Chao Xiang
An Empirical Study of NetOps Capability of Pre-Trained Large Language Models
Sep 19, 2023



Abstract:Nowadays, the versatile capabilities of Pre-trained Large Language Models (LLMs) have attracted much attention from the industry. However, some vertical domains are more interested in the in-domain capabilities of LLMs. For the Networks domain, we present NetEval, an evaluation set for measuring the comprehensive capabilities of LLMs in Network Operations (NetOps). NetEval is designed for evaluating the commonsense knowledge and inference ability in NetOps in a multi-lingual context. NetEval consists of 5,732 questions about NetOps, covering five different sub-domains of NetOps. With NetEval, we systematically evaluate the NetOps capability of 26 publicly available LLMs. The results show that only GPT-4 can achieve a performance competitive to humans. However, some open models like LLaMA 2 demonstrate significant potential.
Learning to Affiliate: Mutual Centralized Learning for Few-shot Classification
Jun 10, 2021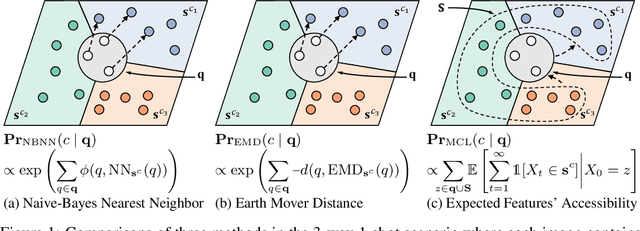
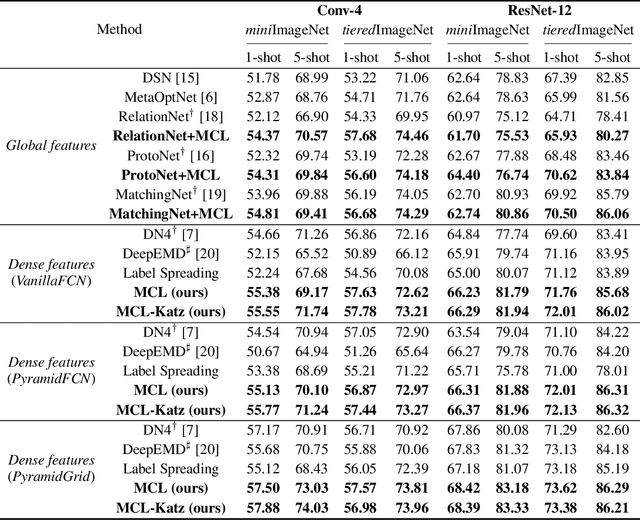
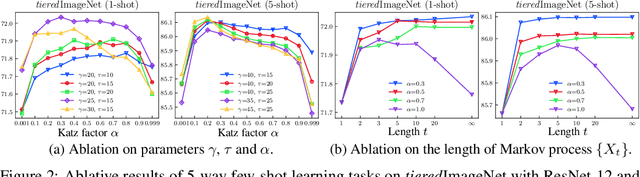
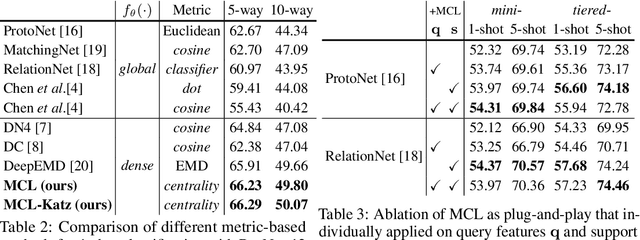
Abstract:Few-shot learning (FSL) aims to learn a classifier that can be easily adapted to accommodate new tasks not seen during training, given only a few examples. To handle the limited-data problem in few-shot regimes, recent methods tend to collectively use a set of local features to densely represent an image instead of using a mixed global feature. They generally explore a unidirectional query-to-support paradigm in FSL, e.g., find the nearest/optimal support feature for each query feature and aggregate these local matches for a joint classification. In this paper, we propose a new method Mutual Centralized Learning (MCL) to fully affiliate the two disjoint sets of dense features in a bidirectional paradigm. We associate each local feature with a particle that can bidirectionally random walk in a discrete feature space by the affiliations. To estimate the class probability, we propose the features' accessibility that measures the expected number of visits to the support features of that class in a Markov process. We relate our method to learning a centrality on an affiliation network and demonstrate its capability to be plugged in existing methods by highlighting centralized local features. Experiments show that our method achieves the state-of-the-art on both miniImageNet and tieredImageNet.
PI-RCNN: An Efficient Multi-sensor 3D Object Detector with Point-based Attentive Cont-conv Fusion Module
Dec 02, 2019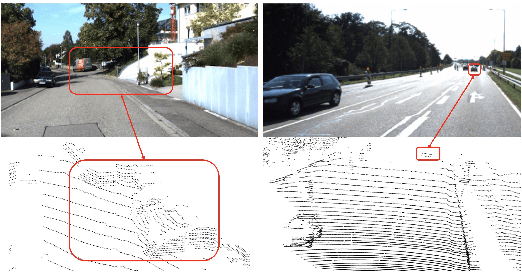
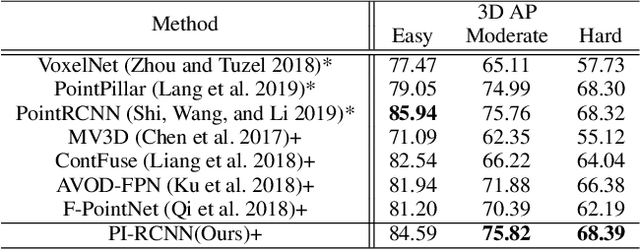
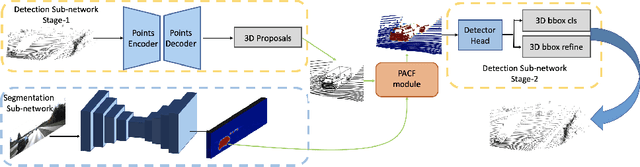
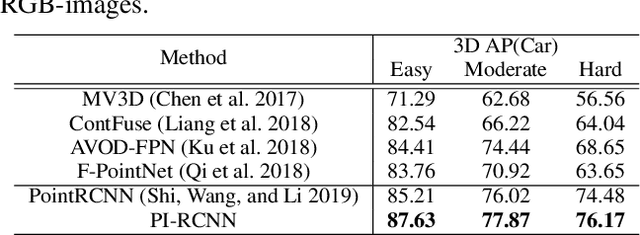
Abstract:LIDAR point clouds and RGB-images are both extremely essential for 3D object detection. So many state-of-the-art 3D detection algorithms dedicate in fusing these two types of data effectively. However, their fusion methods based on Birds Eye View (BEV) or voxel format are not accurate. In this paper, we propose a novel fusion approach named Point-based Attentive Cont-conv Fusion(PACF) module, which fuses multi-sensor features directly on 3D points. Except for continuous convolution, we additionally add a Point-Pooling and an Attentive Aggregation to make the fused features more expressive. Moreover, based on the PACF module, we propose a 3D multi-sensor multi-task network called Pointcloud-Image RCNN(PI-RCNN as brief), which handles the image segmentation and 3D object detection tasks. PI-RCNN employs a segmentation sub-network to extract full-resolution semantic feature maps from images and then fuses the multi-sensor features via powerful PACF module. Beneficial from the effectiveness of the PACF module and the expressive semantic features from the segmentation module, PI-RCNN can improve much in 3D object detection. We demonstrate the effectiveness of the PACF module and PI-RCNN on the KITTI 3D Detection benchmark, and our method can achieve state-of-the-art on the metric of 3D AP.
Fast Approximate Nearest Neighbor Search With The Navigating Spreading-out Graph
Oct 04, 2018
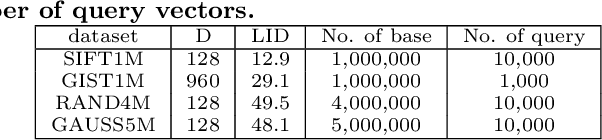
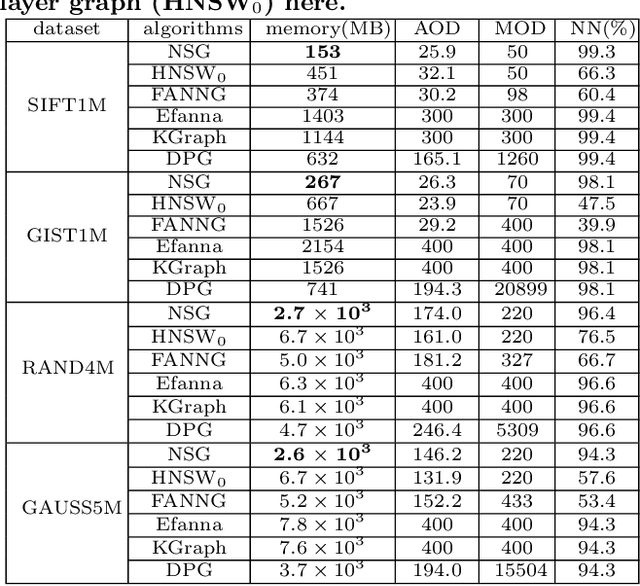
Abstract:Approximate nearest neighbor search (ANNS) is a fundamental problem in databases and data mining. A scalable ANNS algorithm should be both memory efficient and fast. Some early graph-based approaches have shown attractive theoretical guarantees on search time complexity, but they all suffer from the problem of high indexing time complexity. Recently, some graph-based methods have been proposed to reduce indexing complexity by approximating the traditional graphs; these methods have achieved revolutionary performance on million-scale datasets. Yet, they still do not scale to billion-node databases. In our study, to further improve the search-efficiency and scalability of graph-based methods. We start by introducing four aspects: (1) ensuring the connectivity of the graph; (2) lowering the average out-degree of the graph for fast traversal; (3) shortening the search path; and (4) reducing the index size. In this paper, we propose a novel graph structure called Monotonic Relative Neighborhood Graph (MRNG) which guarantees very low search complexity (close to logarithmic time). To further lower the indexing complexity and make it practical for billion-node ANNS problems, we propose a novel graph structure named Navigating Spreading-out Graph (NSG) by approximating the MRNG. The NSG takes the four aspects into account simultaneously. Extensive experiments show that NSG outperforms all the existing algorithms significantly. What's more, NSG shows superior performance in the e-commercial search scenario of Taobao (Alibaba Group) and has been integrated into their search engine at billion-node scale.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge