Yucong Dai
FairAgent: Democratizing Fairness-Aware Machine Learning with LLM-Powered Agents
Oct 05, 2025Abstract:Training fair and unbiased machine learning models is crucial for high-stakes applications, yet it presents significant challenges. Effective bias mitigation requires deep expertise in fairness definitions, metrics, data preprocessing, and machine learning techniques. In addition, the complex process of balancing model performance with fairness requirements while properly handling sensitive attributes makes fairness-aware model development inaccessible to many practitioners. To address these challenges, we introduce FairAgent, an LLM-powered automated system that significantly simplifies fairness-aware model development. FairAgent eliminates the need for deep technical expertise by automatically analyzing datasets for potential biases, handling data preprocessing and feature engineering, and implementing appropriate bias mitigation strategies based on user requirements. Our experiments demonstrate that FairAgent achieves significant performance improvements while significantly reducing development time and expertise requirements, making fairness-aware machine learning more accessible to practitioners.
Causally Fair Node Classification on Non-IID Graph Data
May 03, 2025Abstract:Fair machine learning seeks to identify and mitigate biases in predictions against unfavorable populations characterized by demographic attributes, such as race and gender. Recently, a few works have extended fairness to graph data, such as social networks, but most of them neglect the causal relationships among data instances. This paper addresses the prevalent challenge in fairness-aware ML algorithms, which typically assume Independent and Identically Distributed (IID) data. We tackle the overlooked domain of non-IID, graph-based settings where data instances are interconnected, influencing the outcomes of fairness interventions. We base our research on the Network Structural Causal Model (NSCM) framework and posit two main assumptions: Decomposability and Graph Independence, which enable the computation of interventional distributions in non-IID settings using the $do$-calculus. Based on that, we develop the Message Passing Variational Autoencoder for Causal Inference (MPVA) to compute interventional distributions and facilitate causally fair node classification through estimated interventional distributions. Empirical evaluations on semi-synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate that MPVA outperforms conventional methods by effectively approximating interventional distributions and mitigating bias. The implications of our findings underscore the potential of causality-based fairness in complex ML applications, setting the stage for further research into relaxing the initial assumptions to enhance model fairness.
FairSAM: Fair Classification on Corrupted Data Through Sharpness-Aware Minimization
Mar 29, 2025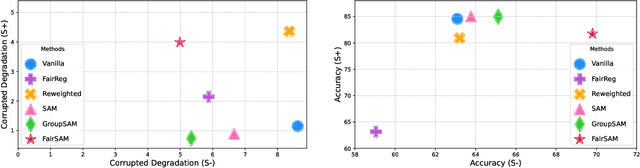
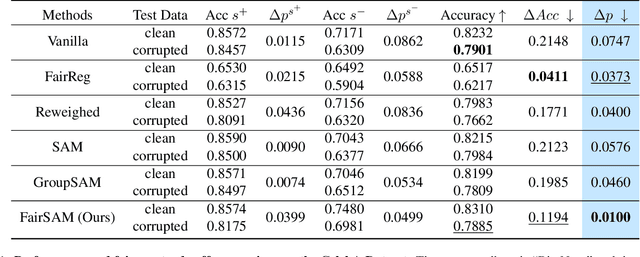

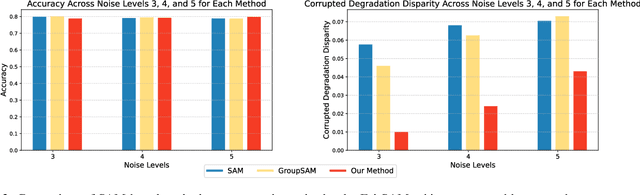
Abstract:Image classification models trained on clean data often suffer from significant performance degradation when exposed to testing corrupted data, such as images with impulse noise, Gaussian noise, or environmental noise. This degradation not only impacts overall performance but also disproportionately affects various demographic subgroups, raising critical algorithmic bias concerns. Although robust learning algorithms like Sharpness-Aware Minimization (SAM) have shown promise in improving overall model robustness and generalization, they fall short in addressing the biased performance degradation across demographic subgroups. Existing fairness-aware machine learning methods - such as fairness constraints and reweighing strategies - aim to reduce performance disparities but hardly maintain robust and equitable accuracy across demographic subgroups when faced with data corruption. This reveals an inherent tension between robustness and fairness when dealing with corrupted data. To address these challenges, we introduce one novel metric specifically designed to assess performance degradation across subgroups under data corruption. Additionally, we propose \textbf{FairSAM}, a new framework that integrates \underline{Fair}ness-oriented strategies into \underline{SAM} to deliver equalized performance across demographic groups under corrupted conditions. Our experiments on multiple real-world datasets and various predictive tasks show that FairSAM successfully reconciles robustness and fairness, offering a structured solution for equitable and resilient image classification in the presence of data corruption.
Fair Diagnosis: Leveraging Causal Modeling to Mitigate Medical Bias
Dec 06, 2024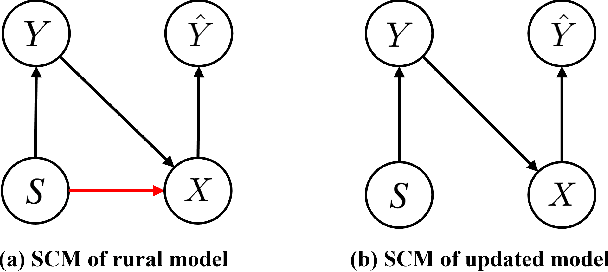
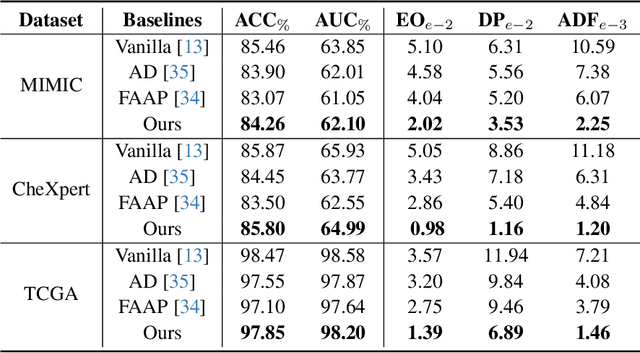
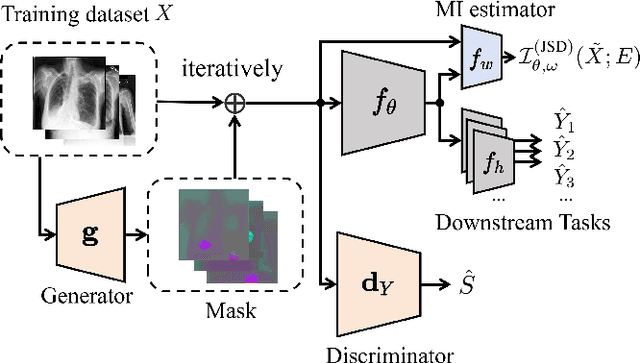
Abstract:In medical image analysis, model predictions can be affected by sensitive attributes, such as race and gender, leading to fairness concerns and potential biases in diagnostic outcomes. To mitigate this, we present a causal modeling framework, which aims to reduce the impact of sensitive attributes on diagnostic predictions. Our approach introduces a novel fairness criterion, \textbf{Diagnosis Fairness}, and a unique fairness metric, leveraging path-specific fairness to control the influence of demographic attributes, ensuring that predictions are primarily informed by clinically relevant features rather than sensitive attributes. By incorporating adversarial perturbation masks, our framework directs the model to focus on critical image regions, suppressing bias-inducing information. Experimental results across multiple datasets demonstrate that our framework effectively reduces bias directly associated with sensitive attributes while preserving diagnostic accuracy. Our findings suggest that causal modeling can enhance both fairness and interpretability in AI-powered clinical decision support systems.
Towards counterfactual fairness thorough auxiliary variables
Dec 06, 2024Abstract:The challenge of balancing fairness and predictive accuracy in machine learning models, especially when sensitive attributes such as race, gender, or age are considered, has motivated substantial research in recent years. Counterfactual fairness ensures that predictions remain consistent across counterfactual variations of sensitive attributes, which is a crucial concept in addressing societal biases. However, existing counterfactual fairness approaches usually overlook intrinsic information about sensitive features, limiting their ability to achieve fairness while simultaneously maintaining performance. To tackle this challenge, we introduce EXOgenous Causal reasoning (EXOC), a novel causal reasoning framework motivated by exogenous variables. It leverages auxiliary variables to uncover intrinsic properties that give rise to sensitive attributes. Our framework explicitly defines an auxiliary node and a control node that contribute to counterfactual fairness and control the information flow within the model. Our evaluation, conducted on synthetic and real-world datasets, validates EXOC's superiority, showing that it outperforms state-of-the-art approaches in achieving counterfactual fairness.
SHED: Shapley-Based Automated Dataset Refinement for Instruction Fine-Tuning
Apr 23, 2024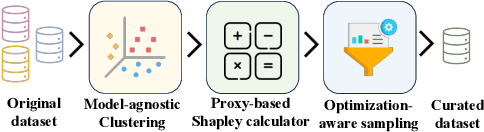

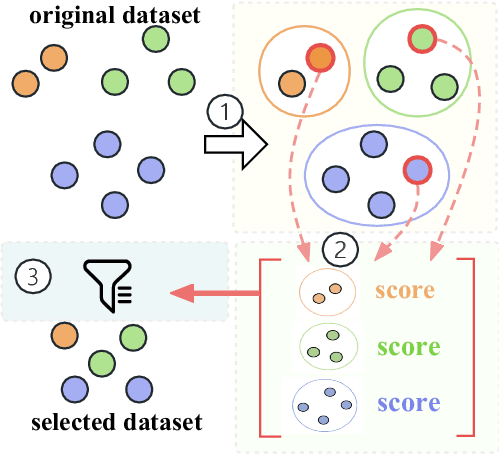
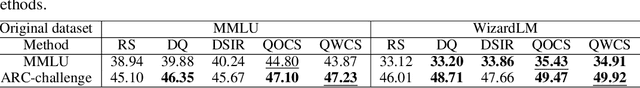
Abstract:The pre-trained Large Language Models (LLMs) can be adapted for many downstream tasks and tailored to align with human preferences through fine-tuning. Recent studies have discovered that LLMs can achieve desirable performance with only a small amount of high-quality data, suggesting that a large amount of the data in these extensive datasets is redundant or even harmful. Identifying high-quality data from vast datasets to curate small yet effective datasets has emerged as a critical challenge. In this paper, we introduce SHED, an automated dataset refinement framework based on Shapley value for instruction fine-tuning. SHED eliminates the need for human intervention or the use of commercial LLMs. Moreover, the datasets curated through SHED exhibit transferability, indicating they can be reused across different LLMs with consistently high performance. We conduct extensive experiments to evaluate the datasets curated by SHED. The results demonstrate SHED's superiority over state-of-the-art methods across various tasks and LLMs; notably, datasets comprising only 10% of the original data selected by SHED achieve performance comparable to or surpassing that of the full datasets.
Coupling Fairness and Pruning in a Single Run: a Bi-level Optimization Perspective
Dec 15, 2023Abstract:Deep neural networks have demonstrated remarkable performance in various tasks. With a growing need for sparse deep learning, model compression techniques, especially pruning, have gained significant attention. However, conventional pruning techniques can inadvertently exacerbate algorithmic bias, resulting in unequal predictions. To address this, we define a fair pruning task where a sparse model is derived subject to fairness requirements. In particular, we propose a framework to jointly optimize the pruning mask and weight update processes with fairness constraints. This framework is engineered to compress models that maintain performance while ensuring fairness in a single execution. To this end, we formulate the fair pruning problem as a novel constrained bi-level optimization task and derive efficient and effective solving strategies. We design experiments spanning various datasets and settings to validate our proposed method. Our empirical analysis contrasts our framework with several mainstream pruning strategies, emphasizing our method's superiority in maintaining model fairness, performance, and efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge