Changxu Wang
Large-Scale Visual Search with Binary Distributed Graph at Alibaba
Feb 09, 2021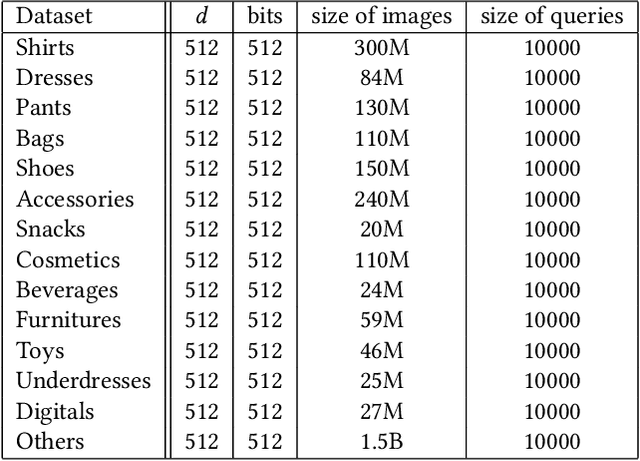
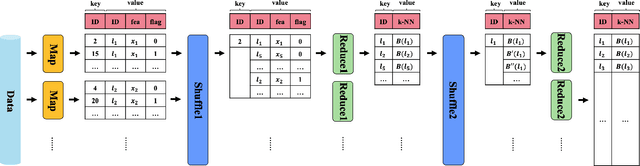
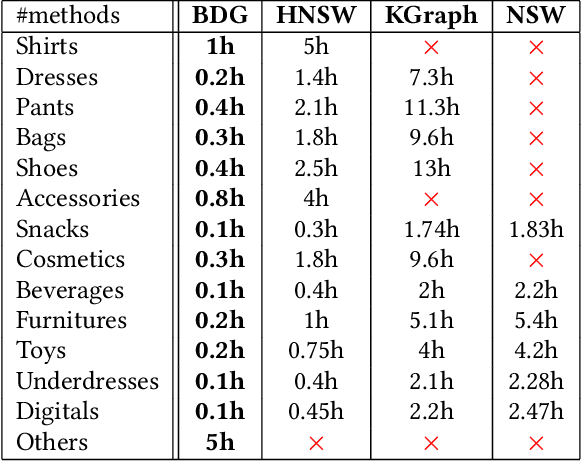
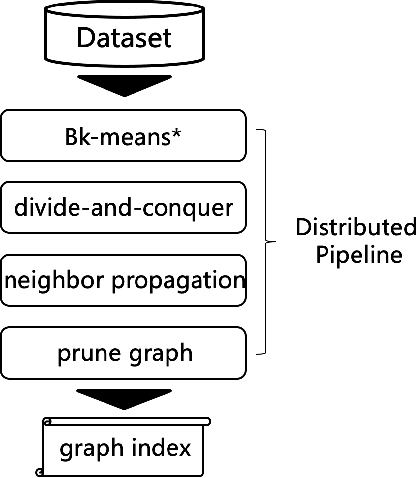
Abstract:Graph-based approximate nearest neighbor search has attracted more and more attentions due to its online search advantages. Numbers of methods studying the enhancement of speed and recall have been put forward. However, few of them focus on the efficiency and scale of offline graph-construction. For a deployed visual search system with several billions of online images in total, building a billion-scale offline graph in hours is essential, which is almost unachievable by most existing methods. In this paper, we propose a novel algorithm called Binary Distributed Graph to solve this problem. Specifically, we combine binary codes with graph structure to speedup online and offline procedures, and achieve comparable performance with the ones in real-value based scenarios by recalling more binary candidates. Furthermore, the graph-construction is optimized to completely distributed implementation, which significantly accelerates the offline process and gets rid of the limitation of memory and disk within a single machine. Experimental comparisons on Alibaba Commodity Data Set (more than three billion images) show that the proposed method outperforms the state-of-the-art with respect to the online/offline trade-off.
Fast Approximate Nearest Neighbor Search With The Navigating Spreading-out Graph
Oct 04, 2018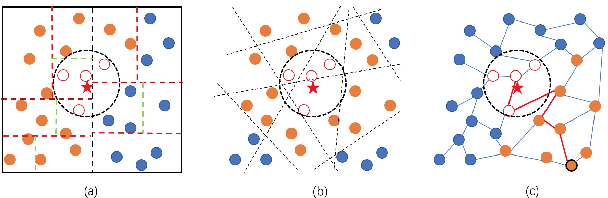
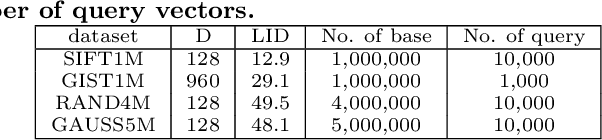
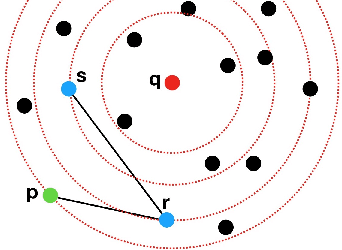
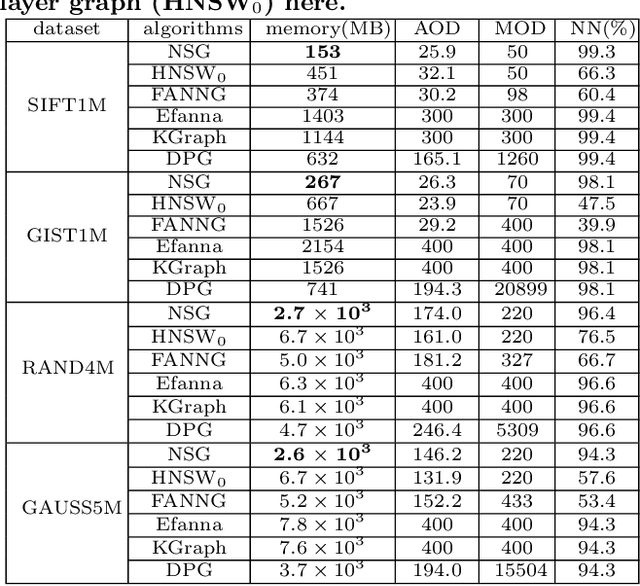
Abstract:Approximate nearest neighbor search (ANNS) is a fundamental problem in databases and data mining. A scalable ANNS algorithm should be both memory efficient and fast. Some early graph-based approaches have shown attractive theoretical guarantees on search time complexity, but they all suffer from the problem of high indexing time complexity. Recently, some graph-based methods have been proposed to reduce indexing complexity by approximating the traditional graphs; these methods have achieved revolutionary performance on million-scale datasets. Yet, they still do not scale to billion-node databases. In our study, to further improve the search-efficiency and scalability of graph-based methods. We start by introducing four aspects: (1) ensuring the connectivity of the graph; (2) lowering the average out-degree of the graph for fast traversal; (3) shortening the search path; and (4) reducing the index size. In this paper, we propose a novel graph structure called Monotonic Relative Neighborhood Graph (MRNG) which guarantees very low search complexity (close to logarithmic time). To further lower the indexing complexity and make it practical for billion-node ANNS problems, we propose a novel graph structure named Navigating Spreading-out Graph (NSG) by approximating the MRNG. The NSG takes the four aspects into account simultaneously. Extensive experiments show that NSG outperforms all the existing algorithms significantly. What's more, NSG shows superior performance in the e-commercial search scenario of Taobao (Alibaba Group) and has been integrated into their search engine at billion-node scale.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge