Bihui Chen
MedSAM2: Segment Anything in 3D Medical Images and Videos
Apr 04, 2025Abstract:Medical image and video segmentation is a critical task for precision medicine, which has witnessed considerable progress in developing task or modality-specific and generalist models for 2D images. However, there have been limited studies on building general-purpose models for 3D images and videos with comprehensive user studies. Here, we present MedSAM2, a promptable segmentation foundation model for 3D image and video segmentation. The model is developed by fine-tuning the Segment Anything Model 2 on a large medical dataset with over 455,000 3D image-mask pairs and 76,000 frames, outperforming previous models across a wide range of organs, lesions, and imaging modalities. Furthermore, we implement a human-in-the-loop pipeline to facilitate the creation of large-scale datasets resulting in, to the best of our knowledge, the most extensive user study to date, involving the annotation of 5,000 CT lesions, 3,984 liver MRI lesions, and 251,550 echocardiogram video frames, demonstrating that MedSAM2 can reduce manual costs by more than 85%. MedSAM2 is also integrated into widely used platforms with user-friendly interfaces for local and cloud deployment, making it a practical tool for supporting efficient, scalable, and high-quality segmentation in both research and healthcare environments.
Low-Rank Rescaled Vision Transformer Fine-Tuning: A Residual Design Approach
Mar 28, 2024



Abstract:Parameter-efficient fine-tuning for pre-trained Vision Transformers aims to adeptly tailor a model to downstream tasks by learning a minimal set of new adaptation parameters while preserving the frozen majority of pre-trained parameters. Striking a balance between retaining the generalizable representation capacity of the pre-trained model and acquiring task-specific features poses a key challenge. Currently, there is a lack of focus on guiding this delicate trade-off. In this study, we approach the problem from the perspective of Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) of pre-trained parameter matrices, providing insights into the tuning dynamics of existing methods. Building upon this understanding, we propose a Residual-based Low-Rank Rescaling (RLRR) fine-tuning strategy. This strategy not only enhances flexibility in parameter tuning but also ensures that new parameters do not deviate excessively from the pre-trained model through a residual design. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves competitive performance across various downstream image classification tasks, all while maintaining comparable new parameters. We believe this work takes a step forward in offering a unified perspective for interpreting existing methods and serves as motivation for the development of new approaches that move closer to effectively considering the crucial trade-off mentioned above. Our code is available at \href{https://github.com/zstarN70/RLRR.git}{https://github.com/zstarN70/RLRR.git}.
AdvFAS: A robust face anti-spoofing framework against adversarial examples
Aug 04, 2023Abstract:Ensuring the reliability of face recognition systems against presentation attacks necessitates the deployment of face anti-spoofing techniques. Despite considerable advancements in this domain, the ability of even the most state-of-the-art methods to defend against adversarial examples remains elusive. While several adversarial defense strategies have been proposed, they typically suffer from constrained practicability due to inevitable trade-offs between universality, effectiveness, and efficiency. To overcome these challenges, we thoroughly delve into the coupled relationship between adversarial detection and face anti-spoofing. Based on this, we propose a robust face anti-spoofing framework, namely AdvFAS, that leverages two coupled scores to accurately distinguish between correctly detected and wrongly detected face images. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework in a variety of settings, including different attacks, datasets, and backbones, meanwhile enjoying high accuracy on clean examples. Moreover, we successfully apply the proposed method to detect real-world adversarial examples.
A Survey of Face Recognition
Dec 26, 2022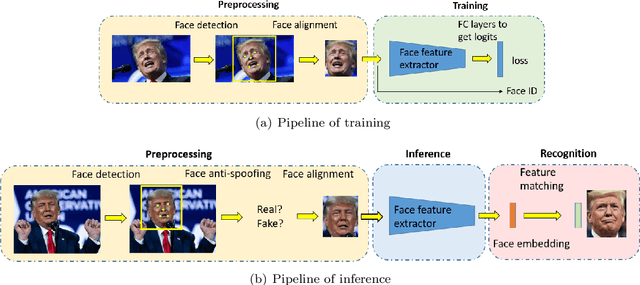
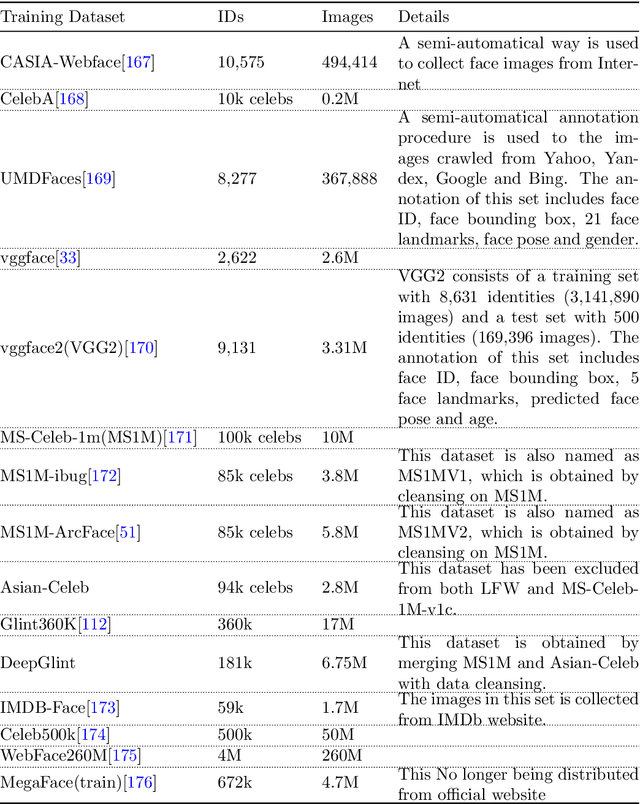
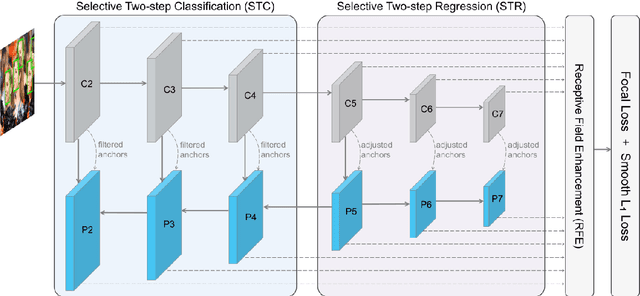
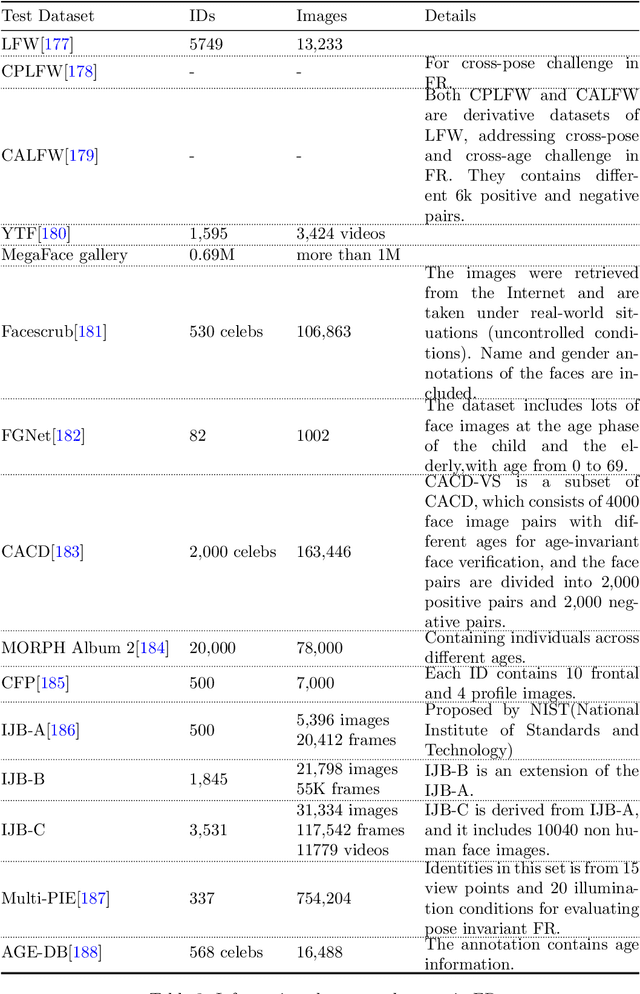
Abstract:Recent years witnessed the breakthrough of face recognition with deep convolutional neural networks. Dozens of papers in the field of FR are published every year. Some of them were applied in the industrial community and played an important role in human life such as device unlock, mobile payment, and so on. This paper provides an introduction to face recognition, including its history, pipeline, algorithms based on conventional manually designed features or deep learning, mainstream training, evaluation datasets, and related applications. We have analyzed and compared state-of-the-art works as many as possible, and also carefully designed a set of experiments to find the effect of backbone size and data distribution. This survey is a material of the tutorial named The Practical Face Recognition Technology in the Industrial World in the FG2023.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge