Chaim Baskin
Step-Wise Refusal Dynamics in Autoregressive and Diffusion Language Models
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Diffusion language models (DLMs) have recently emerged as a promising alternative to autoregressive (AR) models, offering parallel decoding and controllable sampling dynamics while achieving competitive generation quality at scale. Despite this progress, the role of sampling mechanisms in shaping refusal behavior and jailbreak robustness remains poorly understood. In this work, we present a fundamental analytical framework for step-wise refusal dynamics, enabling comparison between AR and diffusion sampling. Our analysis reveals that the sampling strategy itself plays a central role in safety behavior, as a factor distinct from the underlying learned representations. Motivated by this analysis, we introduce the Step-Wise Refusal Internal Dynamics (SRI) signal, which supports interpretability and improved safety for both AR and DLMs. We demonstrate that the geometric structure of SRI captures internal recovery dynamics, and identifies anomalous behavior in harmful generations as cases of \emph{incomplete internal recovery} that are not observable at the text level. This structure enables lightweight inference-time detectors that generalize to unseen attacks while matching or outperforming existing defenses with over $100\times$ lower inference overhead.
PREGEN: Uncovering Latent Thoughts in Composed Video Retrieval
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Composed Video Retrieval (CoVR) aims to retrieve a video based on a query video and a modifying text. Current CoVR methods fail to fully exploit modern Vision-Language Models (VLMs), either using outdated architectures or requiring computationally expensive fine-tuning and slow caption generation. We introduce PREGEN (PRE GENeration extraction), an efficient and powerful CoVR framework that overcomes these limitations. Our approach uniquely pairs a frozen, pre-trained VLM with a lightweight encoding model, eliminating the need for any VLM fine-tuning. We feed the query video and modifying text into the VLM and extract the hidden state of the final token from each layer. A simple encoder is then trained on these pooled representations, creating a semantically rich and compact embedding for retrieval. PREGEN significantly advances the state of the art, surpassing all prior methods on standard CoVR benchmarks with substantial gains in Recall@1 of +27.23 and +69.59. Our method demonstrates robustness across different VLM backbones and exhibits strong zero-shot generalization to more complex textual modifications, highlighting its effectiveness and semantic capabilities.
HERBench: A Benchmark for Multi-Evidence Integration in Video Question Answering
Dec 16, 2025



Abstract:Video Large Language Models (Video-LLMs) are rapidly improving, yet current Video Question Answering (VideoQA) benchmarks often allow questions to be answered from a single salient cue, under-testing reasoning that must aggregate multiple, temporally separated visual evidence. We present HERBench, a VideoQA benchmark purpose-built to assess multi-evidence integration across time. Each question requires aggregating at least three non-overlapping evidential cues across distinct video segments, so neither language priors nor a single snapshot can suffice. HERBench comprises 26K five-way multiple-choice questions organized into twelve compositional tasks that probe identity binding, cross-entity relations, temporal ordering, co-occurrence verification, and counting. To make evidential demand measurable, we introduce the Minimum Required Frame-Set (MRFS), the smallest number of frames a model must fuse to answer correctly, and show that HERBench imposes substantially higher demand than prior datasets (mean MRFS 5.5 vs. 2.6-4.2). Evaluating 13 state-of-the-art Video-LLMs on HERBench reveals pervasive failures: accuracies of 31-42% are only slightly above the 20% random-guess baseline. We disentangle this failure into two critical bottlenecks: (1) a retrieval deficit, where frame selectors overlook key evidence, and (2) a fusion deficit, where models fail to integrate information even when all necessary evidence is provided. By making cross-time evidence both unavoidable and quantifiable, HERBench establishes a principled target for advancing robust, compositional video understanding.
Revisiting Node Affinity Prediction in Temporal Graphs
Oct 08, 2025Abstract:Node affinity prediction is a common task that is widely used in temporal graph learning with applications in social and financial networks, recommender systems, and more. Recent works have addressed this task by adapting state-of-the-art dynamic link property prediction models to node affinity prediction. However, simple heuristics, such as Persistent Forecast or Moving Average, outperform these models. In this work, we analyze the challenges in training current Temporal Graph Neural Networks for node affinity prediction and suggest appropriate solutions. Combining the solutions, we develop NAViS - Node Affinity prediction model using Virtual State, by exploiting the equivalence between heuristics and state space models. While promising, training NAViS is non-trivial. Therefore, we further introduce a novel loss function for node affinity prediction. We evaluate NAViS on TGB and show that it outperforms the state-of-the-art, including heuristics. Our source code is available at https://github.com/orfeld415/NAVIS
FLASH: Flexible Learning of Adaptive Sampling from History in Temporal Graph Neural Networks
Apr 09, 2025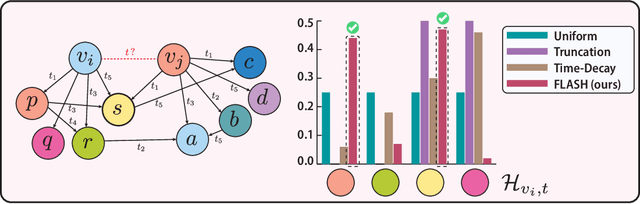

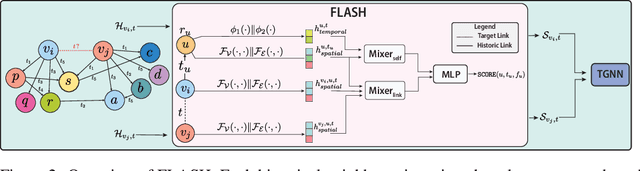

Abstract:Aggregating temporal signals from historic interactions is a key step in future link prediction on dynamic graphs. However, incorporating long histories is resource-intensive. Hence, temporal graph neural networks (TGNNs) often rely on historical neighbors sampling heuristics such as uniform sampling or recent neighbors selection. These heuristics are static and fail to adapt to the underlying graph structure. We introduce FLASH, a learnable and graph-adaptive neighborhood selection mechanism that generalizes existing heuristics. FLASH integrates seamlessly into TGNNs and is trained end-to-end using a self-supervised ranking loss. We provide theoretical evidence that commonly used heuristics hinders TGNNs performance, motivating our design. Extensive experiments across multiple benchmarks demonstrate consistent and significant performance improvements for TGNNs equipped with FLASH.
Enhancing Retinal Vessel Segmentation Generalization via Layout-Aware Generative Modelling
Mar 03, 2025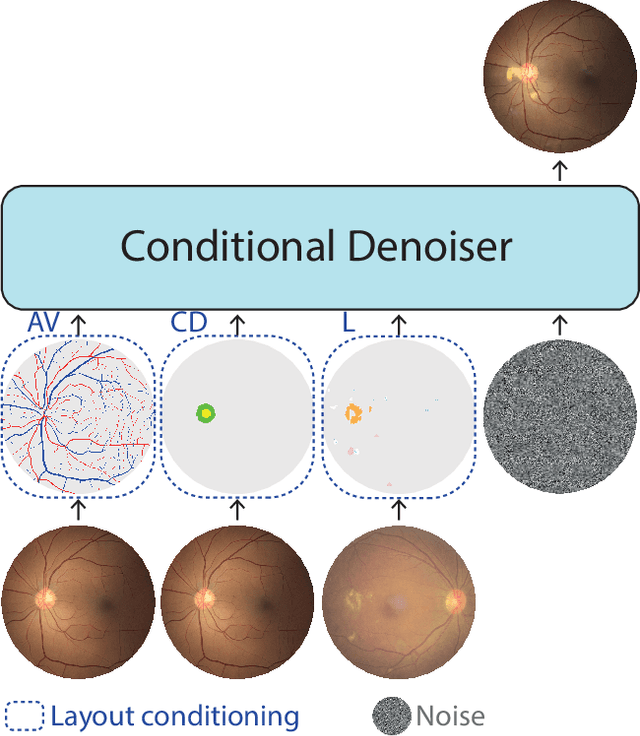
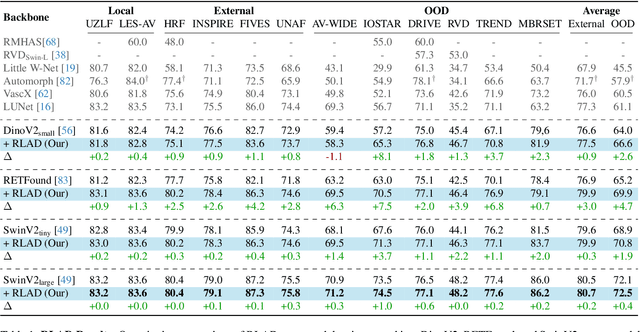
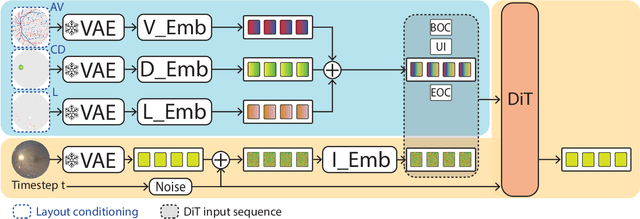
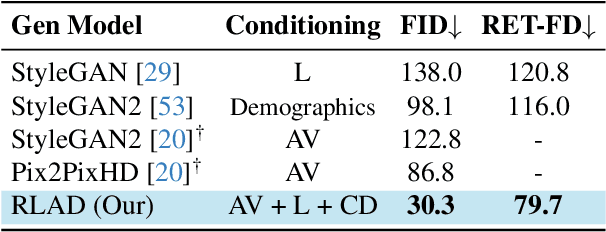
Abstract:Generalization in medical segmentation models is challenging due to limited annotated datasets and imaging variability. To address this, we propose Retinal Layout-Aware Diffusion (RLAD), a novel diffusion-based framework for generating controllable layout-aware images. RLAD conditions image generation on multiple key layout components extracted from real images, ensuring high structural fidelity while enabling diversity in other components. Applied to retinal fundus imaging, we augmented the training datasets by synthesizing paired retinal images and vessel segmentations conditioned on extracted blood vessels from real images, while varying other layout components such as lesions and the optic disc. Experiments demonstrated that RLAD-generated data improved generalization in retinal vessel segmentation by up to 8.1%. Furthermore, we present REYIA, a comprehensive dataset comprising 586 manually segmented retinal images. To foster reproducibility and drive innovation, both our code and dataset will be made publicly accessible.
Adversarial Robustness in Parameter-Space Classifiers
Feb 27, 2025Abstract:Implicit Neural Representations (INRs) have been recently garnering increasing interest in various research fields, mainly due to their ability to represent large, complex data in a compact and continuous manner. Past work further showed that numerous popular downstream tasks can be performed directly in the INR parameter-space. Doing so can substantially reduce the computational resources required to process the represented data in their native domain. A major difficulty in using modern machine-learning approaches, is their high susceptibility to adversarial attacks, which have been shown to greatly limit the reliability and applicability of such methods in a wide range of settings. In this work, we show that parameter-space models trained for classification are inherently robust to adversarial attacks -- without the need of any robust training. To support our claims, we develop a novel suite of adversarial attacks targeting parameter-space classifiers, and furthermore analyze practical considerations of attacking parameter-space classifiers. Code for reproducing all experiments and implementation of all proposed methods will be released upon publication.
On Adversarial Attacks In Acoustic Drone Localization
Feb 27, 2025Abstract:Multi-rotor aerial autonomous vehicles (MAVs, more widely known as "drones") have been generating increased interest in recent years due to their growing applicability in a vast and diverse range of fields (e.g., agriculture, commercial delivery, search and rescue). The sensitivity of visual-based methods to lighting conditions and occlusions had prompted growing study of navigation reliant on other modalities, such as acoustic sensing. A major concern in using drones in scale for tasks in non-controlled environments is the potential threat of adversarial attacks over their navigational systems, exposing users to mission-critical failures, security breaches, and compromised safety outcomes that can endanger operators and bystanders. While previous work shows impressive progress in acoustic-based drone localization, prior research in adversarial attacks over drone navigation only addresses visual sensing-based systems. In this work, we aim to compensate for this gap by supplying a comprehensive analysis of the effect of PGD adversarial attacks over acoustic drone localization. We furthermore develop an algorithm for adversarial perturbation recovery, capable of markedly diminishing the affect of such attacks in our setting. The code for reproducing all experiments will be released upon publication.
T1-PILOT: Optimized Trajectories for T1 Mapping Acceleration
Feb 27, 2025Abstract:Cardiac T1 mapping provides critical quantitative insights into myocardial tissue composition, enabling the assessment of pathologies such as fibrosis, inflammation, and edema. However, the inherently dynamic nature of the heart imposes strict limits on acquisition times, making high-resolution T1 mapping a persistent challenge. Compressed sensing (CS) approaches have reduced scan durations by undersampling k-space and reconstructing images from partial data, and recent studies show that jointly optimizing the undersampling patterns with the reconstruction network can substantially improve performance. Still, most current T1 mapping pipelines rely on static, hand-crafted masks that do not exploit the full acceleration and accuracy potential. In this work, we introduce T1-PILOT: an end-to-end method that explicitly incorporates the T1 signal relaxation model into the sampling-reconstruction framework to guide the learning of non-Cartesian trajectories, crossframe alignment, and T1 decay estimation. Through extensive experiments on the CMRxRecon dataset, T1-PILOT significantly outperforms several baseline strategies (including learned single-mask and fixed radial or golden-angle sampling schemes), achieving higher T1 map fidelity at greater acceleration factors. In particular, we observe consistent gains in PSNR and VIF relative to existing methods, along with marked improvements in delineating finer myocardial structures. Our results highlight that optimizing sampling trajectories in tandem with the physical relaxation model leads to both enhanced quantitative accuracy and reduced acquisition times. Code for reproducing all results will be made publicly available upon publication.
DiTASK: Multi-Task Fine-Tuning with Diffeomorphic Transformations
Feb 09, 2025Abstract:Pre-trained Vision Transformers now serve as powerful tools for computer vision. Yet, efficiently adapting them for multiple tasks remains a challenge that arises from the need to modify the rich hidden representations encoded by the learned weight matrices, without inducing interference between tasks. Current parameter-efficient methods like LoRA, which apply low-rank updates, force tasks to compete within constrained subspaces, ultimately degrading performance. We introduce DiTASK a novel Diffeomorphic Multi-Task Fine-Tuning approach that maintains pre-trained representations by preserving weight matrix singular vectors, while enabling task-specific adaptations through neural diffeomorphic transformations of the singular values. By following this approach, DiTASK enables both shared and task-specific feature modulations with minimal added parameters. Our theoretical analysis shows that DITASK achieves full-rank updates during optimization, preserving the geometric structure of pre-trained features, and establishing a new paradigm for efficient multi-task learning (MTL). Our experiments on PASCAL MTL and NYUD show that DiTASK achieves state-of-the-art performance across four dense prediction tasks, using 75% fewer parameters than existing methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge