Yangqian Wu
CDFI: Cross Domain Feature Interaction for Robust Bronchi Lumen Detection
Apr 18, 2023



Abstract:Endobronchial intervention is increasingly used as a minimally invasive means for the treatment of pulmonary diseases. In order to reduce the difficulty of manipulation in complex airway networks, robust lumen detection is essential for intraoperative guidance. However, these methods are sensitive to visual artifacts which are inevitable during the surgery. In this work, a cross domain feature interaction (CDFI) network is proposed to extract the structural features of lumens, as well as to provide artifact cues to characterize the visual features. To effectively extract the structural and artifact features, the Quadruple Feature Constraints (QFC) module is designed to constrain the intrinsic connections of samples with various imaging-quality. Furthermore, we design a Guided Feature Fusion (GFF) module to supervise the model for adaptive feature fusion based on different types of artifacts. Results show that the features extracted by the proposed method can preserve the structural information of lumen in the presence of large visual variations, bringing much-improved lumen detection accuracy.
Multi-site, Multi-domain Airway Tree Modeling : A Public Benchmark for Pulmonary Airway Segmentation
Mar 10, 2023



Abstract:Open international challenges are becoming the de facto standard for assessing computer vision and image analysis algorithms. In recent years, new methods have extended the reach of pulmonary airway segmentation that is closer to the limit of image resolution. Since EXACT'09 pulmonary airway segmentation, limited effort has been directed to quantitative comparison of newly emerged algorithms driven by the maturity of deep learning based approaches and clinical drive for resolving finer details of distal airways for early intervention of pulmonary diseases. Thus far, public annotated datasets are extremely limited, hindering the development of data-driven methods and detailed performance evaluation of new algorithms. To provide a benchmark for the medical imaging community, we organized the Multi-site, Multi-domain Airway Tree Modeling (ATM'22), which was held as an official challenge event during the MICCAI 2022 conference. ATM'22 provides large-scale CT scans with detailed pulmonary airway annotation, including 500 CT scans (300 for training, 50 for validation, and 150 for testing). The dataset was collected from different sites and it further included a portion of noisy COVID-19 CTs with ground-glass opacity and consolidation. Twenty-three teams participated in the entire phase of the challenge and the algorithms for the top ten teams are reviewed in this paper. Quantitative and qualitative results revealed that deep learning models embedded with the topological continuity enhancement achieved superior performance in general. ATM'22 challenge holds as an open-call design, the training data and the gold standard evaluation are available upon successful registration via its homepage.
LTSP: Long-Term Slice Propagation for Accurate Airway Segmentation
Feb 13, 2022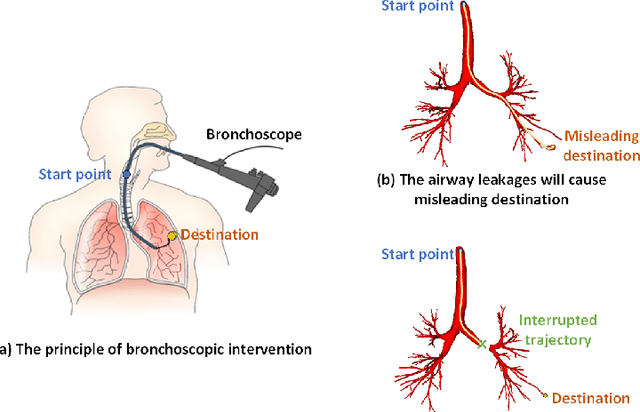
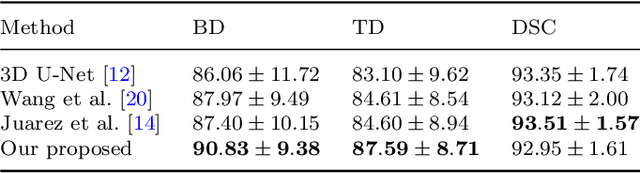
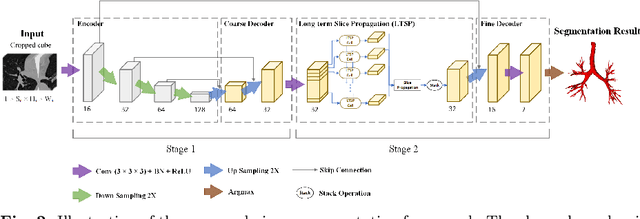
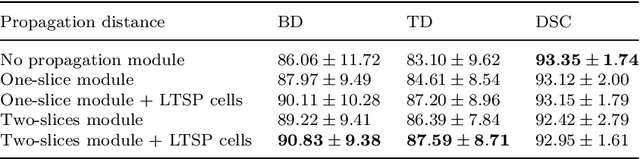
Abstract:Purpose: Bronchoscopic intervention is a widely-used clinical technique for pulmonary diseases, which requires an accurate and topological complete airway map for its localization and guidance. The airway map could be extracted from chest computed tomography (CT) scans automatically by airway segmentation methods. Due to the complex tree-like structure of the airway, preserving its topology completeness while maintaining the segmentation accuracy is a challenging task. Methods: In this paper, a long-term slice propagation (LTSP) method is proposed for accurate airway segmentation from pathological CT scans. We also design a two-stage end-to-end segmentation framework utilizing the LTSP method in the decoding process. Stage 1 is used to generate a coarse feature map by an encoder-decoder architecture. Stage 2 is to adopt the proposed LTSP method for exploiting the continuity information and enhancing the weak airway features in the coarse feature map. The final segmentation result is predicted from the refined feature map. Results: Extensive experiments were conducted to evaluate the performance of the proposed method on 70 clinical CT scans. The results demonstrate the considerable improvements of the proposed method compared to some state-of-the-art methods as most breakages are eliminated and more tiny bronchi are detected. The ablation studies further confirm the effectiveness of the constituents of the proposed method. Conclusion: Slice continuity information is beneficial to accurate airway segmentation. Furthermore, by propagating the long-term slice feature, the airway topology connectivity is preserved with overall segmentation accuracy maintained.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge