Po-Wei Chou
PyTouch: A Machine Learning Library for Touch Processing
May 26, 2021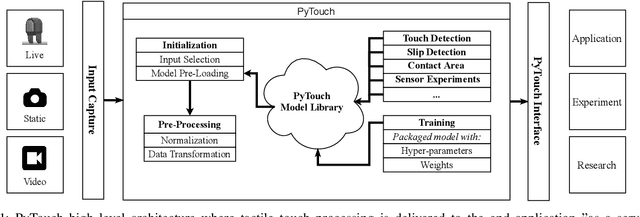
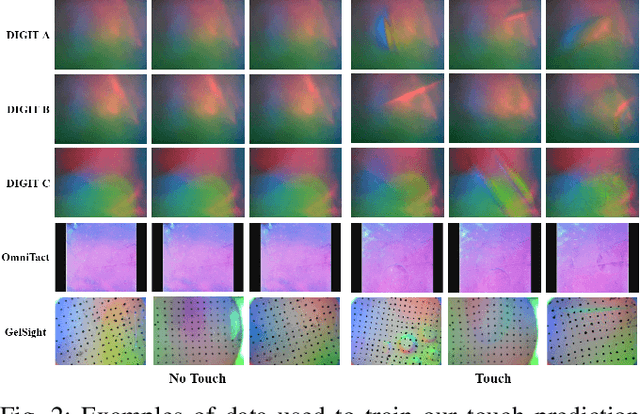
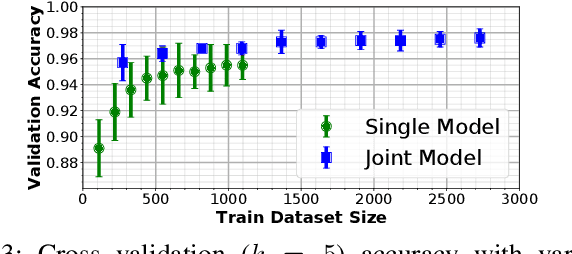
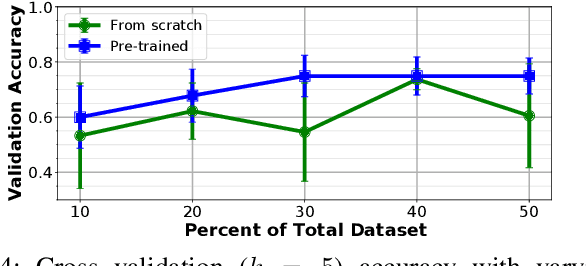
Abstract:With the increased availability of rich tactile sensors, there is an equally proportional need for open-source and integrated software capable of efficiently and effectively processing raw touch measurements into high-level signals that can be used for control and decision-making. In this paper, we present PyTouch -- the first machine learning library dedicated to the processing of touch sensing signals. PyTouch, is designed to be modular, easy-to-use and provides state-of-the-art touch processing capabilities as a service with the goal of unifying the tactile sensing community by providing a library for building scalable, proven, and performance-validated modules over which applications and research can be built upon. We evaluate PyTouch on real-world data from several tactile sensors on touch processing tasks such as touch detection, slip and object pose estimations. PyTouch is open-sourced at https://github.com/facebookresearch/pytouch .
TACTO: A Fast, Flexible and Open-source Simulator for High-Resolution Vision-based Tactile Sensors
Dec 15, 2020
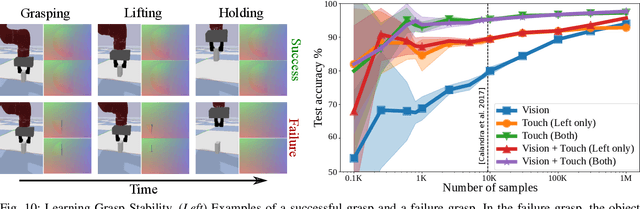
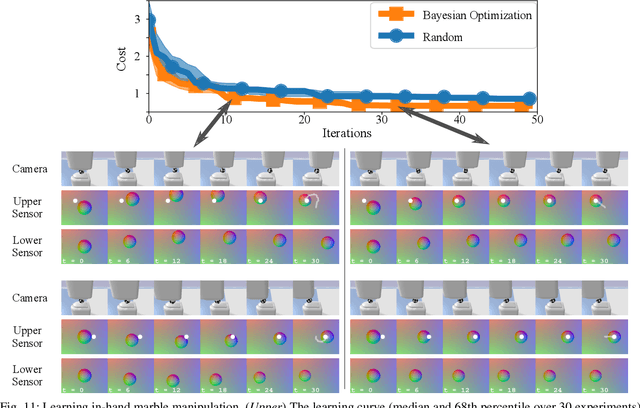
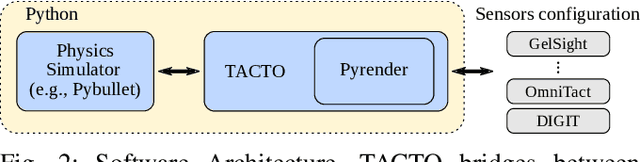
Abstract:Simulators perform an important role in prototyping, debugging and benchmarking new advances in robotics and learning for control. Although many physics engines exist, some aspects of the real-world are harder than others to simulate. One of the aspects that have so far eluded accurate simulation is touch sensing. To address this gap, we present TACTO -- a fast, flexible and open-source simulator for vision-based tactile sensors. This simulator allows to render realistic high-resolution touch readings at hundreds of frames per second, and can be easily configured to simulate different vision-based tactile sensors, including GelSight, DIGIT and OmniTact. In this paper, we detail the principles that drove the implementation of TACTO and how they are reflected in its architecture. We demonstrate TACTO on a perceptual task, by learning to predict grasp stability using touch from 1 million grasps, and on a marble manipulation control task. We believe that TACTO is a step towards the widespread adoption of touch sensing in robotic applications, and to enable machine learning practitioners interested in multi-modal learning and control. TACTO is open-source at https://github.com/facebookresearch/tacto.
DIGIT: A Novel Design for a Low-Cost Compact High-Resolution Tactile Sensor with Application to In-Hand Manipulation
May 29, 2020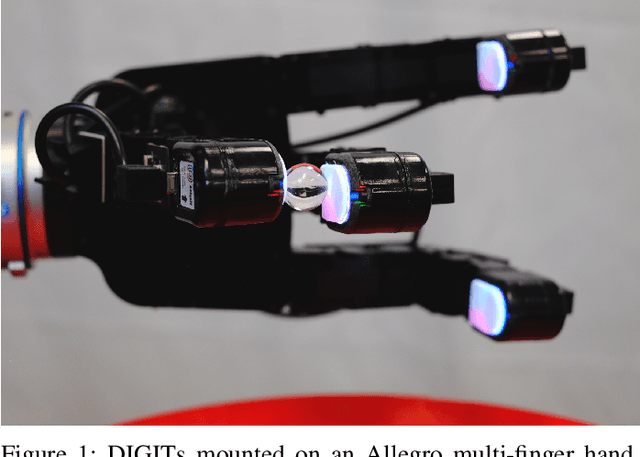
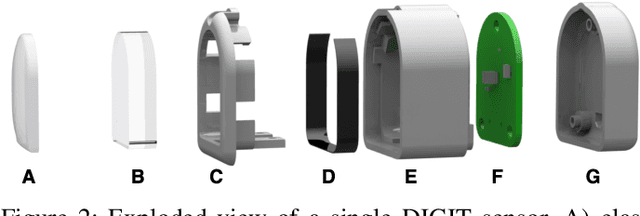

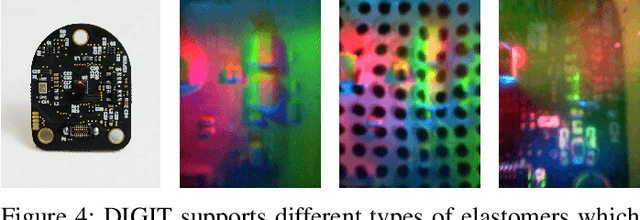
Abstract:Despite decades of research, general purpose in-hand manipulation remains one of the unsolved challenges of robotics. One of the contributing factors that limit current robotic manipulation systems is the difficulty of precisely sensing contact forces -- sensing and reasoning about contact forces are crucial to accurately control interactions with the environment. As a step towards enabling better robotic manipulation, we introduce DIGIT, an inexpensive, compact, and high-resolution tactile sensor geared towards in-hand manipulation. DIGIT improves upon past vision-based tactile sensors by miniaturizing the form factor to be mountable on multi-fingered hands, and by providing several design improvements that result in an easier, more repeatable manufacturing process, and enhanced reliability. We demonstrate the capabilities of the DIGIT sensor by training deep neural network model-based controllers to manipulate glass marbles in-hand with a multi-finger robotic hand. To provide the robotic community access to reliable and low-cost tactile sensors, we open-source the DIGIT design at https://digit.ml/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge