Anusha Kamath
FiMI: A Domain-Specific Language Model for Indian Finance Ecosystem
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:We present FiMI (Finance Model for India), a domain-specialized financial language model developed for Indian digital payment systems. We develop two model variants: FiMI Base and FiMI Instruct. FiMI adapts the Mistral Small 24B architecture through a multi-stage training pipeline, beginning with continuous pre-training on 68 Billion tokens of curated financial, multilingual (English, Hindi, Hinglish), and synthetic data. This is followed by instruction fine-tuning and domain-specific supervised fine-tuning focused on multi-turn, tool-driven conversations that model real-world workflows, such as transaction disputes and mandate lifecycle management. Evaluations reveal that FiMI Base achieves a 20% improvement over the Mistral Small 24B Base model on finance reasoning benchmark, while FiMI Instruct outperforms the Mistral Small 24B Instruct model by 87% on domain-specific tool-calling. Moreover, FiMI achieves these significant domain gains while maintaining comparable performance to models of similar size on general benchmarks.
Towards Reliable ML Feature Engineering via Planning in Constrained-Topology of LLM Agents
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Recent advances in code generation models have unlocked unprecedented opportunities for automating feature engineering, yet their adoption in real-world ML teams remains constrained by critical challenges: (i) the scarcity of datasets capturing the iterative and complex coding processes of production-level feature engineering, (ii) limited integration and personalization of widely used coding agents, such as CoPilot and Devin, with a team's unique tools, codebases, workflows, and practices, and (iii) suboptimal human-AI collaboration due to poorly timed or insufficient feedback. We address these challenges with a planner-guided, constrained-topology multi-agent framework that generates code for repositories in a multi-step fashion. The LLM-powered planner leverages a team's environment, represented as a graph, to orchestrate calls to available agents, generate context-aware prompts, and use downstream failures to retroactively correct upstream artifacts. It can request human intervention at critical steps, ensuring generated code is reliable, maintainable, and aligned with team expectations. On a novel in-house dataset, our approach achieves 38% and 150% improvement in the evaluation metric over manually crafted and unplanned workflows respectively. In practice, when building features for recommendation models serving over 120 million users, our approach has delivered real-world impact by reducing feature engineering cycles from three weeks to a single day.
Benchmarking Hindi LLMs: A New Suite of Datasets and a Comparative Analysis
Aug 27, 2025Abstract:Evaluating instruction-tuned Large Language Models (LLMs) in Hindi is challenging due to a lack of high-quality benchmarks, as direct translation of English datasets fails to capture crucial linguistic and cultural nuances. To address this, we introduce a suite of five Hindi LLM evaluation datasets: IFEval-Hi, MT-Bench-Hi, GSM8K-Hi, ChatRAG-Hi, and BFCL-Hi. These were created using a methodology that combines from-scratch human annotation with a translate-and-verify process. We leverage this suite to conduct an extensive benchmarking of open-source LLMs supporting Hindi, providing a detailed comparative analysis of their current capabilities. Our curation process also serves as a replicable methodology for developing benchmarks in other low-resource languages.
Generating Situated Reflection Triggers about Alternative Solution Paths: A Case Study of Generative AI for Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning
Apr 28, 2024



Abstract:An advantage of Large Language Models (LLMs) is their contextualization capability - providing different responses based on student inputs like solution strategy or prior discussion, to potentially better engage students than standard feedback. We present a design and evaluation of a proof-of-concept LLM application to offer students dynamic and contextualized feedback. Specifically, we augment an Online Programming Exercise bot for a college-level Cloud Computing course with ChatGPT, which offers students contextualized reflection triggers during a collaborative query optimization task in database design. We demonstrate that LLMs can be used to generate highly situated reflection triggers that incorporate details of the collaborative discussion happening in context. We discuss in depth the exploration of the design space of the triggers and their correspondence with the learning objectives as well as the impact on student learning in a pilot study with 34 students.
Robust Candidate Generation for Entity Linking on Short Social Media Texts
Oct 14, 2022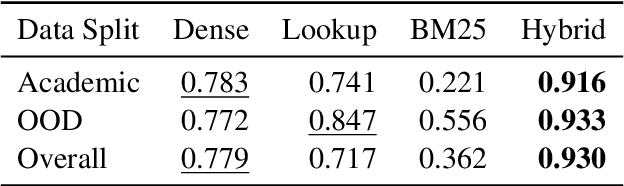
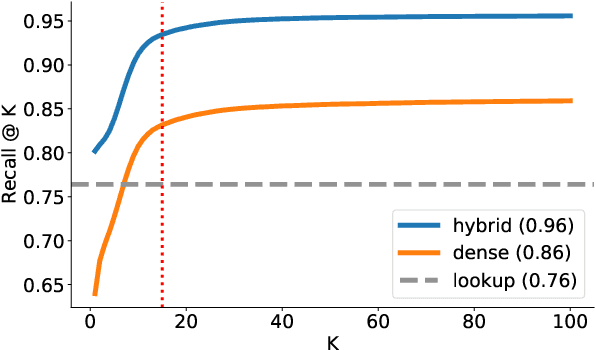
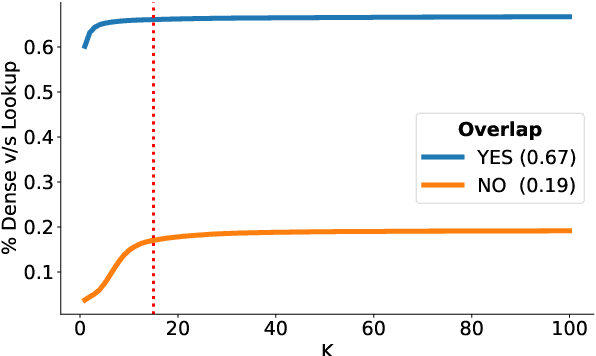
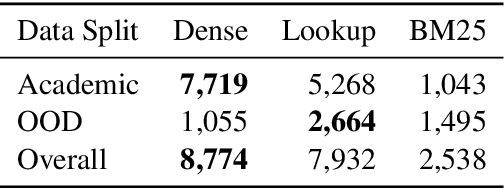
Abstract:Entity Linking (EL) is the gateway into Knowledge Bases. Recent advances in EL utilize dense retrieval approaches for Candidate Generation, which addresses some of the shortcomings of the Lookup based approach of matching NER mentions against pre-computed dictionaries. In this work, we show that in the domain of Tweets, such methods suffer as users often include informal spelling, limited context, and lack of specificity, among other issues. We investigate these challenges on a large and recent Tweets benchmark for EL, empirically evaluate lookup and dense retrieval approaches, and demonstrate a hybrid solution using long contextual representation from Wikipedia is necessary to achieve considerable gains over previous work, achieving 0.93 recall.
Modular Approach to Machine Reading Comprehension: Mixture of Task-Aware Experts
Oct 04, 2022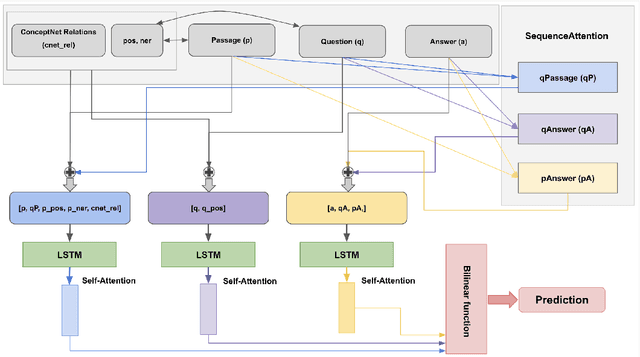
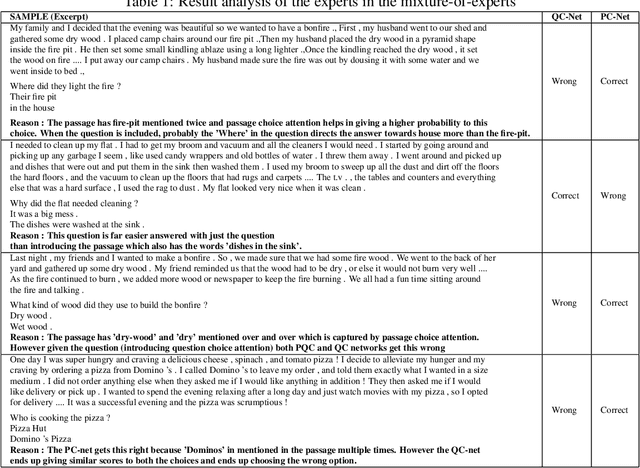
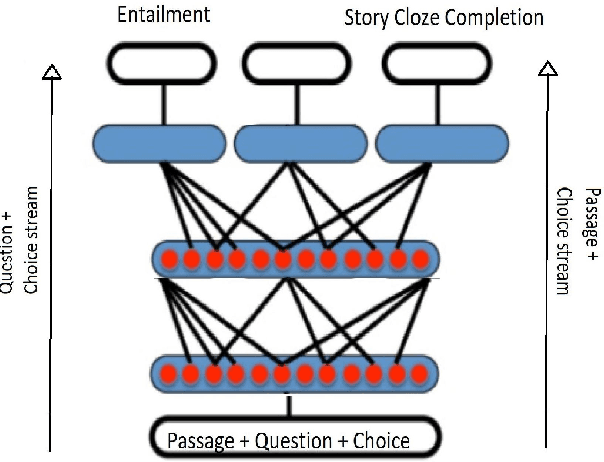
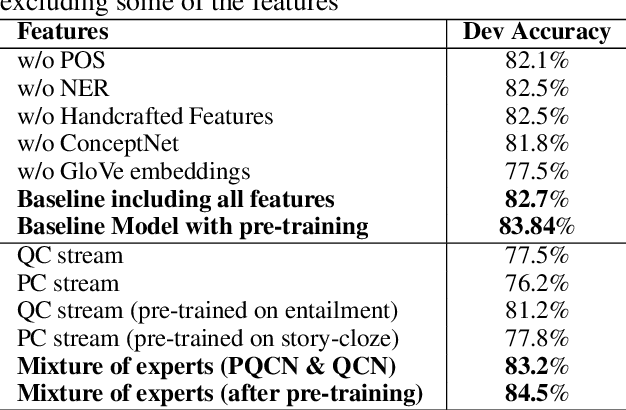
Abstract:In this work we present a Mixture of Task-Aware Experts Network for Machine Reading Comprehension on a relatively small dataset. We particularly focus on the issue of common-sense learning, enforcing the common ground knowledge by specifically training different expert networks to capture different kinds of relationships between each passage, question and choice triplet. Moreover, we take inspi ration on the recent advancements of multitask and transfer learning by training each network a relevant focused task. By making the mixture-of-networks aware of a specific goal by enforcing a task and a relationship, we achieve state-of-the-art results and reduce over-fitting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge