Bo Feng
NarrativeTrack: Evaluating Video Language Models Beyond the Frame
Jan 03, 2026Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have achieved impressive progress in vision-language reasoning, yet their ability to understand temporally unfolding narratives in videos remains underexplored. True narrative understanding requires grounding who is doing what, when, and where, maintaining coherent entity representations across dynamic visual and temporal contexts. We introduce NarrativeTrack, the first benchmark to evaluate narrative understanding in MLLMs through fine-grained entity-centric reasoning. Unlike existing benchmarks limited to short clips or coarse scene-level semantics, we decompose videos into constituent entities and examine their continuity via a Compositional Reasoning Progression (CRP), a structured evaluation framework that progressively increases narrative complexity across three dimensions: entity existence, entity changes, and entity ambiguity. CRP challenges models to advance from temporal persistence to contextual evolution and fine-grained perceptual reasoning. A fully automated entity-centric pipeline enables scalable extraction of temporally grounded entity representations, providing the foundation for CRP. Evaluations of state-of-the-art MLLMs reveal that models fail to robustly track entities across visual transitions and temporal dynamics, often hallucinating identity under context shifts. Open-source general-purpose MLLMs exhibit strong perceptual grounding but weak temporal coherence, while video-specific MLLMs capture temporal context yet hallucinate entity's contexts. These findings uncover a fundamental trade-off between perceptual grounding and temporal reasoning, indicating that narrative understanding emerges only from their integration. NarrativeTrack provides the first systematic framework to diagnose and advance temporally grounded narrative comprehension in MLLMs.
Breaking Down Video LLM Benchmarks: Knowledge, Spatial Perception, or True Temporal Understanding?
May 20, 2025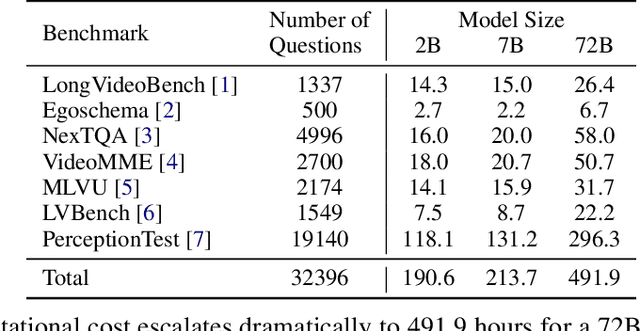
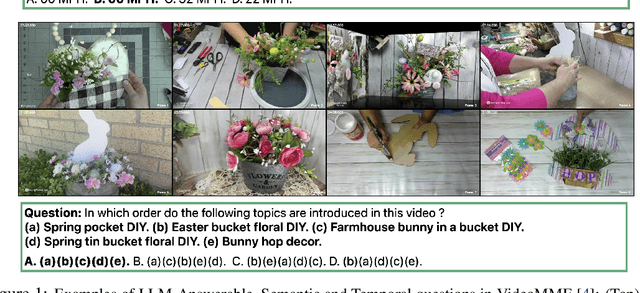
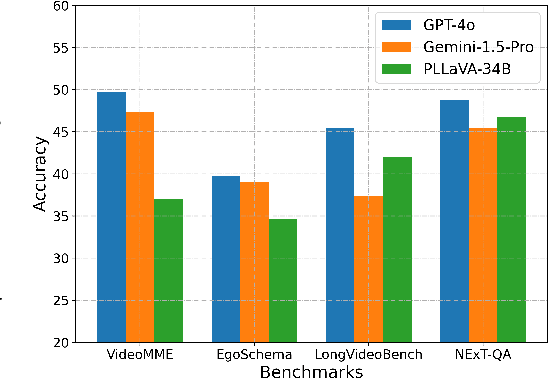
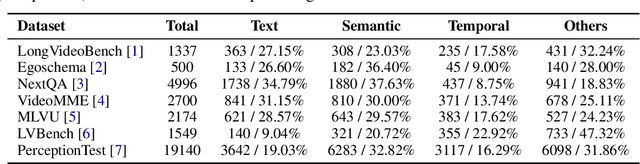
Abstract:Existing video understanding benchmarks often conflate knowledge-based and purely image-based questions, rather than clearly isolating a model's temporal reasoning ability, which is the key aspect that distinguishes video understanding from other modalities. We identify two major limitations that obscure whether higher scores truly indicate stronger understanding of the dynamic content in videos: (1) strong language priors, where models can answer questions without watching the video; and (2) shuffling invariance, where models maintain similar performance on certain questions even when video frames are temporally shuffled. To alleviate these issues, we propose VBenchComp, an automated pipeline that categorizes questions into different domains: LLM-Answerable, Semantic, and Temporal. Specifically, LLM-Answerable questions can be answered without viewing the video; Semantic questions remain answerable even when the video frames are shuffled; and Temporal questions require understanding the correct temporal order of frames. The rest of the questions are labeled as Others. This can enable fine-grained evaluation of different capabilities of a video LLM. Our analysis reveals nuanced model weaknesses that are hidden by traditional overall scores, and we offer insights and recommendations for designing future benchmarks that more accurately assess video LLMs.
Large Language Models Are More Persuasive Than Incentivized Human Persuaders
May 14, 2025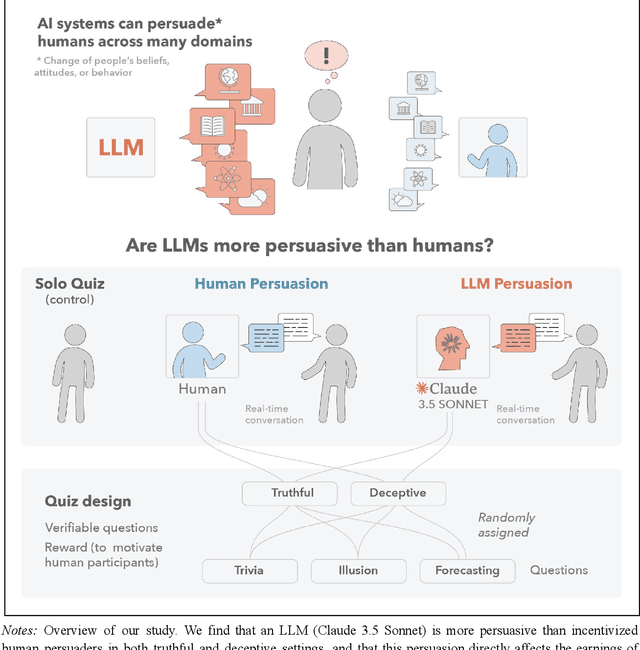
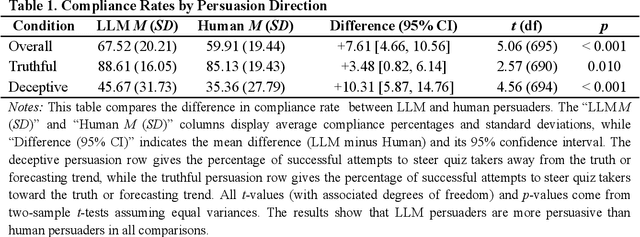
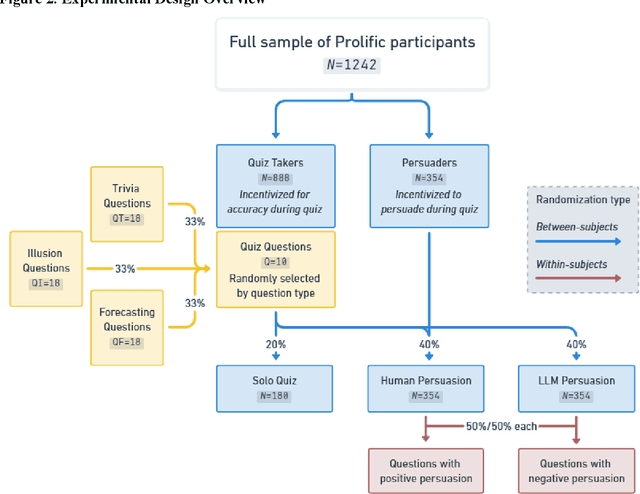
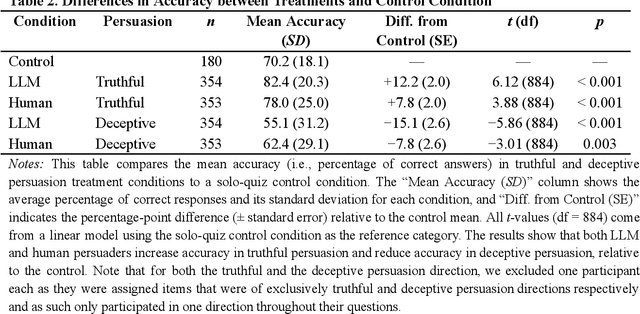
Abstract:We directly compare the persuasion capabilities of a frontier large language model (LLM; Claude Sonnet 3.5) against incentivized human persuaders in an interactive, real-time conversational quiz setting. In this preregistered, large-scale incentivized experiment, participants (quiz takers) completed an online quiz where persuaders (either humans or LLMs) attempted to persuade quiz takers toward correct or incorrect answers. We find that LLM persuaders achieved significantly higher compliance with their directional persuasion attempts than incentivized human persuaders, demonstrating superior persuasive capabilities in both truthful (toward correct answers) and deceptive (toward incorrect answers) contexts. We also find that LLM persuaders significantly increased quiz takers' accuracy, leading to higher earnings, when steering quiz takers toward correct answers, and significantly decreased their accuracy, leading to lower earnings, when steering them toward incorrect answers. Overall, our findings suggest that AI's persuasion capabilities already exceed those of humans that have real-money bonuses tied to performance. Our findings of increasingly capable AI persuaders thus underscore the urgency of emerging alignment and governance frameworks.
StreamBridge: Turning Your Offline Video Large Language Model into a Proactive Streaming Assistant
May 08, 2025Abstract:We present StreamBridge, a simple yet effective framework that seamlessly transforms offline Video-LLMs into streaming-capable models. It addresses two fundamental challenges in adapting existing models into online scenarios: (1) limited capability for multi-turn real-time understanding, and (2) lack of proactive response mechanisms. Specifically, StreamBridge incorporates (1) a memory buffer combined with a round-decayed compression strategy, supporting long-context multi-turn interactions, and (2) a decoupled, lightweight activation model that can be effortlessly integrated into existing Video-LLMs, enabling continuous proactive responses. To further support StreamBridge, we construct Stream-IT, a large-scale dataset tailored for streaming video understanding, featuring interleaved video-text sequences and diverse instruction formats. Extensive experiments show that StreamBridge significantly improves the streaming understanding capabilities of offline Video-LLMs across various tasks, outperforming even proprietary models such as GPT-4o and Gemini 1.5 Pro. Simultaneously, it achieves competitive or superior performance on standard video understanding benchmarks.
TrojText: Test-time Invisible Textual Trojan Insertion
Mar 03, 2023



Abstract:In Natural Language Processing (NLP), intelligent neuron models can be susceptible to textual Trojan attacks. Such attacks occur when Trojan models behave normally for standard inputs but generate malicious output for inputs that contain a specific trigger. Syntactic-structure triggers, which are invisible, are becoming more popular for Trojan attacks because they are difficult to detect and defend against. However, these types of attacks require a large corpus of training data to generate poisoned samples with the necessary syntactic structures for Trojan insertion. Obtaining such data can be difficult for attackers, and the process of generating syntactic poisoned triggers and inserting Trojans can be time-consuming. This paper proposes a solution called TrojText, which aims to determine whether invisible textual Trojan attacks can be performed more efficiently and cost-effectively without training data. The proposed approach, called the Representation-Logit Trojan Insertion (RLI) algorithm, uses smaller sampled test data instead of large training data to achieve the desired attack. The paper also introduces two additional techniques, namely the accumulated gradient ranking (AGR) and Trojan Weights Pruning (TWP), to reduce the number of tuned parameters and the attack overhead. The TrojText approach was evaluated on three datasets (AG's News, SST-2, and OLID) using three NLP models (BERT, XLNet, and DeBERTa). The experiments demonstrated that the TrojText approach achieved a 98.35\% classification accuracy for test sentences in the target class on the BERT model for the AG's News dataset. The source code for TrojText is available at https://github.com/UCF-ML-Research/TrojText.
GTrans: Spatiotemporal Autoregressive Transformer with Graph Embeddings for Nowcasting Extreme Events
Jan 18, 2022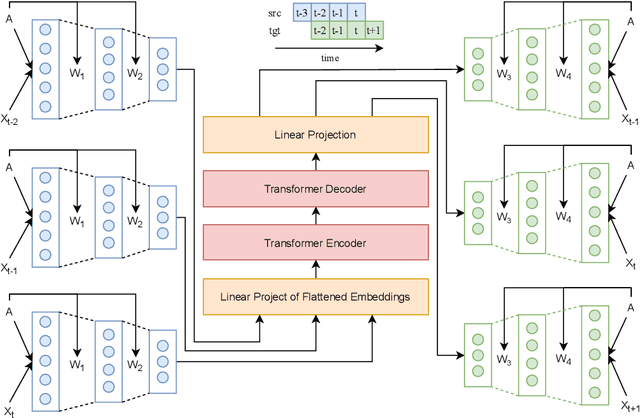
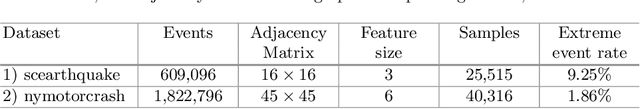

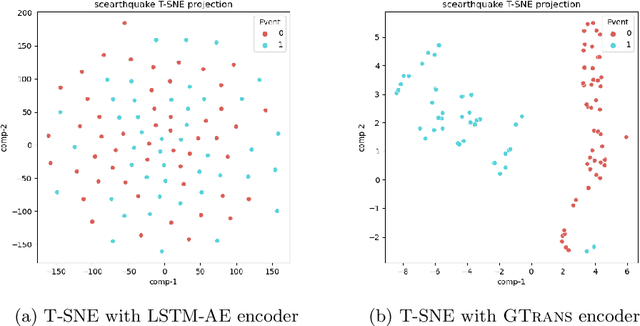
Abstract:Spatiotemporal time series nowcasting should preserve temporal and spatial dynamics in the sense that generated new sequences from models respect the covariance relationship from history. Conventional feature extractors are built with deep convolutional neural networks (CNN). However, CNN models have limits to image-like applications where data can be formed with high-dimensional arrays. In contrast, applications in social networks, road traffic, physics, and chemical property prediction where data features can be organized with nodes and edges of graphs. Transformer architecture is an emerging method for predictive models, bringing high accuracy and efficiency due to attention mechanism design. This paper proposes a spatiotemporal model, namely GTrans, that transforms data features into graph embeddings and predicts temporal dynamics with a transformer model. According to our experiments, we demonstrate that GTrans can model spatial and temporal dynamics and nowcasts extreme events for datasets. Furthermore, in all the experiments, GTrans can achieve the highest F1 and F2 scores in binary-class prediction tests than the baseline models.
Earthquake Nowcasting with Deep Learning
Dec 18, 2021



Abstract:We review previous approaches to nowcasting earthquakes and introduce new approaches based on deep learning using three distinct models based on recurrent neural networks and transformers. We discuss different choices for observables and measures presenting promising initial results for a region of Southern California from 1950-2020. Earthquake activity is predicted as a function of 0.1-degree spatial bins for time periods varying from two weeks to four years. The overall quality is measured by the Nash Sutcliffe Efficiency comparing the deviation of nowcast and observation with the variance over time in each spatial region. The software is available as open-source together with the preprocessed data from the USGS.
Top 3 in FG 2021 Families In the Wild Kinship Verification Challenge
Oct 27, 2021



Abstract:Kinship verification is the task of determining whether a parent-child, sibling, or grandparent-grandchild relationship exists between two people and is important in social media applications, forensic investigations, finding missing children, and reuniting families. We demonstrate high quality kinship verification by participating in the 2021 Recognizing Families in the Wild challenge which provides the largest publicly available dataset in the field. Our approach is among the top 3 winning entries in the competition. We ensemble models written by both human experts and OpenAI Codex. We make our models and code publicly available.
Inverse Kinematics and Dexterous Workspace Formulation for 2-Segment Continuum Robots with Inextensible Segments
Oct 05, 2021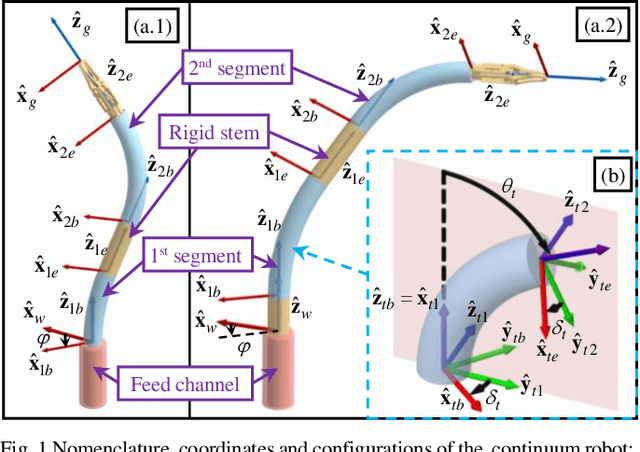
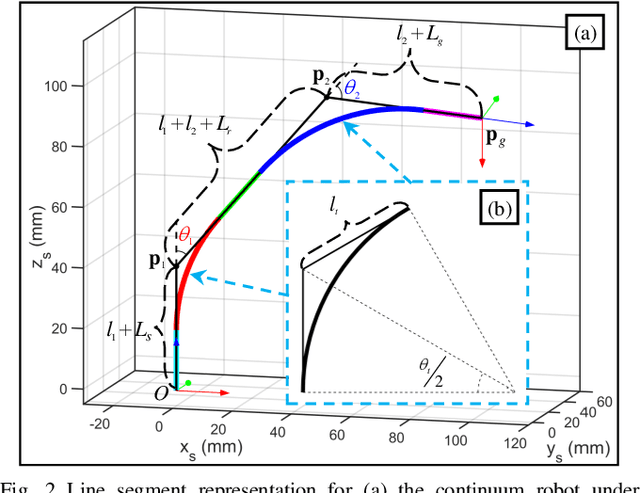
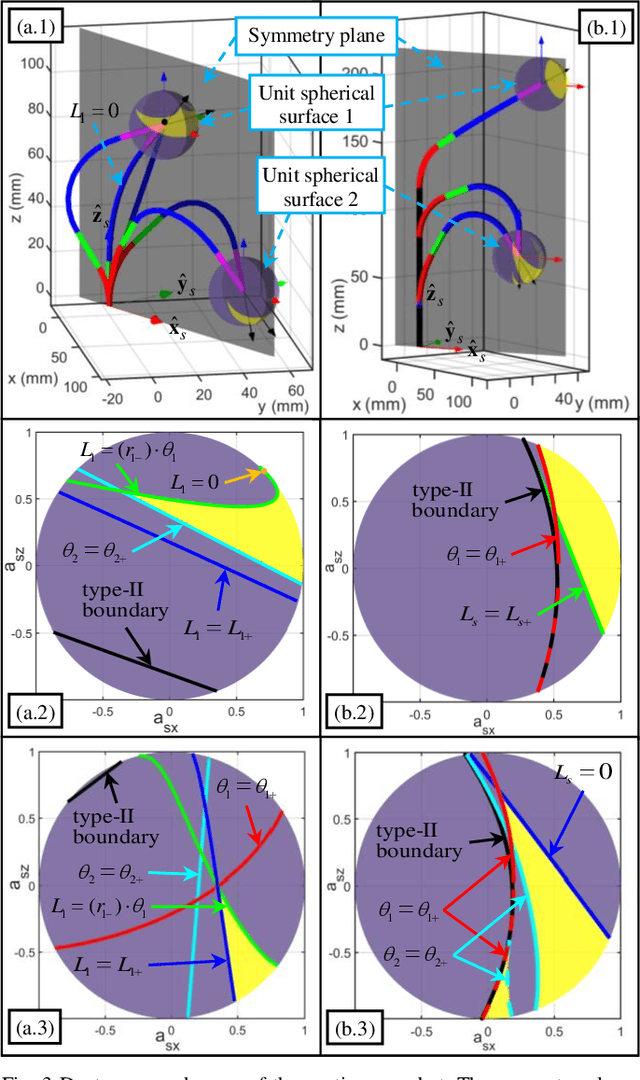
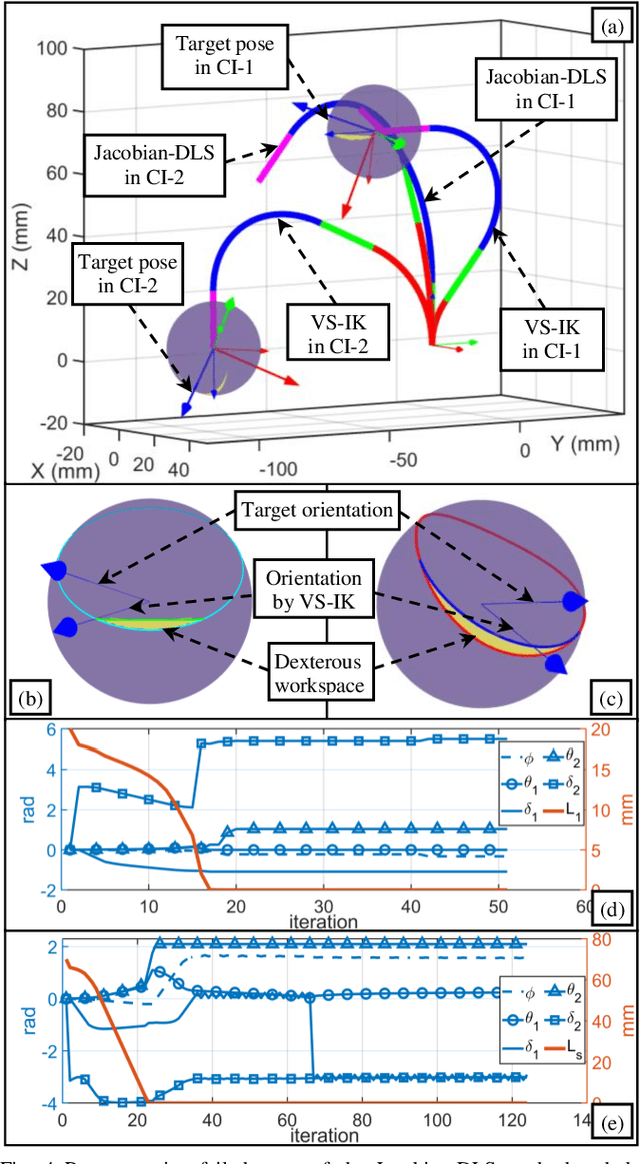
Abstract:The inverse kinematics (IK) problem of continuum robots has been investigated in depth in the past decades. Under the constant-curvature bending assumption, closed-form IK solution has been obtained for continuum robots with variable segment lengths. Attempting to close the gap towards a complete solution, this paper presents an efficient solution for the IK problem of 2-segment continuum robots with one or two inextensible segments (a.k.a, constant segment lengths). Via representing the robot's shape as piecewise line segments, the configuration variables are separated from the IK formulation such that solving a one-variable nonlinear equation leads to the solution of the entire IK problem. Furthermore, an in-depth investigation of the boundaries of the dexterous workspace of the end effector caused by the configuration variables limits as well as the angular velocity singularities of the continuum robots was established. This dexterous workspace formulation, which is derived for the first time to the best of the authors' knowledge, is particularly useful to find the closest orientation to a target pose when the target orientation is out of the dexterous workspace. In the comparative simulation studies between the proposed method and the Jacobian-based IK method involving 500,000 cases, the proposed variable separation method solved 100% of the IK problems with much higher computational efficiency.
Spatial Attention-based Non-reference Perceptual Quality Prediction Network for Omnidirectional Images
Mar 10, 2021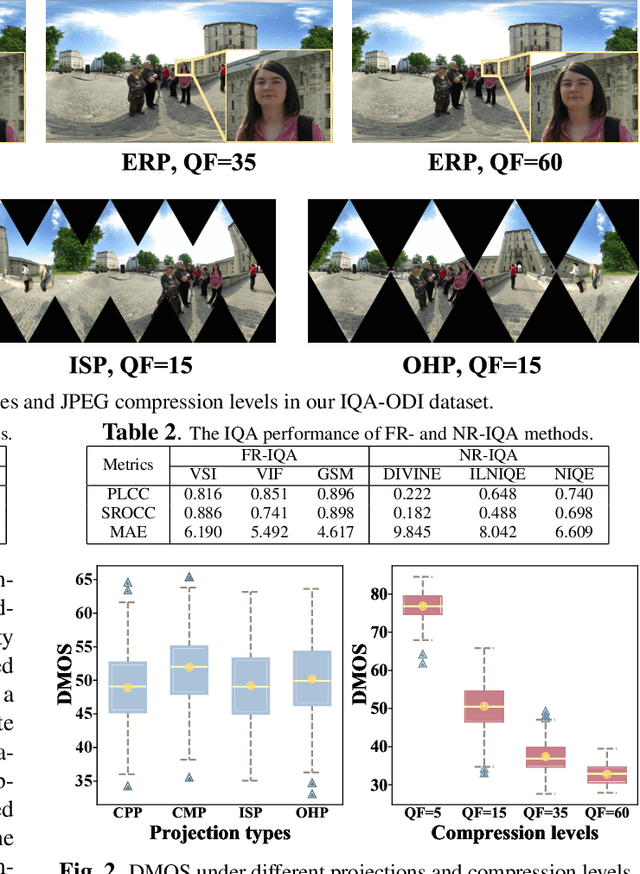
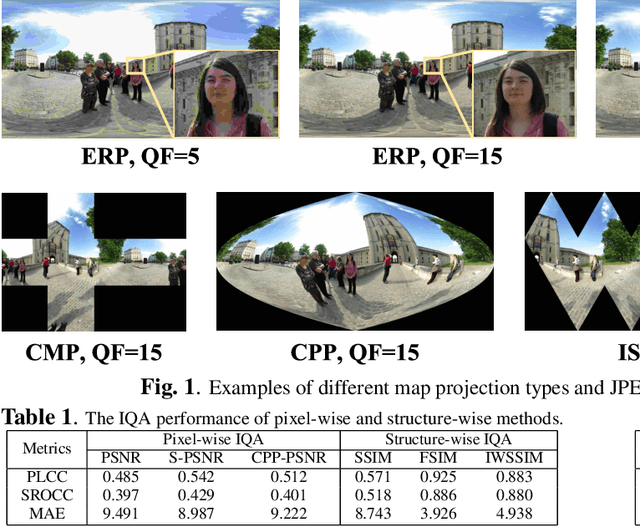
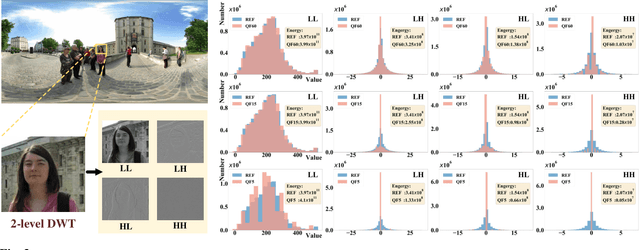
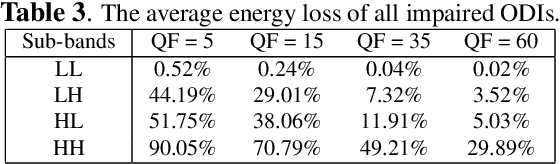
Abstract:Due to the strong correlation between visual attention and perceptual quality, many methods attempt to use human saliency information for image quality assessment. Although this mechanism can get good performance, the networks require human saliency labels, which is not easily accessible for omnidirectional images (ODI). To alleviate this issue, we propose a spatial attention-based perceptual quality prediction network for non-reference quality assessment on ODIs (SAP-net). To drive our SAP-net, we establish a large-scale IQA dataset of ODIs (IQA-ODI), which is composed of subjective scores of 200 subjects on 1,080 ODIs. In IQA-ODI, there are 120 high quality ODIs as reference, and 960 ODIs with impairments in both JPEG compression and map projection. Without any human saliency labels, our network can adaptively estimate human perceptual quality on impaired ODIs through a self-attention manner, which significantly promotes the prediction performance of quality scores. Moreover, our method greatly reduces the computational complexity in quality assessment task on ODIs. Extensive experiments validate that our network outperforms 9 state-of-the-art methods for quality assessment on ODIs. The dataset and code have been available on \url{ https://github.com/yanglixiaoshen/SAP-Net}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge