Brian Yang
Tony
OpenAI GPT-5 System Card
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:This is the system card published alongside the OpenAI GPT-5 launch, August 2025. GPT-5 is a unified system with a smart and fast model that answers most questions, a deeper reasoning model for harder problems, and a real-time router that quickly decides which model to use based on conversation type, complexity, tool needs, and explicit intent (for example, if you say 'think hard about this' in the prompt). The router is continuously trained on real signals, including when users switch models, preference rates for responses, and measured correctness, improving over time. Once usage limits are reached, a mini version of each model handles remaining queries. This system card focuses primarily on gpt-5-thinking and gpt-5-main, while evaluations for other models are available in the appendix. The GPT-5 system not only outperforms previous models on benchmarks and answers questions more quickly, but -- more importantly -- is more useful for real-world queries. We've made significant advances in reducing hallucinations, improving instruction following, and minimizing sycophancy, and have leveled up GPT-5's performance in three of ChatGPT's most common uses: writing, coding, and health. All of the GPT-5 models additionally feature safe-completions, our latest approach to safety training to prevent disallowed content. Similarly to ChatGPT agent, we have decided to treat gpt-5-thinking as High capability in the Biological and Chemical domain under our Preparedness Framework, activating the associated safeguards. While we do not have definitive evidence that this model could meaningfully help a novice to create severe biological harm -- our defined threshold for High capability -- we have chosen to take a precautionary approach.
Tractable Joint Prediction and Planning over Discrete Behavior Modes for Urban Driving
Mar 12, 2024Abstract:Significant progress has been made in training multimodal trajectory forecasting models for autonomous driving. However, effectively integrating these models with downstream planners and model-based control approaches is still an open problem. Although these models have conventionally been evaluated for open-loop prediction, we show that they can be used to parameterize autoregressive closed-loop models without retraining. We consider recent trajectory prediction approaches which leverage learned anchor embeddings to predict multiple trajectories, finding that these anchor embeddings can parameterize discrete and distinct modes representing high-level driving behaviors. We propose to perform fully reactive closed-loop planning over these discrete latent modes, allowing us to tractably model the causal interactions between agents at each step. We validate our approach on a suite of more dynamic merging scenarios, finding that our approach avoids the $\textit{frozen robot problem}$ which is pervasive in conventional planners. Our approach also outperforms the previous state-of-the-art in CARLA on challenging dense traffic scenarios when evaluated at realistic speeds.
Diffusion-ES: Gradient-free Planning with Diffusion for Autonomous Driving and Zero-Shot Instruction Following
Feb 09, 2024



Abstract:Diffusion models excel at modeling complex and multimodal trajectory distributions for decision-making and control. Reward-gradient guided denoising has been recently proposed to generate trajectories that maximize both a differentiable reward function and the likelihood under the data distribution captured by a diffusion model. Reward-gradient guided denoising requires a differentiable reward function fitted to both clean and noised samples, limiting its applicability as a general trajectory optimizer. In this paper, we propose DiffusionES, a method that combines gradient-free optimization with trajectory denoising to optimize black-box non-differentiable objectives while staying in the data manifold. Diffusion-ES samples trajectories during evolutionary search from a diffusion model and scores them using a black-box reward function. It mutates high-scoring trajectories using a truncated diffusion process that applies a small number of noising and denoising steps, allowing for much more efficient exploration of the solution space. We show that DiffusionES achieves state-of-the-art performance on nuPlan, an established closed-loop planning benchmark for autonomous driving. Diffusion-ES outperforms existing sampling-based planners, reactive deterministic or diffusion-based policies, and reward-gradient guidance. Additionally, we show that unlike prior guidance methods, our method can optimize non-differentiable language-shaped reward functions generated by few-shot LLM prompting. When guided by a human teacher that issues instructions to follow, our method can generate novel, highly complex behaviors, such as aggressive lane weaving, which are not present in the training data. This allows us to solve the hardest nuPlan scenarios which are beyond the capabilities of existing trajectory optimization methods and driving policies.
Fully Autonomous Real-World Reinforcement Learning for Mobile Manipulation
Aug 03, 2021



Abstract:We study how robots can autonomously learn skills that require a combination of navigation and grasping. While reinforcement learning in principle provides for automated robotic skill learning, in practice reinforcement learning in the real world is challenging and often requires extensive instrumentation and supervision. Our aim is to devise a robotic reinforcement learning system for learning navigation and manipulation together, in an autonomous way without human intervention, enabling continual learning under realistic assumptions. Our proposed system, ReLMM, can learn continuously on a real-world platform without any environment instrumentation, without human intervention, and without access to privileged information, such as maps, objects positions, or a global view of the environment. Our method employs a modularized policy with components for manipulation and navigation, where manipulation policy uncertainty drives exploration for the navigation controller, and the manipulation module provides rewards for navigation. We evaluate our method on a room cleanup task, where the robot must navigate to and pick up items scattered on the floor. After a grasp curriculum training phase, ReLMM can learn navigation and grasping together fully automatically, in around 40 hours of autonomous real-world training.
DIGIT: A Novel Design for a Low-Cost Compact High-Resolution Tactile Sensor with Application to In-Hand Manipulation
May 29, 2020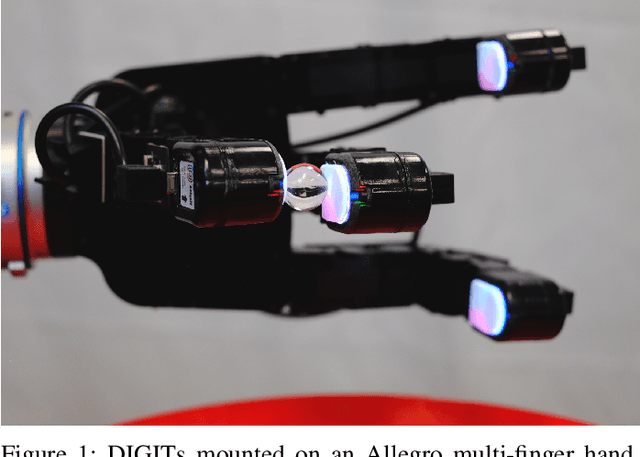
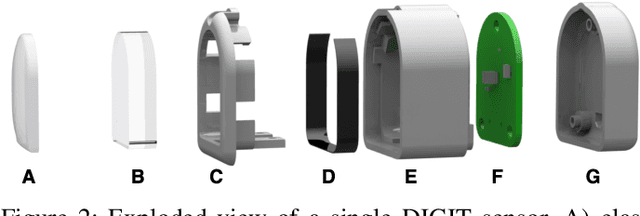

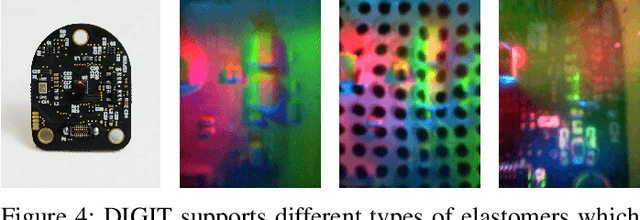
Abstract:Despite decades of research, general purpose in-hand manipulation remains one of the unsolved challenges of robotics. One of the contributing factors that limit current robotic manipulation systems is the difficulty of precisely sensing contact forces -- sensing and reasoning about contact forces are crucial to accurately control interactions with the environment. As a step towards enabling better robotic manipulation, we introduce DIGIT, an inexpensive, compact, and high-resolution tactile sensor geared towards in-hand manipulation. DIGIT improves upon past vision-based tactile sensors by miniaturizing the form factor to be mountable on multi-fingered hands, and by providing several design improvements that result in an easier, more repeatable manufacturing process, and enhanced reliability. We demonstrate the capabilities of the DIGIT sensor by training deep neural network model-based controllers to manipulate glass marbles in-hand with a multi-finger robotic hand. To provide the robotic community access to reliable and low-cost tactile sensors, we open-source the DIGIT design at https://digit.ml/.
Morphology-Agnostic Visual Robotic Control
Dec 31, 2019

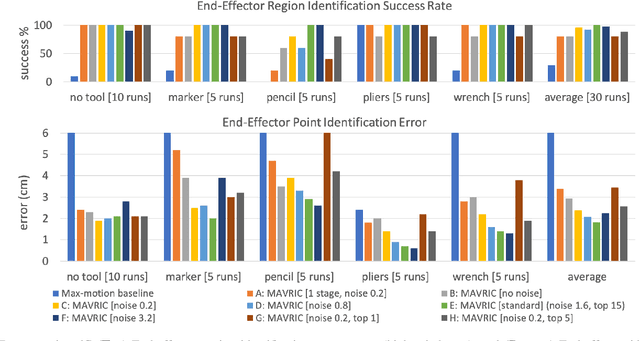
Abstract:Existing approaches for visuomotor robotic control typically require characterizing the robot in advance by calibrating the camera or performing system identification. We propose MAVRIC, an approach that works with minimal prior knowledge of the robot's morphology, and requires only a camera view containing the robot and its environment and an unknown control interface. MAVRIC revolves around a mutual information-based method for self-recognition, which discovers visual "control points" on the robot body within a few seconds of exploratory interaction, and these control points in turn are then used for visual servoing. MAVRIC can control robots with imprecise actuation, no proprioceptive feedback, unknown morphologies including novel tools, unknown camera poses, and even unsteady handheld cameras. We demonstrate our method on visually-guided 3D point reaching, trajectory following, and robot-to-robot imitation.
REPLAB: A Reproducible Low-Cost Arm Benchmark Platform for Robotic Learning
May 17, 2019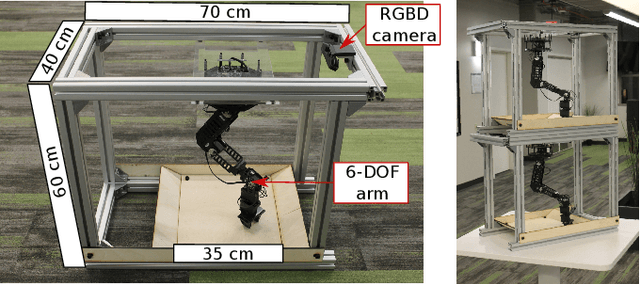

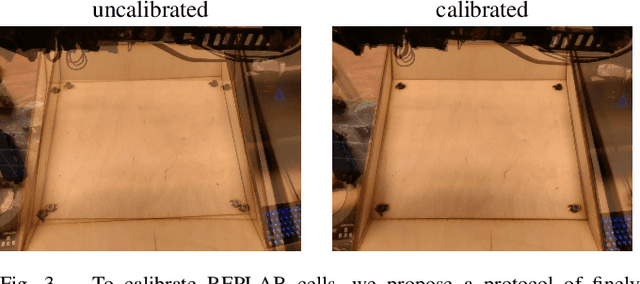
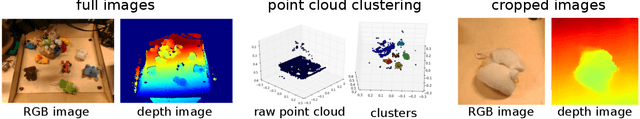
Abstract:Standardized evaluation measures have aided in the progress of machine learning approaches in disciplines such as computer vision and machine translation. In this paper, we make the case that robotic learning would also benefit from benchmarking, and present the "REPLAB" platform for benchmarking vision-based manipulation tasks. REPLAB is a reproducible and self-contained hardware stack (robot arm, camera, and workspace) that costs about 2000 USD, occupies a cuboid of size 70x40x60 cm, and permits full assembly within a few hours. Through this low-cost, compact design, REPLAB aims to drive wide participation by lowering the barrier to entry into robotics and to enable easy scaling to many robots. We envision REPLAB as a framework for reproducible research across manipulation tasks, and as a step in this direction, we define a template for a grasping benchmark consisting of a task definition, evaluation protocol, performance measures, and a dataset of 92k grasp attempts. We implement, evaluate, and analyze several previously proposed grasping approaches to establish baselines for this benchmark. Finally, we also implement and evaluate a deep reinforcement learning approach for 3D reaching tasks on our REPLAB platform. Project page with assembly instructions, code, and videos: https://goo.gl/5F9dP4.
Data-efficient Learning of Morphology and Controller for a Microrobot
May 03, 2019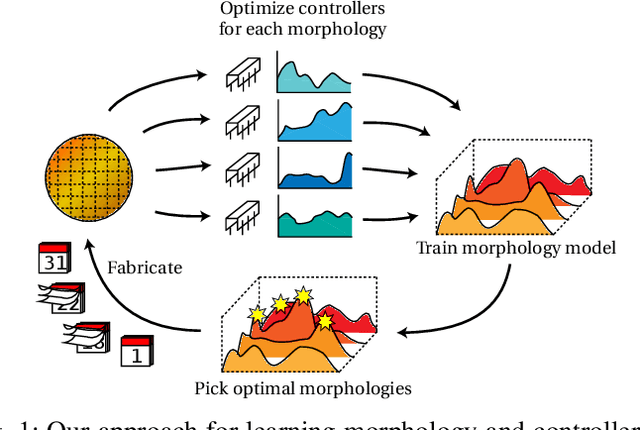
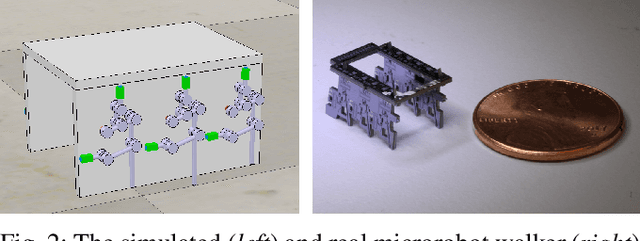
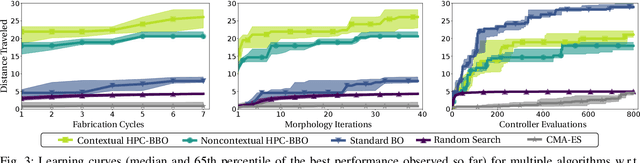
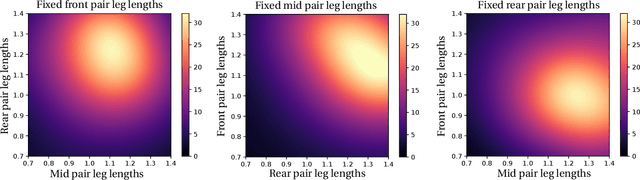
Abstract:Robot design is often a slow and difficult process requiring the iterative construction and testing of prototypes, with the goal of sequentially optimizing the design. For most robots, this process is further complicated by the need, when validating the capabilities of the hardware to solve the desired task, to already have an appropriate controller, which is in turn designed and tuned for the specific hardware. In this paper, we propose a novel approach, HPC-BBO, to efficiently and automatically design hardware configurations, and evaluate them by also automatically tuning the corresponding controller. HPC-BBO is based on a hierarchical Bayesian optimization process which iteratively optimizes morphology configurations (based on the performance of the previous designs during the controller learning process) and subsequently learns the corresponding controllers (exploiting the knowledge collected from optimizing for previous morphologies). Moreover, HPC-BBO can select a "batch" of multiple morphology designs at once, thus parallelizing hardware validation and reducing the number of time-consuming production cycles. We validate HPC-BBO on the design of the morphology and controller for a simulated 6-legged microrobot. Experimental results show that HPC-BBO outperforms multiple competitive baselines, and yields a $360\%$ reduction in production cycles over standard Bayesian optimization, thus reducing the hypothetical manufacturing time of our microrobot from 21 to 4 months.
Learning Flexible and Reusable Locomotion Primitives for a Microrobot
Mar 01, 2018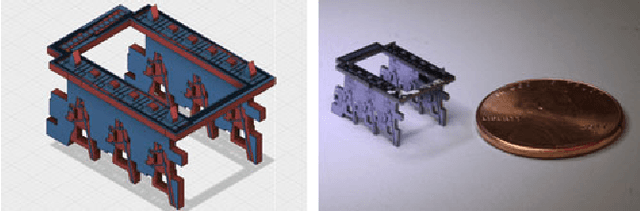
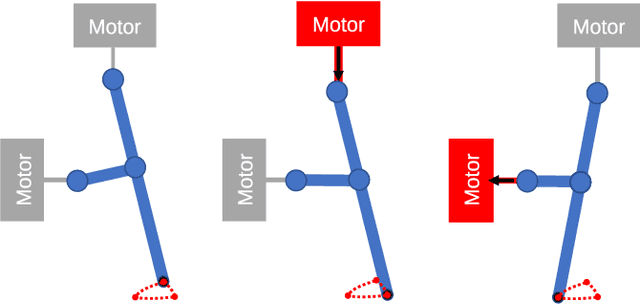
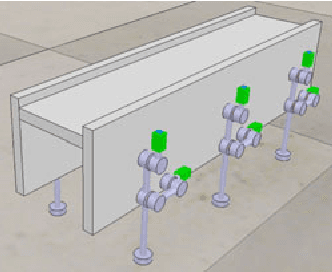
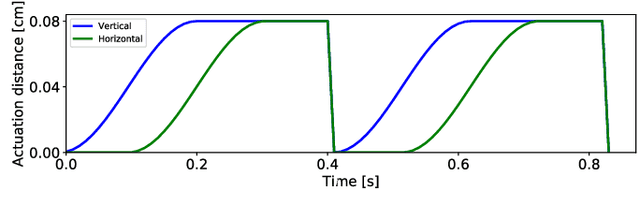
Abstract:The design of gaits for robot locomotion can be a daunting process which requires significant expert knowledge and engineering. This process is even more challenging for robots that do not have an accurate physical model, such as compliant or micro-scale robots. Data-driven gait optimization provides an automated alternative to analytical gait design. In this paper, we propose a novel approach to efficiently learn a wide range of locomotion tasks with walking robots. This approach formalizes locomotion as a contextual policy search task to collect data, and subsequently uses that data to learn multi-objective locomotion primitives that can be used for planning. As a proof-of-concept we consider a simulated hexapod modeled after a recently developed microrobot, and we thoroughly evaluate the performance of this microrobot on different tasks and gaits. Our results validate the proposed controller and learning scheme on single and multi-objective locomotion tasks. Moreover, the experimental simulations show that without any prior knowledge about the robot used (e.g., dynamics model), our approach is capable of learning locomotion primitives within 250 trials and subsequently using them to successfully navigate through a maze.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge