Yuki Arase
DiVA: Fine-grained Factuality Verification with Agentic-Discriminative Verifier
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Despite the significant advancements of Large Language Models (LLMs), their factuality remains a critical challenge, fueling growing interest in factuality verification. Existing research on factuality verification primarily conducts binary judgments (e.g., correct or incorrect), which fails to distinguish varying degrees of error severity. This limits its utility for applications such as fine-grained evaluation and preference optimization. To bridge this gap, we propose the Agentic Discriminative Verifier (DiVA), a hybrid framework that synergizes the agentic search capabilities of generative models with the precise scoring aptitude of discriminative models. We also construct a new benchmark, FGVeriBench, as a robust testbed for fine-grained factuality verification. Experimental results on FGVeriBench demonstrate that our DiVA significantly outperforms existing methods on factuality verification for both general and multi-hop questions.
Reasoning Model Is Superior LLM-Judge, Yet Suffers from Biases
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:This paper presents the first systematic comparison investigating whether Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) are superior judge to non-reasoning LLMs. Our empirical analysis yields four key findings: 1) LRMs outperform non-reasoning LLMs in terms of judgment accuracy, particularly on reasoning-intensive tasks; 2) LRMs demonstrate superior instruction-following capabilities in evaluation contexts; 3) LRMs exhibit enhanced robustness against adversarial attacks targeting judgment tasks; 4) However, LRMs still exhibit strong biases in superficial quality. To improve the robustness against biases, we propose PlanJudge, an evaluation strategy that prompts the model to generate an explicit evaluation plan before execution. Despite its simplicity, our experiments demonstrate that PlanJudge significantly mitigates biases in both LRMs and standard LLMs.
Adaptive LoRA Merge with Parameter Pruning for Low-Resource Generation
May 30, 2025Abstract:This study proposes a simple yet effective LoRA merge method to achieve LLM adaptation for low-resource language generation tasks. The LoRA merge technique, which integrates multiple LoRA modules trained on different tasks, has gained attention as an effective and efficient approach for adapting LLMs to target tasks. However, previous methods are limited in adaptability as they keep the LoRA parameters frozen. Additionally, the low-resource problem has been out of their scope. We propose a LoRA merge method that updates and prunes LoRA parameters through fine-tuning with minimal target task data, which allows finer-grained adjustments of LoRA parameters and enhancement of task adaptability. Extensive experiments have been conducted taking summarization as a benchmark task. Our datasets cover various domains and multiple languages of English and Japanese. The results confirm that the proposed method achieves significant and consistent improvements in task adaptability over the previous methods.
Hallucination Detection using Multi-View Attention Features
Apr 06, 2025Abstract:This study tackles token-level hallucination detection in outputs of large language models. Previous studies revealed that attention exhibits irregular patterns when hallucination occurs. Inspired by this, we extract features from the attention matrix that provide complementary views of (a) the average attention each token receives, which helps identify whether certain tokens are overly influential or ignored, (b) the diversity of attention each token receives, which reveals whether attention is biased toward specific subsets, and (c) the diversity of tokens a token attends to during generation, which indicates whether the model references a narrow or broad range of information. These features are input to a Transformer-based classifier to conduct token-level classification to identify hallucinated spans. Experimental results indicate that the proposed method outperforms strong baselines on hallucination detection with longer input contexts, i.e., data-to-text and summarization tasks.
Aligning Sentence Simplification with ESL Learner's Proficiency for Language Acquisition
Feb 17, 2025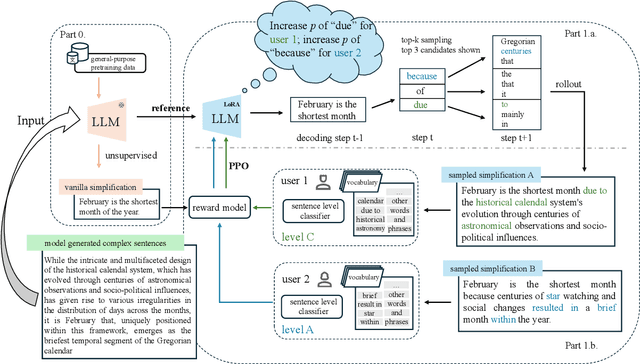
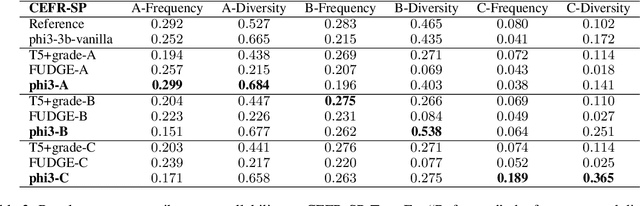
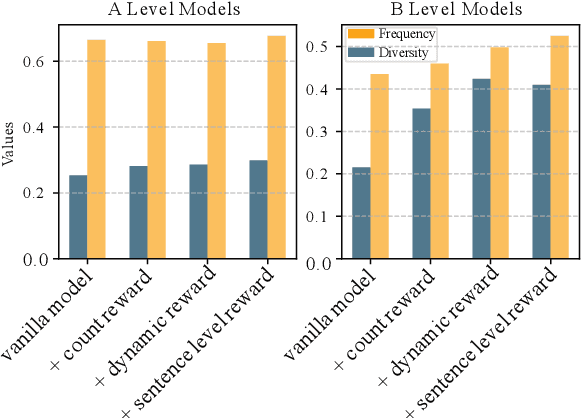
Abstract:Text simplification is crucial for improving accessibility and comprehension for English as a Second Language (ESL) learners. This study goes a step further and aims to facilitate ESL learners' language acquisition by simplification. Specifically, we propose simplifying complex sentences to appropriate levels for learners while also increasing vocabulary coverage of the target level in the simplifications. We achieve this without a parallel corpus by conducting reinforcement learning on a large language model. Our method employs token-level and sentence-level rewards, and iteratively trains the model on its self-generated outputs to guide the model to search for simplification hypotheses that satisfy the target attributes. Experiment results on CEFR-SP and TurkCorpus datasets show that the proposed method can effectively increase the frequency and diversity of vocabulary of the target level by more than $20\%$ compared to baseline models, while maintaining high simplification quality.
Edit-Constrained Decoding for Sentence Simplification
Sep 28, 2024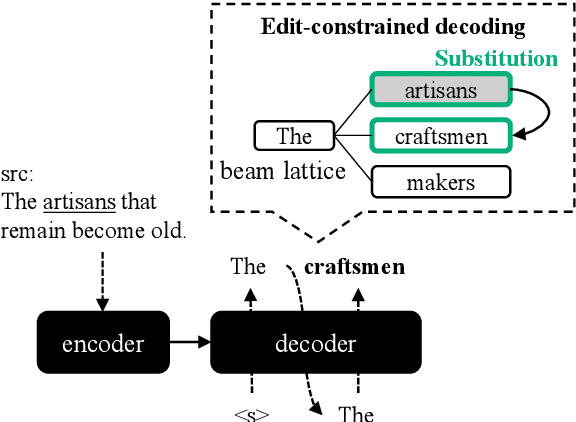
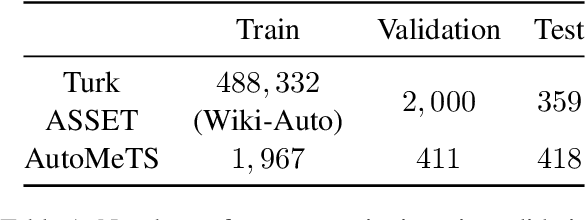
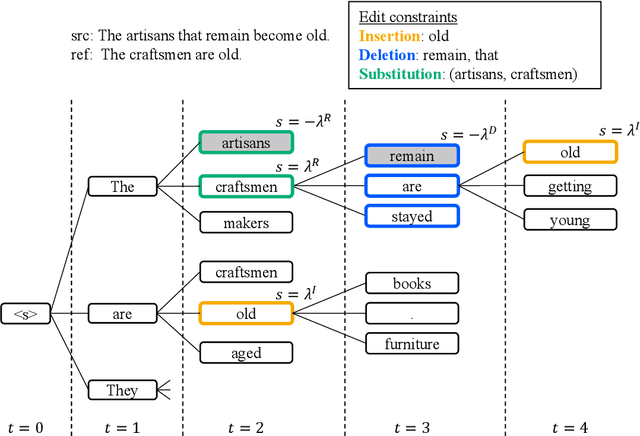
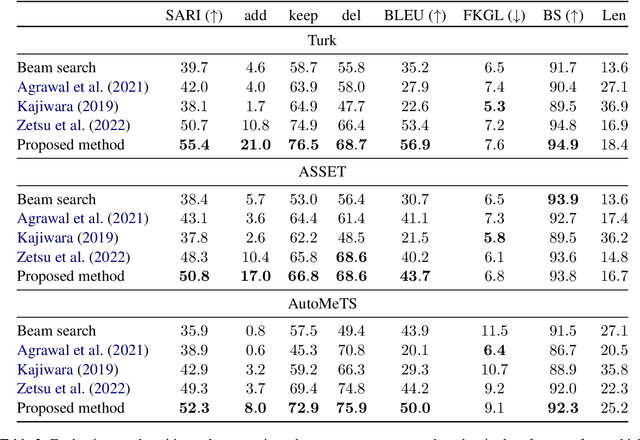
Abstract:We propose edit operation based lexically constrained decoding for sentence simplification. In sentence simplification, lexical paraphrasing is one of the primary procedures for rewriting complex sentences into simpler correspondences. While previous studies have confirmed the efficacy of lexically constrained decoding on this task, their constraints can be loose and may lead to sub-optimal generation. We address this problem by designing constraints that replicate the edit operations conducted in simplification and defining stricter satisfaction conditions. Our experiments indicate that the proposed method consistently outperforms the previous studies on three English simplification corpora commonly used in this task.
Distilling Monolingual and Crosslingual Word-in-Context Representations
Sep 13, 2024Abstract:In this study, we propose a method that distils representations of word meaning in context from a pre-trained masked language model in both monolingual and crosslingual settings. Word representations are the basis for context-aware lexical semantics and unsupervised semantic textual similarity (STS) estimation. Different from existing approaches, our method does not require human-annotated corpora nor updates of the parameters of the pre-trained model. The latter feature is appealing for practical scenarios where the off-the-shelf pre-trained model is a common asset among different applications. Specifically, our method learns to combine the outputs of different hidden layers of the pre-trained model using self-attention. Our auto-encoder based training only requires an automatically generated corpus. To evaluate the performance of the proposed approach, we performed extensive experiments using various benchmark tasks. The results on the monolingual tasks confirmed that our representations exhibited a competitive performance compared to that of the previous study for the context-aware lexical semantic tasks and outperformed it for STS estimation. The results of the crosslingual tasks revealed that the proposed method largely improved crosslingual word representations of multilingual pre-trained models.
An In-depth Evaluation of GPT-4 in Sentence Simplification with Error-based Human Assessment
Mar 08, 2024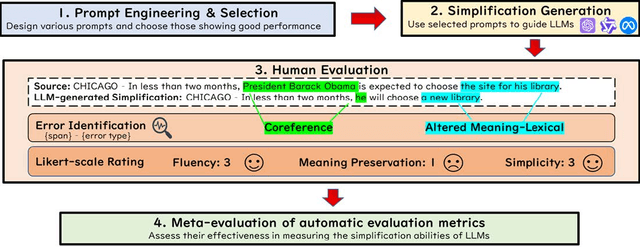

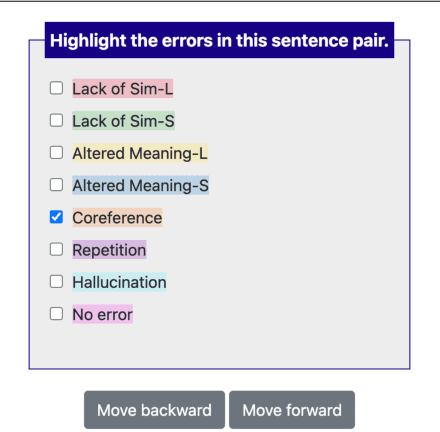
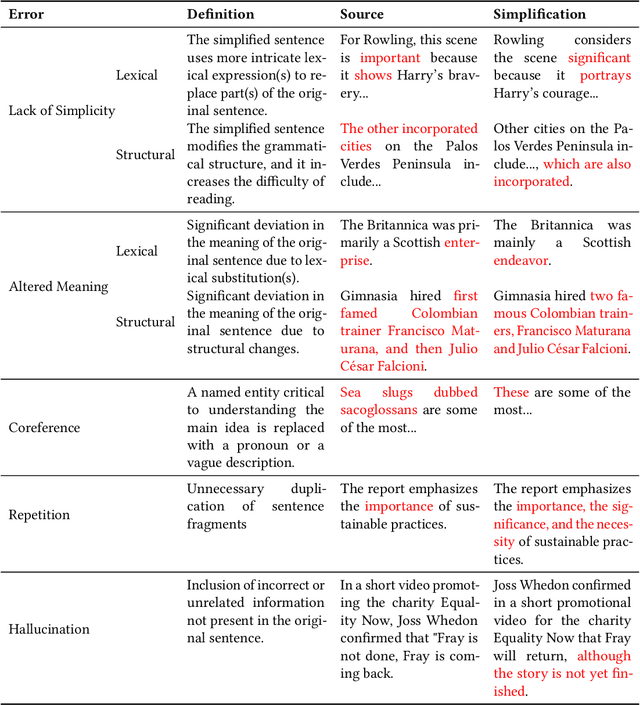
Abstract:Sentence simplification, which rewrites a sentence to be easier to read and understand, is a promising technique to help people with various reading difficulties. With the rise of advanced large language models (LLMs), evaluating their performance in sentence simplification has become imperative. Recent studies have used both automatic metrics and human evaluations to assess the simplification abilities of LLMs. However, the suitability of existing evaluation methodologies for LLMs remains in question. First, the suitability of current automatic metrics on LLMs' simplification evaluation is still uncertain. Second, current human evaluation approaches in sentence simplification often fall into two extremes: they are either too superficial, failing to offer a clear understanding of the models' performance, or overly detailed, making the annotation process complex and prone to inconsistency, which in turn affects the evaluation's reliability. To address these problems, this study provides in-depth insights into LLMs' performance while ensuring the reliability of the evaluation. We design an error-based human annotation framework to assess the GPT-4's simplification capabilities. Results show that GPT-4 generally generates fewer erroneous simplification outputs compared to the current state-of-the-art. However, LLMs have their limitations, as seen in GPT-4's struggles with lexical paraphrasing. Furthermore, we conduct meta-evaluations on widely used automatic metrics using our human annotations. We find that while these metrics are effective for significant quality differences, they lack sufficient sensitivity to assess the overall high-quality simplification by GPT-4.
Surveying (Dis)Parities and Concerns of Compute Hungry NLP Research
Jun 29, 2023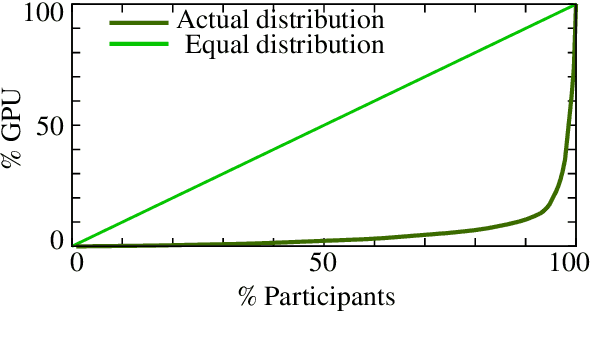

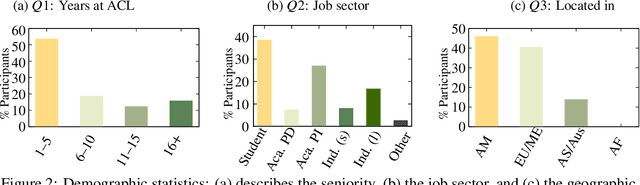
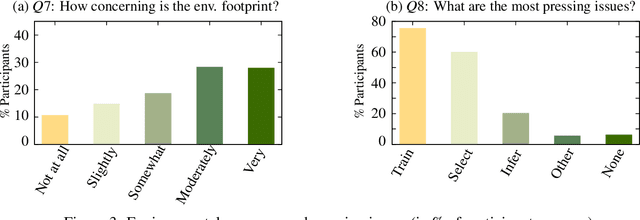
Abstract:Many recent improvements in NLP stem from the development and use of large pre-trained language models (PLMs) with billions of parameters. Large model sizes makes computational cost one of the main limiting factors for training and evaluating such models; and has raised severe concerns about the sustainability, reproducibility, and inclusiveness for researching PLMs. These concerns are often based on personal experiences and observations. However, there had not been any large-scale surveys that investigate them. In this work, we provide a first attempt to quantify these concerns regarding three topics, namely, environmental impact, equity, and impact on peer reviewing. By conducting a survey with 312 participants from the NLP community, we capture existing (dis)parities between different and within groups with respect to seniority, academia, and industry; and their impact on the peer reviewing process. For each topic, we provide an analysis and devise recommendations to mitigate found disparities, some of which already successfully implemented. Finally, we discuss additional concerns raised by many participants in free-text responses.
Unbalanced Optimal Transport for Unbalanced Word Alignment
Jun 07, 2023Abstract:Monolingual word alignment is crucial to model semantic interactions between sentences. In particular, null alignment, a phenomenon in which words have no corresponding counterparts, is pervasive and critical in handling semantically divergent sentences. Identification of null alignment is useful on its own to reason about the semantic similarity of sentences by indicating there exists information inequality. To achieve unbalanced word alignment that values both alignment and null alignment, this study shows that the family of optimal transport (OT), i.e., balanced, partial, and unbalanced OT, are natural and powerful approaches even without tailor-made techniques. Our extensive experiments covering unsupervised and supervised settings indicate that our generic OT-based alignment methods are competitive against the state-of-the-arts specially designed for word alignment, remarkably on challenging datasets with high null alignment frequencies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge