Betty van Aken
Surveying (Dis)Parities and Concerns of Compute Hungry NLP Research
Jun 29, 2023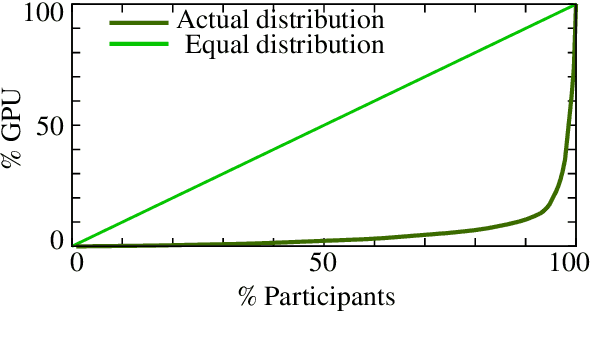

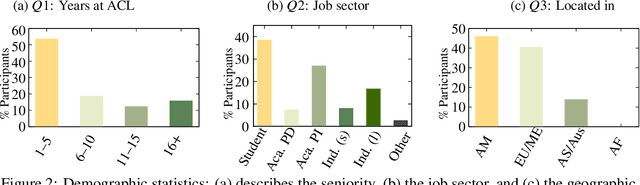
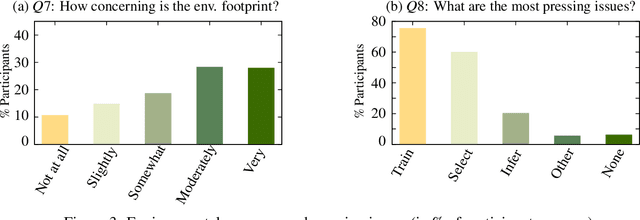
Abstract:Many recent improvements in NLP stem from the development and use of large pre-trained language models (PLMs) with billions of parameters. Large model sizes makes computational cost one of the main limiting factors for training and evaluating such models; and has raised severe concerns about the sustainability, reproducibility, and inclusiveness for researching PLMs. These concerns are often based on personal experiences and observations. However, there had not been any large-scale surveys that investigate them. In this work, we provide a first attempt to quantify these concerns regarding three topics, namely, environmental impact, equity, and impact on peer reviewing. By conducting a survey with 312 participants from the NLP community, we capture existing (dis)parities between different and within groups with respect to seniority, academia, and industry; and their impact on the peer reviewing process. For each topic, we provide an analysis and devise recommendations to mitigate found disparities, some of which already successfully implemented. Finally, we discuss additional concerns raised by many participants in free-text responses.
This Patient Looks Like That Patient: Prototypical Networks for Interpretable Diagnosis Prediction from Clinical Text
Oct 16, 2022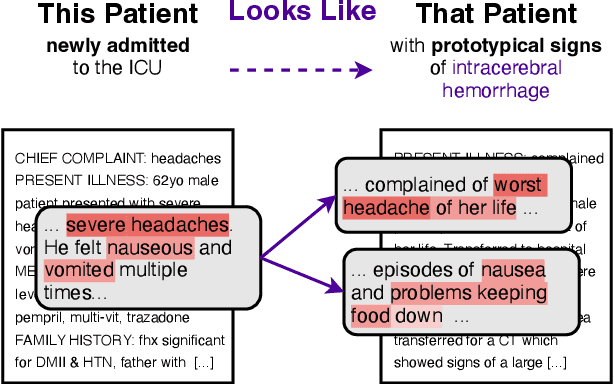
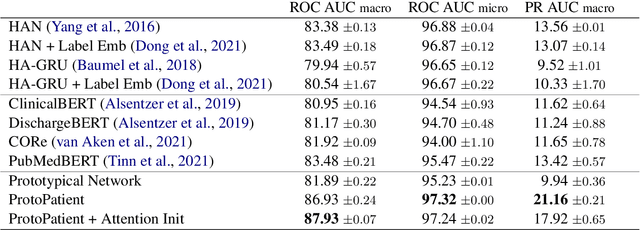
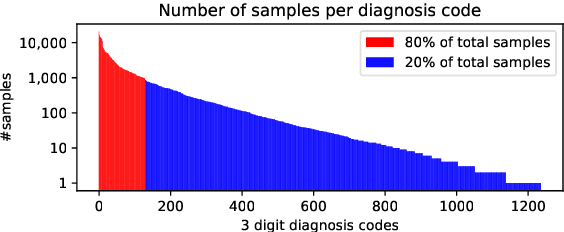
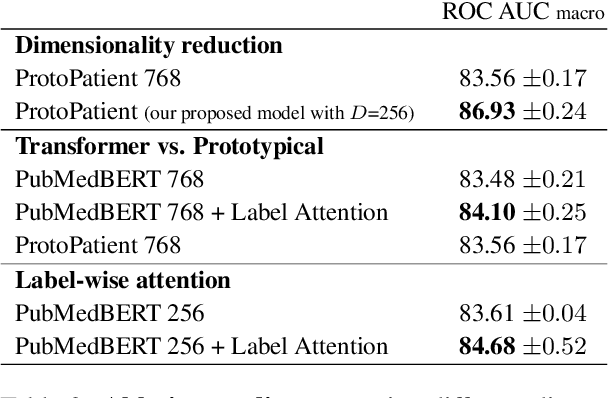
Abstract:The use of deep neural models for diagnosis prediction from clinical text has shown promising results. However, in clinical practice such models must not only be accurate, but provide doctors with interpretable and helpful results. We introduce ProtoPatient, a novel method based on prototypical networks and label-wise attention with both of these abilities. ProtoPatient makes predictions based on parts of the text that are similar to prototypical patients - providing justifications that doctors understand. We evaluate the model on two publicly available clinical datasets and show that it outperforms existing baselines. Quantitative and qualitative evaluations with medical doctors further demonstrate that the model provides valuable explanations for clinical decision support.
Cross-Lingual Knowledge Transfer for Clinical Phenotyping
Aug 03, 2022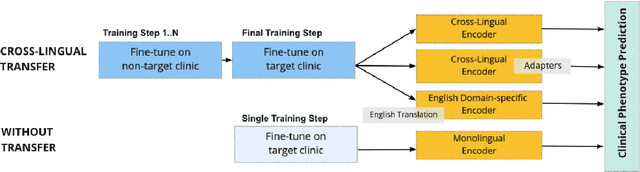
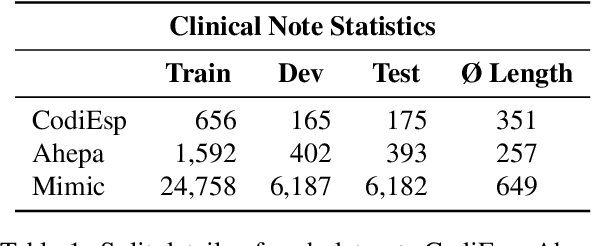

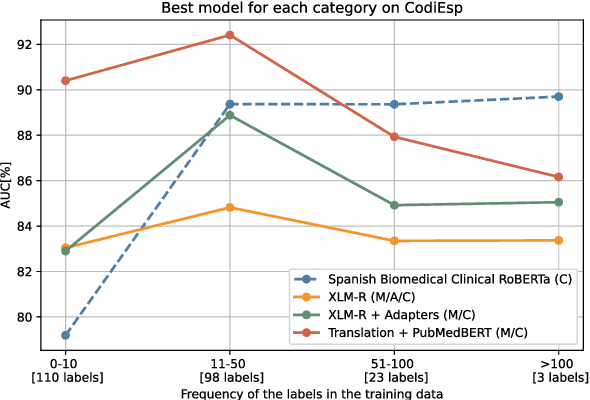
Abstract:Clinical phenotyping enables the automatic extraction of clinical conditions from patient records, which can be beneficial to doctors and clinics worldwide. However, current state-of-the-art models are mostly applicable to clinical notes written in English. We therefore investigate cross-lingual knowledge transfer strategies to execute this task for clinics that do not use the English language and have a small amount of in-domain data available. We evaluate these strategies for a Greek and a Spanish clinic leveraging clinical notes from different clinical domains such as cardiology, oncology and the ICU. Our results reveal two strategies that outperform the state-of-the-art: Translation-based methods in combination with domain-specific encoders and cross-lingual encoders plus adapters. We find that these strategies perform especially well for classifying rare phenotypes and we advise on which method to prefer in which situation. Our results show that using multilingual data overall improves clinical phenotyping models and can compensate for data sparseness.
* LREC 2022 submmision: January 2022
What Do You See in this Patient? Behavioral Testing of Clinical NLP Models
Nov 30, 2021



Abstract:Decision support systems based on clinical notes have the potential to improve patient care by pointing doctors towards overseen risks. Predicting a patient's outcome is an essential part of such systems, for which the use of deep neural networks has shown promising results. However, the patterns learned by these networks are mostly opaque and previous work revealed flaws regarding the reproduction of unintended biases. We thus introduce an extendable testing framework that evaluates the behavior of clinical outcome models regarding changes of the input. The framework helps to understand learned patterns and their influence on model decisions. In this work, we apply it to analyse the change in behavior with regard to the patient characteristics gender, age and ethnicity. Our evaluation of three current clinical NLP models demonstrates the concrete effects of these characteristics on the models' decisions. They show that model behavior varies drastically even when fine-tuned on the same data and that allegedly best-performing models have not always learned the most medically plausible patterns.
Clinical Outcome Prediction from Admission Notes using Self-Supervised Knowledge Integration
Feb 08, 2021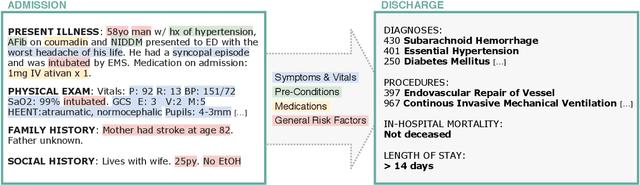
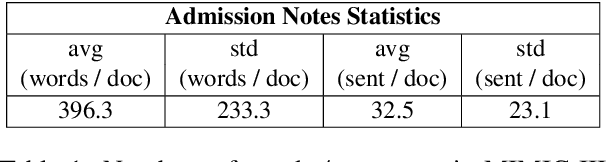
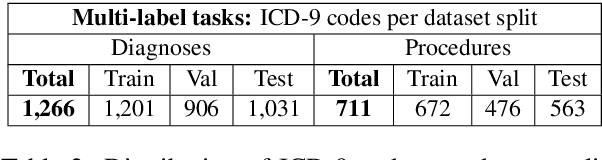
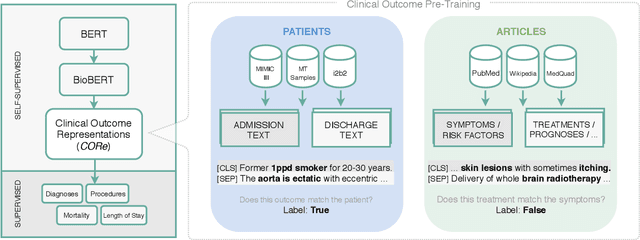
Abstract:Outcome prediction from clinical text can prevent doctors from overlooking possible risks and help hospitals to plan capacities. We simulate patients at admission time, when decision support can be especially valuable, and contribute a novel admission to discharge task with four common outcome prediction targets: Diagnoses at discharge, procedures performed, in-hospital mortality and length-of-stay prediction. The ideal system should infer outcomes based on symptoms, pre-conditions and risk factors of a patient. We evaluate the effectiveness of language models to handle this scenario and propose clinical outcome pre-training to integrate knowledge about patient outcomes from multiple public sources. We further present a simple method to incorporate ICD code hierarchy into the models. We show that our approach improves performance on the outcome tasks against several baselines. A detailed analysis reveals further strengths of the model, including transferability, but also weaknesses such as handling of vital values and inconsistencies in the underlying data.
VisBERT: Hidden-State Visualizations for Transformers
Nov 09, 2020

Abstract:Explainability and interpretability are two important concepts, the absence of which can and should impede the application of well-performing neural networks to real-world problems. At the same time, they are difficult to incorporate into the large, black-box models that achieve state-of-the-art results in a multitude of NLP tasks. Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) is one such black-box model. It has become a staple architecture to solve many different NLP tasks and has inspired a number of related Transformer models. Understanding how these models draw conclusions is crucial for both their improvement and application. We contribute to this challenge by presenting VisBERT, a tool for visualizing the contextual token representations within BERT for the task of (multi-hop) Question Answering. Instead of analyzing attention weights, we focus on the hidden states resulting from each encoder block within the BERT model. This way we can observe how the semantic representations are transformed throughout the layers of the model. VisBERT enables users to get insights about the model's internal state and to explore its inference steps or potential shortcomings. The tool allows us to identify distinct phases in BERT's transformations that are similar to a traditional NLP pipeline and offer insights during failed predictions.
* Published in WWW '20: Companion Proceedings of the Web Conference 2020
Learning Contextualized Document Representations for Healthcare Answer Retrieval
Feb 03, 2020
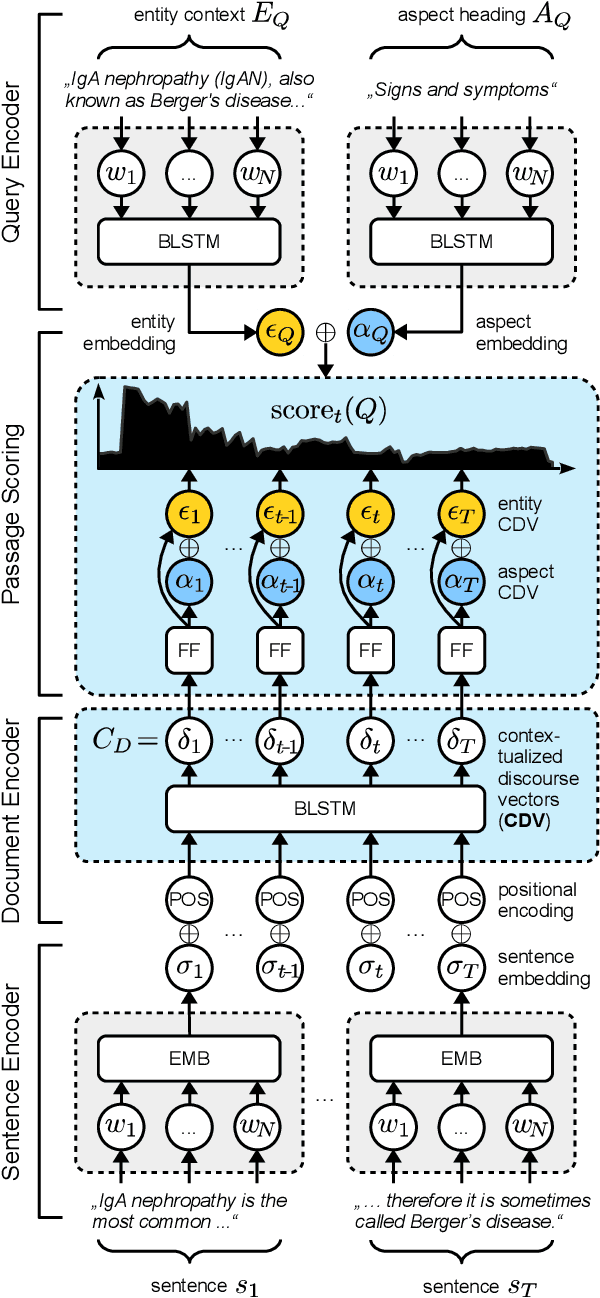
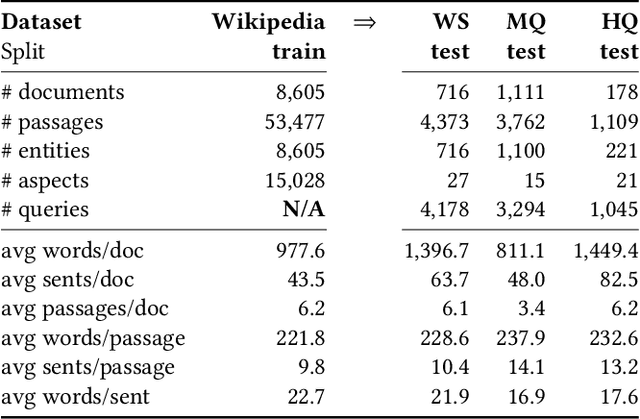
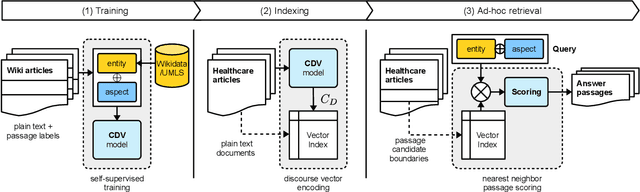
Abstract:We present Contextual Discourse Vectors (CDV), a distributed document representation for efficient answer retrieval from long healthcare documents. Our approach is based on structured query tuples of entities and aspects from free text and medical taxonomies. Our model leverages a dual encoder architecture with hierarchical LSTM layers and multi-task training to encode the position of clinical entities and aspects alongside the document discourse. We use our continuous representations to resolve queries with short latency using approximate nearest neighbor search on sentence level. We apply the CDV model for retrieving coherent answer passages from nine English public health resources from the Web, addressing both patients and medical professionals. Because there is no end-to-end training data available for all application scenarios, we train our model with self-supervised data from Wikipedia. We show that our generalized model significantly outperforms several state-of-the-art baselines for healthcare passage ranking and is able to adapt to heterogeneous domains without additional fine-tuning.
How Does BERT Answer Questions? A Layer-Wise Analysis of Transformer Representations
Sep 11, 2019



Abstract:Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) reach state-of-the-art results in a variety of Natural Language Processing tasks. However, understanding of their internal functioning is still insufficient and unsatisfactory. In order to better understand BERT and other Transformer-based models, we present a layer-wise analysis of BERT's hidden states. Unlike previous research, which mainly focuses on explaining Transformer models by their attention weights, we argue that hidden states contain equally valuable information. Specifically, our analysis focuses on models fine-tuned on the task of Question Answering (QA) as an example of a complex downstream task. We inspect how QA models transform token vectors in order to find the correct answer. To this end, we apply a set of general and QA-specific probing tasks that reveal the information stored in each representation layer. Our qualitative analysis of hidden state visualizations provides additional insights into BERT's reasoning process. Our results show that the transformations within BERT go through phases that are related to traditional pipeline tasks. The system can therefore implicitly incorporate task-specific information into its token representations. Furthermore, our analysis reveals that fine-tuning has little impact on the models' semantic abilities and that prediction errors can be recognized in the vector representations of even early layers.
Challenges for Toxic Comment Classification: An In-Depth Error Analysis
Sep 20, 2018



Abstract:Toxic comment classification has become an active research field with many recently proposed approaches. However, while these approaches address some of the task's challenges others still remain unsolved and directions for further research are needed. To this end, we compare different deep learning and shallow approaches on a new, large comment dataset and propose an ensemble that outperforms all individual models. Further, we validate our findings on a second dataset. The results of the ensemble enable us to perform an extensive error analysis, which reveals open challenges for state-of-the-art methods and directions towards pending future research. These challenges include missing paradigmatic context and inconsistent dataset labels.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge