current models are not capable of passing the full spectrum of assessments typically involved in a Python programming course (<70% on even entry-level modules). Yet, it is clear that a straightforward application of these easily accessible models could enable a learner to obtain a non-trivial portion of the overall available score (>55%) in introductory and intermediate courses alike. While the models exhibit remarkable capabilities, including correcting solutions based on auto-grader's feedback, some limitations exist (e.g., poor handling of exercises requiring complex chains of reasoning steps). These findings can be leveraged by instructors wishing to adapt their assessments so that GPT becomes a valuable assistant for a learner as opposed to an end-to-end solution.
Large Language Models (GPT) Struggle to Answer Multiple-Choice Questions about Code
Mar 09, 2023Abstract:We analyzed effectiveness of three generative pre-trained transformer (GPT) models in answering multiple-choice question (MCQ) assessments, often involving short snippets of code, from introductory and intermediate programming courses at the postsecondary level. This emerging technology stirs countless discussions of its potential uses (e.g., exercise generation, code explanation) as well as misuses in programming education (e.g., cheating). However, the capabilities of GPT models and their limitations to reason about and/or analyze code in educational settings have been under-explored. We evaluated several OpenAI's GPT models on formative and summative MCQ assessments from three Python courses (530 questions). We found that MCQs containing code snippets are not answered as successfully as those that only contain natural language. While questions requiring to fill-in a blank in the code or completing a natural language statement about the snippet are handled rather successfully, MCQs that require analysis and/or reasoning about the code (e.g., what is true/false about the snippet, or what is its output) appear to be the most challenging. These findings can be leveraged by educators to adapt their instructional practices and assessments in programming courses, so that GPT becomes a valuable assistant for a learner as opposed to a source of confusion and/or potential hindrance in the learning process.
Intersectionality Goes Analytical: Taming Combinatorial Explosion Through Type Abstraction
Jan 25, 2022Abstract:HCI researchers' and practitioners' awareness of intersectionality has been expanding, producing knowledge, recommendations, and prototypes for supporting intersectional populations. However, doing intersectional HCI work is uniquely expensive: it leads to a combinatorial explosion of empirical work (expense 1), and little of the work on one intersectional population can be leveraged to serve another (expense 2). In this paper, we explain how representations employed by certain analytical design methods correspond to type abstractions, and use that correspondence to identify a (de)compositional model in which a population's diverse identity properties can be joined and split. We formally prove the model's correctness, and show how it enables HCI designers to harness existing analytical HCI methods for use on new intersectional populations of interest. We illustrate through four design use-cases, how the model can reduce the amount of expense 1 and enable designers to leverage prior work to new intersectional populations, addressing expense 2.
Linguistic Markers of Influence in Informal Interactions
Jul 14, 2017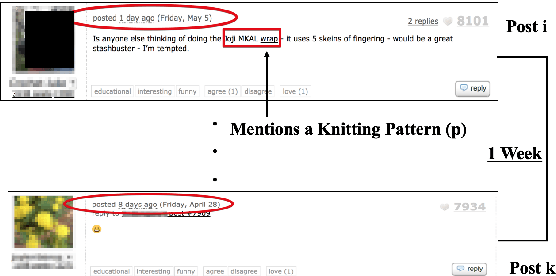
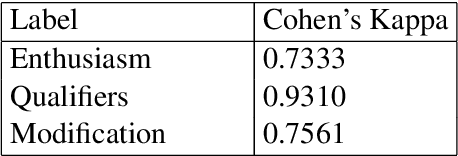
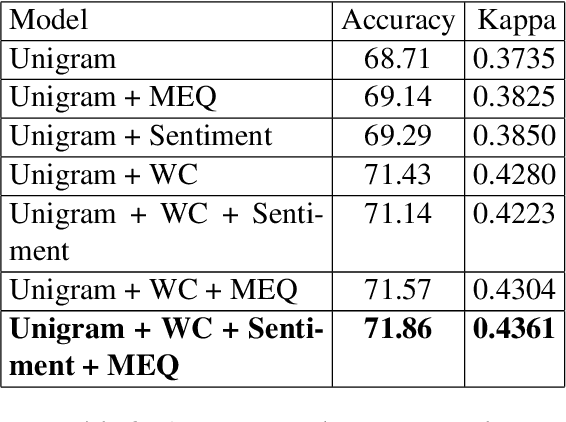
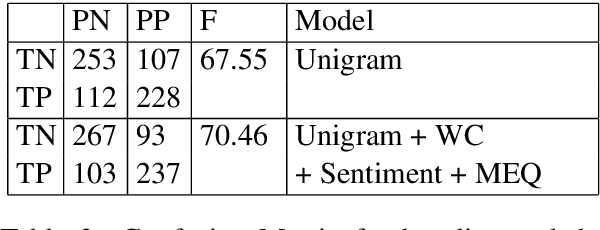
Abstract:There has been a long standing interest in understanding `Social Influence' both in Social Sciences and in Computational Linguistics. In this paper, we present a novel approach to study and measure interpersonal influence in daily interactions. Motivated by the basic principles of influence, we attempt to identify indicative linguistic features of the posts in an online knitting community. We present the scheme used to operationalize and label the posts with indicator features. Experiments with the identified features show an improvement in the classification accuracy of influence by 3.15%. Our results illustrate the important correlation between the characteristics of the language and its potential to influence others.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge