Fast Approximate Nearest Neighbor Search With The Navigating Spreading-out Graph
Paper and Code
Oct 04, 2018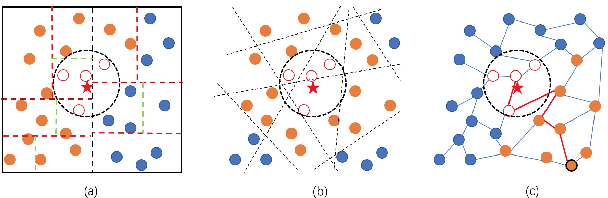
Approximate nearest neighbor search (ANNS) is a fundamental problem in databases and data mining. A scalable ANNS algorithm should be both memory efficient and fast. Some early graph-based approaches have shown attractive theoretical guarantees on search time complexity, but they all suffer from the problem of high indexing time complexity. Recently, some graph-based methods have been proposed to reduce indexing complexity by approximating the traditional graphs; these methods have achieved revolutionary performance on million-scale datasets. Yet, they still do not scale to billion-node databases. In our study, to further improve the search-efficiency and scalability of graph-based methods. We start by introducing four aspects: (1) ensuring the connectivity of the graph; (2) lowering the average out-degree of the graph for fast traversal; (3) shortening the search path; and (4) reducing the index size. In this paper, we propose a novel graph structure called Monotonic Relative Neighborhood Graph (MRNG) which guarantees very low search complexity (close to logarithmic time). To further lower the indexing complexity and make it practical for billion-node ANNS problems, we propose a novel graph structure named Navigating Spreading-out Graph (NSG) by approximating the MRNG. The NSG takes the four aspects into account simultaneously. Extensive experiments show that NSG outperforms all the existing algorithms significantly. What's more, NSG shows superior performance in the e-commercial search scenario of Taobao (Alibaba Group) and has been integrated into their search engine at billion-node scale.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge