Bowei Tian
Convergence of Spectral Principal Paths: How Deep Networks Distill Linear Representations from Noisy Inputs
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:High-level representations have become a central focus in enhancing AI transparency and control, shifting attention from individual neurons or circuits to structured semantic directions that align with human-interpretable concepts. Motivated by the Linear Representation Hypothesis (LRH), we propose the Input-Space Linearity Hypothesis (ISLH), which posits that concept-aligned directions originate in the input space and are selectively amplified with increasing depth. We then introduce the Spectral Principal Path (SPP) framework, which formalizes how deep networks progressively distill linear representations along a small set of dominant spectral directions. Building on this framework, we further demonstrate the multimodal robustness of these representations in Vision-Language Models (VLMs). By bridging theoretical insights with empirical validation, this work advances a structured theory of representation formation in deep networks, paving the way for improving AI robustness, fairness, and transparency.
Invisible Tokens, Visible Bills: The Urgent Need to Audit Hidden Operations in Opaque LLM Services
May 24, 2025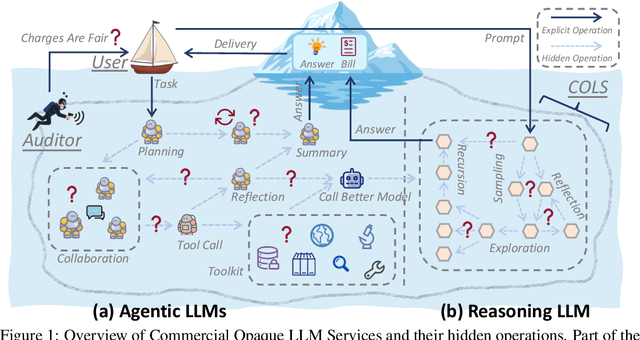
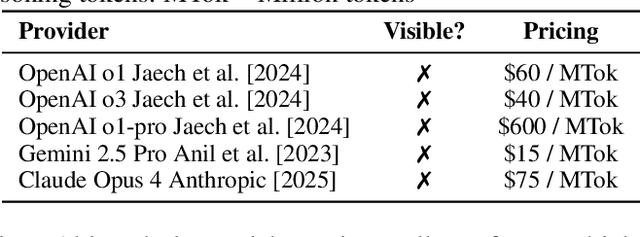
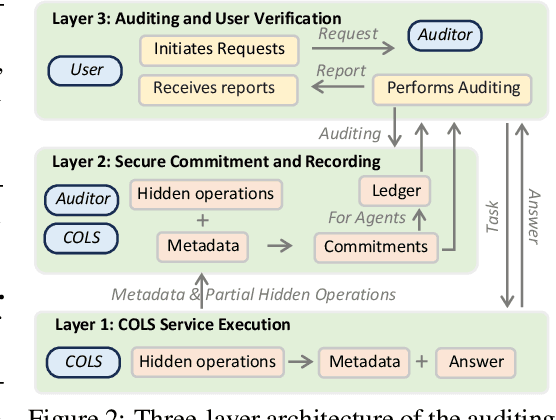

Abstract:Modern large language model (LLM) services increasingly rely on complex, often abstract operations, such as multi-step reasoning and multi-agent collaboration, to generate high-quality outputs. While users are billed based on token consumption and API usage, these internal steps are typically not visible. We refer to such systems as Commercial Opaque LLM Services (COLS). This position paper highlights emerging accountability challenges in COLS: users are billed for operations they cannot observe, verify, or contest. We formalize two key risks: \textit{quantity inflation}, where token and call counts may be artificially inflated, and \textit{quality downgrade}, where providers might quietly substitute lower-cost models or tools. Addressing these risks requires a diverse set of auditing strategies, including commitment-based, predictive, behavioral, and signature-based methods. We further explore the potential of complementary mechanisms such as watermarking and trusted execution environments to enhance verifiability without compromising provider confidentiality. We also propose a modular three-layer auditing framework for COLS and users that enables trustworthy verification across execution, secure logging, and user-facing auditability without exposing proprietary internals. Our aim is to encourage further research and policy development toward transparency, auditability, and accountability in commercial LLM services.
CoIn: Counting the Invisible Reasoning Tokens in Commercial Opaque LLM APIs
May 19, 2025Abstract:As post-training techniques evolve, large language models (LLMs) are increasingly augmented with structured multi-step reasoning abilities, often optimized through reinforcement learning. These reasoning-enhanced models outperform standard LLMs on complex tasks and now underpin many commercial LLM APIs. However, to protect proprietary behavior and reduce verbosity, providers typically conceal the reasoning traces while returning only the final answer. This opacity introduces a critical transparency gap: users are billed for invisible reasoning tokens, which often account for the majority of the cost, yet have no means to verify their authenticity. This opens the door to token count inflation, where providers may overreport token usage or inject synthetic, low-effort tokens to inflate charges. To address this issue, we propose CoIn, a verification framework that audits both the quantity and semantic validity of hidden tokens. CoIn constructs a verifiable hash tree from token embedding fingerprints to check token counts, and uses embedding-based relevance matching to detect fabricated reasoning content. Experiments demonstrate that CoIn, when deployed as a trusted third-party auditor, can effectively detect token count inflation with a success rate reaching up to 94.7%, showing the strong ability to restore billing transparency in opaque LLM services. The dataset and code are available at https://github.com/CASE-Lab-UMD/LLM-Auditing-CoIn.
SymRTLO: Enhancing RTL Code Optimization with LLMs and Neuron-Inspired Symbolic Reasoning
Apr 14, 2025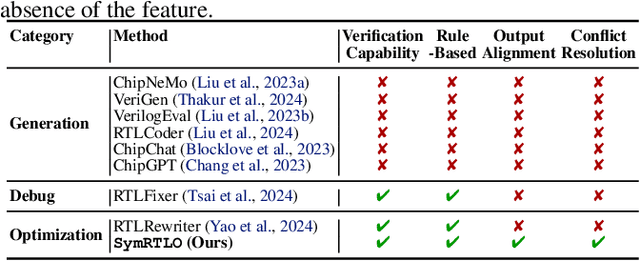
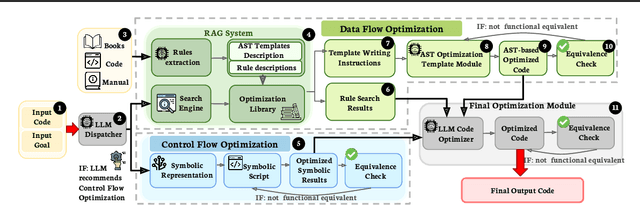

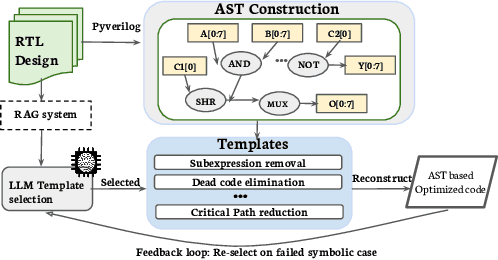
Abstract:Optimizing Register Transfer Level (RTL) code is crucial for improving the power, performance, and area (PPA) of digital circuits in the early stages of synthesis. Manual rewriting, guided by synthesis feedback, can yield high-quality results but is time-consuming and error-prone. Most existing compiler-based approaches have difficulty handling complex design constraints. Large Language Model (LLM)-based methods have emerged as a promising alternative to address these challenges. However, LLM-based approaches often face difficulties in ensuring alignment between the generated code and the provided prompts. This paper presents SymRTLO, a novel neuron-symbolic RTL optimization framework that seamlessly integrates LLM-based code rewriting with symbolic reasoning techniques. Our method incorporates a retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) system of optimization rules and Abstract Syntax Tree (AST)-based templates, enabling LLM-based rewriting that maintains syntactic correctness while minimizing undesired circuit behaviors. A symbolic module is proposed for analyzing and optimizing finite state machine (FSM) logic, allowing fine-grained state merging and partial specification handling beyond the scope of pattern-based compilers. Furthermore, a fast verification pipeline, combining formal equivalence checks with test-driven validation, further reduces the complexity of verification. Experiments on the RTL-Rewriter benchmark with Synopsys Design Compiler and Yosys show that SymRTLO improves power, performance, and area (PPA) by up to 43.9%, 62.5%, and 51.1%, respectively, compared to the state-of-the-art methods.
An Effective and Resilient Backdoor Attack Framework against Deep Neural Networks and Vision Transformers
Dec 09, 2024



Abstract:Recent studies have revealed the vulnerability of Deep Neural Network (DNN) models to backdoor attacks. However, existing backdoor attacks arbitrarily set the trigger mask or use a randomly selected trigger, which restricts the effectiveness and robustness of the generated backdoor triggers. In this paper, we propose a novel attention-based mask generation methodology that searches for the optimal trigger shape and location. We also introduce a Quality-of-Experience (QoE) term into the loss function and carefully adjust the transparency value of the trigger in order to make the backdoored samples to be more natural. To further improve the prediction accuracy of the victim model, we propose an alternating retraining algorithm in the backdoor injection process. The victim model is retrained with mixed poisoned datasets in even iterations and with only benign samples in odd iterations. Besides, we launch the backdoor attack under a co-optimized attack framework that alternately optimizes the backdoor trigger and backdoored model to further improve the attack performance. Apart from DNN models, we also extend our proposed attack method against vision transformers. We evaluate our proposed method with extensive experiments on VGG-Flower, CIFAR-10, GTSRB, CIFAR-100, and ImageNette datasets. It is shown that we can increase the attack success rate by as much as 82\% over baselines when the poison ratio is low and achieve a high QoE of the backdoored samples. Our proposed backdoor attack framework also showcases robustness against state-of-the-art backdoor defenses.
Fair Diagnosis: Leveraging Causal Modeling to Mitigate Medical Bias
Dec 06, 2024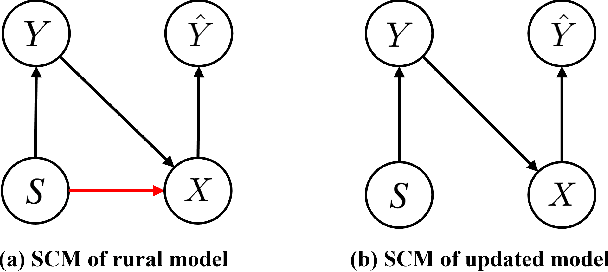
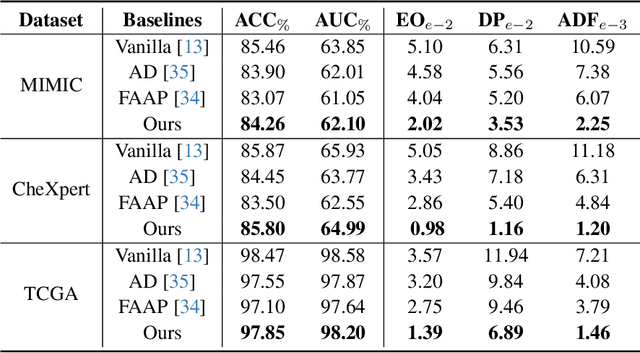
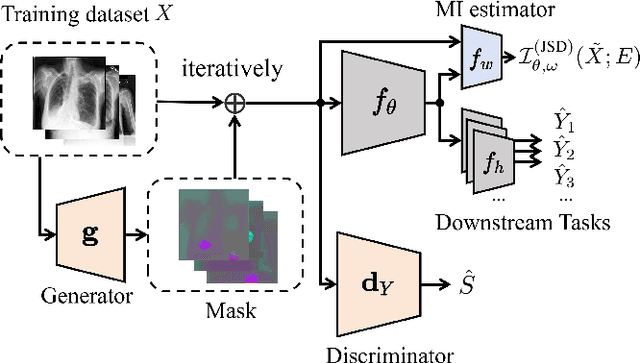
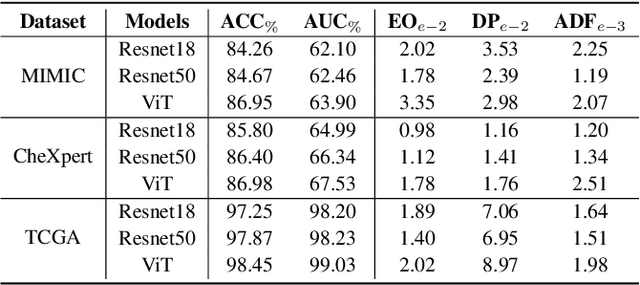
Abstract:In medical image analysis, model predictions can be affected by sensitive attributes, such as race and gender, leading to fairness concerns and potential biases in diagnostic outcomes. To mitigate this, we present a causal modeling framework, which aims to reduce the impact of sensitive attributes on diagnostic predictions. Our approach introduces a novel fairness criterion, \textbf{Diagnosis Fairness}, and a unique fairness metric, leveraging path-specific fairness to control the influence of demographic attributes, ensuring that predictions are primarily informed by clinically relevant features rather than sensitive attributes. By incorporating adversarial perturbation masks, our framework directs the model to focus on critical image regions, suppressing bias-inducing information. Experimental results across multiple datasets demonstrate that our framework effectively reduces bias directly associated with sensitive attributes while preserving diagnostic accuracy. Our findings suggest that causal modeling can enhance both fairness and interpretability in AI-powered clinical decision support systems.
Towards counterfactual fairness thorough auxiliary variables
Dec 06, 2024Abstract:The challenge of balancing fairness and predictive accuracy in machine learning models, especially when sensitive attributes such as race, gender, or age are considered, has motivated substantial research in recent years. Counterfactual fairness ensures that predictions remain consistent across counterfactual variations of sensitive attributes, which is a crucial concept in addressing societal biases. However, existing counterfactual fairness approaches usually overlook intrinsic information about sensitive features, limiting their ability to achieve fairness while simultaneously maintaining performance. To tackle this challenge, we introduce EXOgenous Causal reasoning (EXOC), a novel causal reasoning framework motivated by exogenous variables. It leverages auxiliary variables to uncover intrinsic properties that give rise to sensitive attributes. Our framework explicitly defines an auxiliary node and a control node that contribute to counterfactual fairness and control the information flow within the model. Our evaluation, conducted on synthetic and real-world datasets, validates EXOC's superiority, showing that it outperforms state-of-the-art approaches in achieving counterfactual fairness.
Megatron: Evasive Clean-Label Backdoor Attacks against Vision Transformer
Dec 06, 2024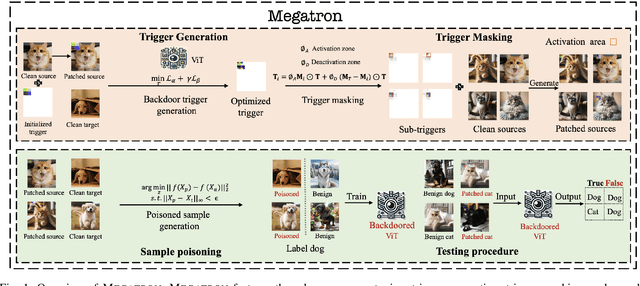
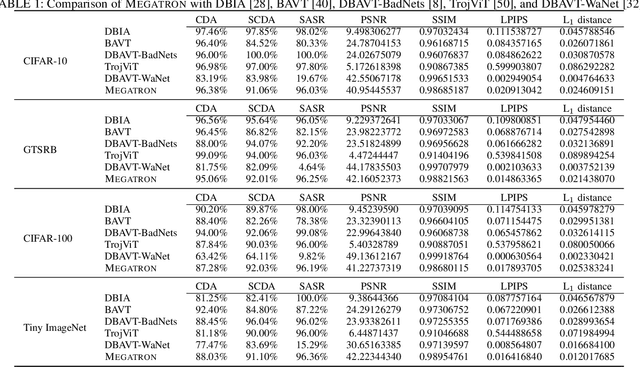
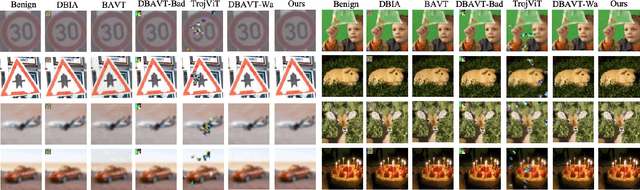
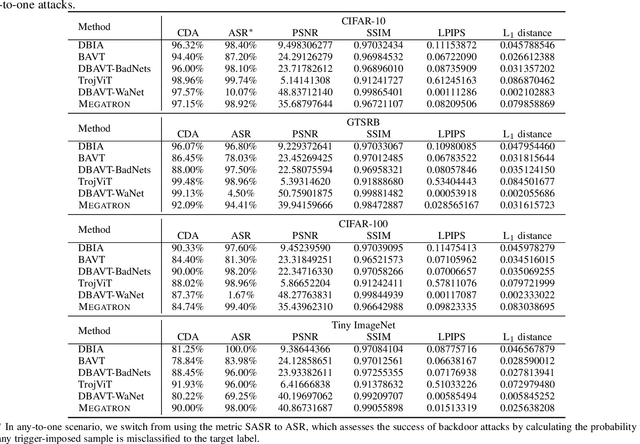
Abstract:Vision transformers have achieved impressive performance in various vision-related tasks, but their vulnerability to backdoor attacks is under-explored. A handful of existing works focus on dirty-label attacks with wrongly-labeled poisoned training samples, which may fail if a benign model trainer corrects the labels. In this paper, we propose Megatron, an evasive clean-label backdoor attack against vision transformers, where the attacker injects the backdoor without manipulating the data-labeling process. To generate an effective trigger, we customize two loss terms based on the attention mechanism used in transformer networks, i.e., latent loss and attention diffusion loss. The latent loss aligns the last attention layer between triggered samples and clean samples of the target label. The attention diffusion loss emphasizes the attention diffusion area that encompasses the trigger. A theoretical analysis is provided to underpin the rationale behind the attention diffusion loss. Extensive experiments on CIFAR-10, GTSRB, CIFAR-100, and Tiny ImageNet demonstrate the effectiveness of Megatron. Megatron can achieve attack success rates of over 90% even when the position of the trigger is slightly shifted during testing. Furthermore, Megatron achieves better evasiveness than baselines regarding both human visual inspection and defense strategies (i.e., DBAVT, BAVT, Beatrix, TeCo, and SAGE).
One Communication Round is All It Needs for Federated Fine-Tuning Foundation Models
Dec 05, 2024Abstract:The recent advancement of large foundation models (FMs) has increased the demand for fine-tuning these models on large-scale and cross-domain datasets. To address this, federated fine-tuning has emerged as a solution, allowing models to be fine-tuned on distributed datasets across multiple devices while ensuring data privacy. However, the substantial parameter size of FMs and the multi-round communication required by traditional federated fine-tuning algorithms result in prohibitively high communication costs, challenging the practicality of federated fine-tuning. In this paper, we are the first to reveal, both theoretically and empirically, that the traditional multi-round aggregation algorithms may not be necessary for federated fine-tuning large FMs. Our experiments reveal that a single round of communication (i.e., one-shot federated fine-tuning) yields a global model performance comparable to that achieved through multiple rounds of communication. Through rigorous mathematical and empirical analyses, we demonstrate that large FMs, due to their extensive parameter sizes and pre-training on general tasks, achieve significantly lower training loss in one-shot federated fine-tuning compared to smaller models. Our extensive experiments show that one-shot federated fine-tuning not only reduces communication costs but also enables asynchronous aggregation, enhances privacy, and maintains performance consistency with multi-round federated fine-tuning for models larger than 1 billion parameters, on text generation and text-to-image generation tasks. Our findings have the potential to revolutionize federated fine-tuning in practice, enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and expanding accessibility for large-scale models. This breakthrough paves the way for broader adoption and application of federated fine-tuning across various domains.
Router-Tuning: A Simple and Effective Approach for Enabling Dynamic-Depth in Transformers
Oct 17, 2024Abstract:Traditional transformer models often allocate a fixed amount of computational resources to every input token, leading to inefficient and unnecessary computation. To address this, the Mixture of Depths (MoD) was introduced to dynamically adjust the computational depth by skipping less important layers. Despite its promise, current MoD approaches remain under-explored and face two main challenges: (1) \textit{high training costs due to the need to train the entire model along with the routers that determine which layers to skip}, and (2) \textit{the risk of performance degradation when important layers are bypassed}. In response to the first issue, we propose Router-Tuning, a method that fine-tunes only the router on a small dataset, drastically reducing the computational overhead associated with full model training. For the second challenge, we propose MindSkip, which deploys \textit{Attention with Dynamic Depths}. This method preserves the model's performance while significantly enhancing computational and memory efficiency. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach delivers competitive results while dramatically improving the computation efficiency, e.g., 21\% speedup and only a 0.2\% performance drop. The code is released at \url{https://github.com/CASE-Lab-UMD/Router-Tuning}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge