Ashkan Pakzad
Towards order of magnitude X-ray dose reduction in breast cancer imaging using phase contrast and deep denoising
May 09, 2025Abstract:Breast cancer is the most frequently diagnosed human cancer in the United States at present. Early detection is crucial for its successful treatment. X-ray mammography and digital breast tomosynthesis are currently the main methods for breast cancer screening. However, both have known limitations in terms of their sensitivity and specificity to breast cancers, while also frequently causing patient discomfort due to the requirement for breast compression. Breast computed tomography is a promising alternative, however, to obtain high-quality images, the X-ray dose needs to be sufficiently high. As the breast is highly radiosensitive, dose reduction is particularly important. Phase-contrast computed tomography (PCT) has been shown to produce higher-quality images at lower doses and has no need for breast compression. It is demonstrated in the present study that, when imaging full fresh mastectomy samples with PCT, deep learning-based image denoising can further reduce the radiation dose by a factor of 16 or more, without any loss of image quality. The image quality has been assessed both in terms of objective metrics, such as spatial resolution and contrast-to-noise ratio, as well as in an observer study by experienced medical imaging specialists and radiologists. This work was carried out in preparation for live patient PCT breast cancer imaging, initially at specialized synchrotron facilities.
A data-centric deep learning approach to airway segmentation
Jul 29, 2023Abstract:The morphology and distribution of airway tree abnormalities enables diagnosis and disease characterisation across a variety of chronic respiratory conditions. In this regard, airway segmentation plays a critical role in the production of the outline of the entire airway tree to enable estimation of disease extent and severity. In this study, we propose a data-centric deep learning technique to segment the airway tree. The proposed technique utilises interpolation and image split to improve data usefulness and quality. Then, an ensemble learning strategy is implemented to aggregate the segmented airway trees at different scales. In terms of segmentation performance (dice similarity coefficient), our method outperforms the baseline model by 2.5% on average when a combined loss is used. Further, our proposed technique has a low GPU usage and high flexibility enabling it to be deployed on any 2D deep learning model.
Efficient automatic segmentation for multi-level pulmonary arteries: The PARSE challenge
Apr 07, 2023



Abstract:Efficient automatic segmentation of multi-level (i.e. main and branch) pulmonary arteries (PA) in CTPA images plays a significant role in clinical applications. However, most existing methods concentrate only on main PA or branch PA segmentation separately and ignore segmentation efficiency. Besides, there is no public large-scale dataset focused on PA segmentation, which makes it highly challenging to compare the different methods. To benchmark multi-level PA segmentation algorithms, we organized the first \textbf{P}ulmonary \textbf{AR}tery \textbf{SE}gmentation (PARSE) challenge. On the one hand, we focus on both the main PA and the branch PA segmentation. On the other hand, for better clinical application, we assign the same score weight to segmentation efficiency (mainly running time and GPU memory consumption during inference) while ensuring PA segmentation accuracy. We present a summary of the top algorithms and offer some suggestions for efficient and accurate multi-level PA automatic segmentation. We provide the PARSE challenge as open-access for the community to benchmark future algorithm developments at \url{https://parse2022.grand-challenge.org/Parse2022/}.
Multi-site, Multi-domain Airway Tree Modeling : A Public Benchmark for Pulmonary Airway Segmentation
Mar 10, 2023



Abstract:Open international challenges are becoming the de facto standard for assessing computer vision and image analysis algorithms. In recent years, new methods have extended the reach of pulmonary airway segmentation that is closer to the limit of image resolution. Since EXACT'09 pulmonary airway segmentation, limited effort has been directed to quantitative comparison of newly emerged algorithms driven by the maturity of deep learning based approaches and clinical drive for resolving finer details of distal airways for early intervention of pulmonary diseases. Thus far, public annotated datasets are extremely limited, hindering the development of data-driven methods and detailed performance evaluation of new algorithms. To provide a benchmark for the medical imaging community, we organized the Multi-site, Multi-domain Airway Tree Modeling (ATM'22), which was held as an official challenge event during the MICCAI 2022 conference. ATM'22 provides large-scale CT scans with detailed pulmonary airway annotation, including 500 CT scans (300 for training, 50 for validation, and 150 for testing). The dataset was collected from different sites and it further included a portion of noisy COVID-19 CTs with ground-glass opacity and consolidation. Twenty-three teams participated in the entire phase of the challenge and the algorithms for the top ten teams are reviewed in this paper. Quantitative and qualitative results revealed that deep learning models embedded with the topological continuity enhancement achieved superior performance in general. ATM'22 challenge holds as an open-call design, the training data and the gold standard evaluation are available upon successful registration via its homepage.
Airway measurement by refinement of synthetic images improves mortality prediction in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Aug 30, 2022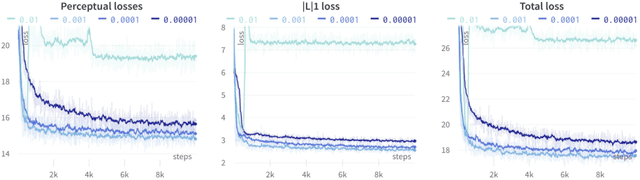
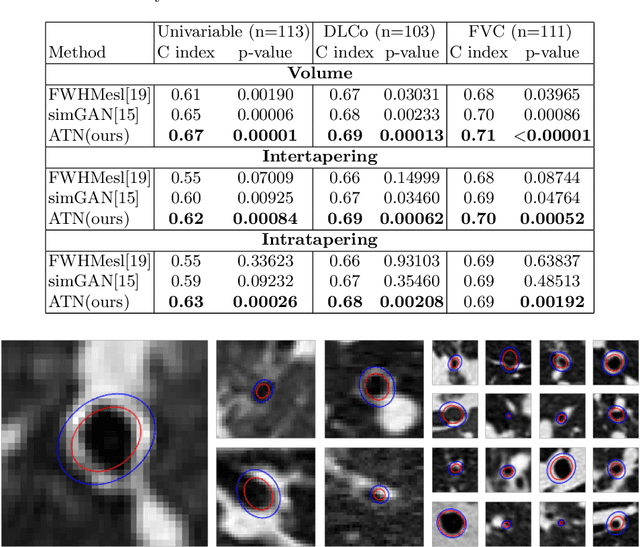
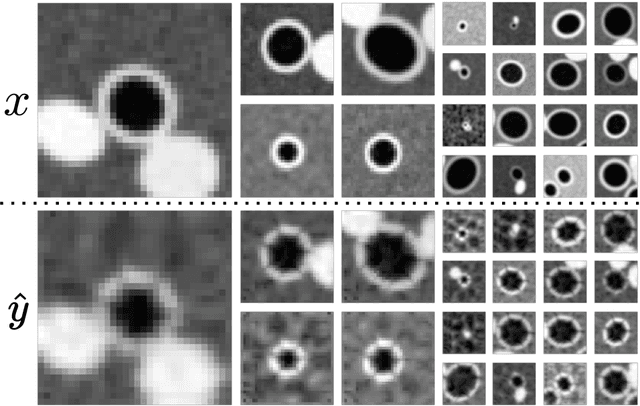
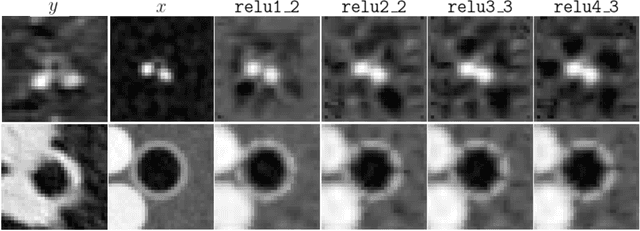
Abstract:Several chronic lung diseases, like idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) are characterised by abnormal dilatation of the airways. Quantification of airway features on computed tomography (CT) can help characterise disease progression. Physics based airway measurement algorithms have been developed, but have met with limited success in part due to the sheer diversity of airway morphology seen in clinical practice. Supervised learning methods are also not feasible due to the high cost of obtaining precise airway annotations. We propose synthesising airways by style transfer using perceptual losses to train our model, Airway Transfer Network (ATN). We compare our ATN model with a state-of-the-art GAN-based network (simGAN) using a) qualitative assessment; b) assessment of the ability of ATN and simGAN based CT airway metrics to predict mortality in a population of 113 patients with IPF. ATN was shown to be quicker and easier to train than simGAN. ATN-based airway measurements were also found to be consistently stronger predictors of mortality than simGAN-derived airway metrics on IPF CTs. Airway synthesis by a transformation network that refines synthetic data using perceptual losses is a realistic alternative to GAN-based methods for clinical CT analyses of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Our source code can be found at https://github.com/ashkanpakzad/ATN that is compatible with the existing open-source airway analysis framework, AirQuant.
Evaluation of automated airway morphological quantification for assessing fibrosing lung disease
Nov 19, 2021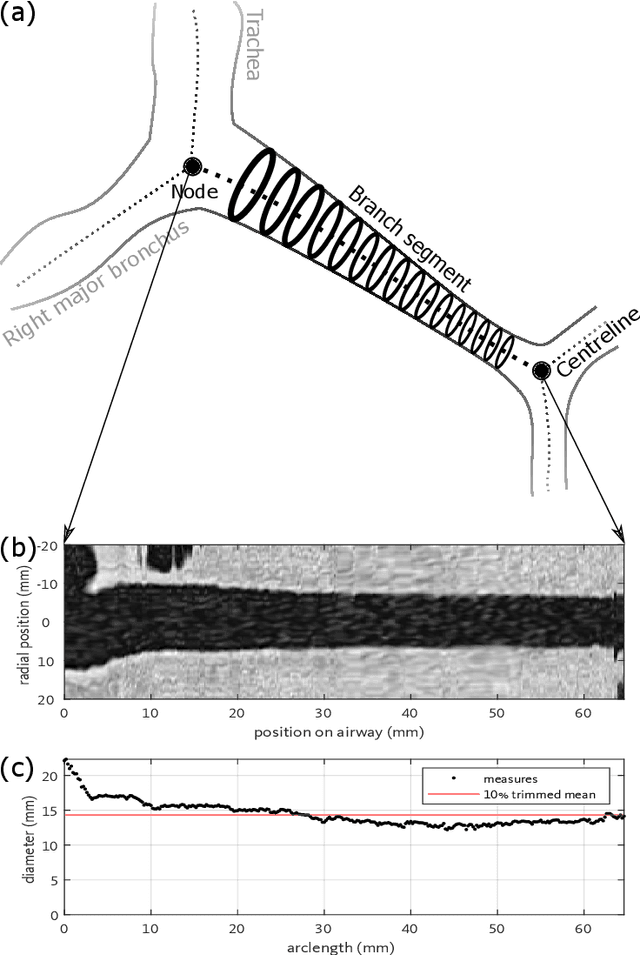
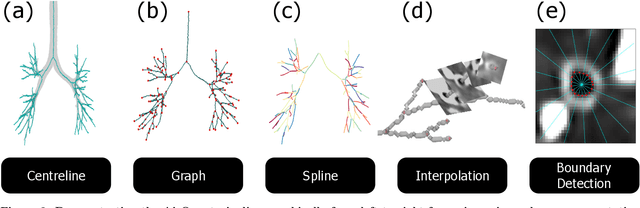
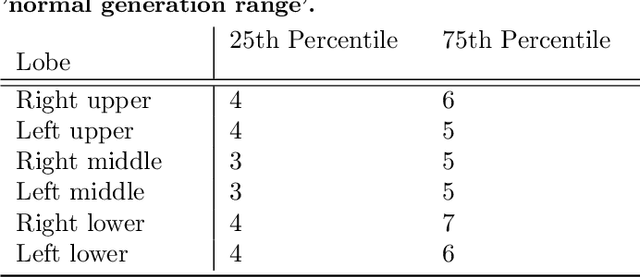
Abstract:Abnormal airway dilatation, termed traction bronchiectasis, is a typical feature of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). Volumetric computed tomography (CT) imaging captures the loss of normal airway tapering in IPF. We postulated that automated quantification of airway abnormalities could provide estimates of IPF disease extent and severity. We propose AirQuant, an automated computational pipeline that systematically parcellates the airway tree into its lobes and generational branches from a deep learning based airway segmentation, deriving airway structural measures from chest CT. Importantly, AirQuant prevents the occurrence of spurious airway branches by thick wave propagation and removes loops in the airway-tree by graph search, overcoming limitations of existing airway skeletonisation algorithms. Tapering between airway segments (intertapering) and airway tortuosity computed by AirQuant were compared between 14 healthy participants and 14 IPF patients. Airway intertapering was significantly reduced in IPF patients, and airway tortuosity was significantly increased when compared to healthy controls. Differences were most marked in the lower lobes, conforming to the typical distribution of IPF-related damage. AirQuant is an open-source pipeline that avoids limitations of existing airway quantification algorithms and has clinical interpretability. Automated airway measurements may have potential as novel imaging biomarkers of IPF severity and disease extent.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge