Anita Sarma
Tag that issue: Applying API-domain labels in issue tracking systems
Apr 06, 2023Abstract:Labeling issues with the skills required to complete them can help contributors to choose tasks in Open Source Software projects. However, manually labeling issues is time-consuming and error-prone, and current automated approaches are mostly limited to classifying issues as bugs/non-bugs. We investigate the feasibility and relevance of automatically labeling issues with what we call "API-domains," which are high-level categories of APIs. Therefore, we posit that the APIs used in the source code affected by an issue can be a proxy for the type of skills (e.g., DB, security, UI) needed to work on the issue. We ran a user study (n=74) to assess API-domain labels' relevancy to potential contributors, leveraged the issues' descriptions and the project history to build prediction models, and validated the predictions with contributors (n=20) of the projects. Our results show that (i) newcomers to the project consider API-domain labels useful in choosing tasks, (ii) labels can be predicted with a precision of 84% and a recall of 78.6% on average, (iii) the results of the predictions reached up to 71.3% in precision and 52.5% in recall when training with a project and testing in another (transfer learning), and (iv) project contributors consider most of the predictions helpful in identifying needed skills. These findings suggest our approach can be applied in practice to automatically label issues, assisting developers in finding tasks that better match their skills.
Intersectionality Goes Analytical: Taming Combinatorial Explosion Through Type Abstraction
Jan 25, 2022Abstract:HCI researchers' and practitioners' awareness of intersectionality has been expanding, producing knowledge, recommendations, and prototypes for supporting intersectional populations. However, doing intersectional HCI work is uniquely expensive: it leads to a combinatorial explosion of empirical work (expense 1), and little of the work on one intersectional population can be leveraged to serve another (expense 2). In this paper, we explain how representations employed by certain analytical design methods correspond to type abstractions, and use that correspondence to identify a (de)compositional model in which a population's diverse identity properties can be joined and split. We formally prove the model's correctness, and show how it enables HCI designers to harness existing analytical HCI methods for use on new intersectional populations of interest. We illustrate through four design use-cases, how the model can reduce the amount of expense 1 and enable designers to leverage prior work to new intersectional populations, addressing expense 2.
Can I Solve It? Identifying APIs Required to Complete OSS Task
Mar 23, 2021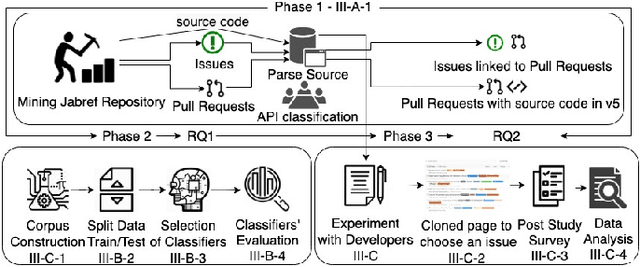
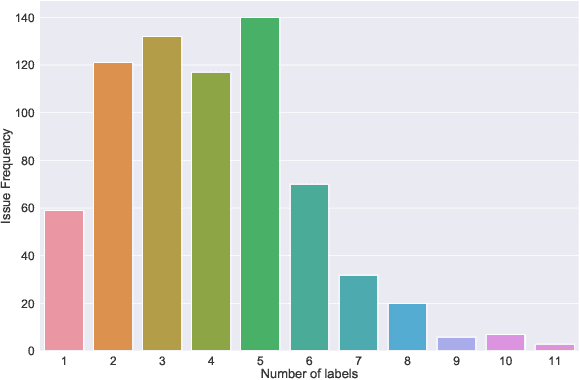
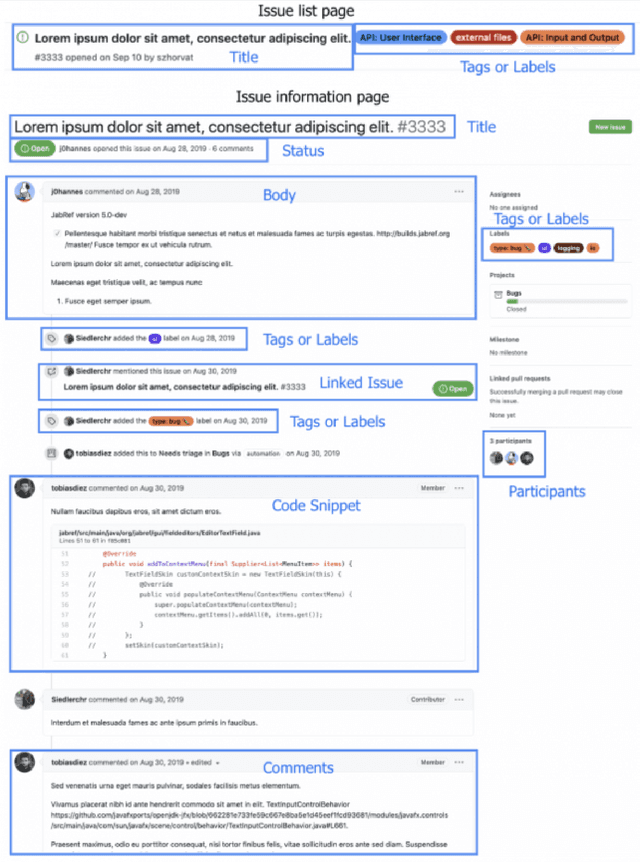
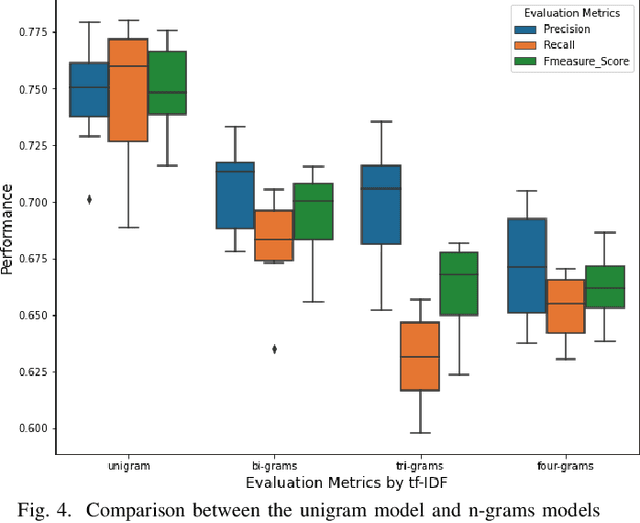
Abstract:Open Source Software projects add labels to open issues to help contributors choose tasks. However, manually labeling issues is time-consuming and error-prone. Current automatic approaches for creating labels are mostly limited to classifying issues as a bug/non-bug. In this paper, we investigate the feasibility and relevance of labeling issues with the domain of the APIs required to complete the tasks. We leverage the issues' description and the project history to build prediction models, which resulted in precision up to 82% and recall up to 97.8%. We also ran a user study (n=74) to assess these labels' relevancy to potential contributors. The results show that the labels were useful to participants in choosing tasks, and the API-domain labels were selected more often than the existing architecture-based labels. Our results can inspire the creation of tools to automatically label issues, helping developers to find tasks that better match their skills.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge