Andrew J. Taylor
Control Barrier Functions and Input-to-State Safety with Application to Automated Vehicles
Jun 07, 2022



Abstract:Balancing safety and performance is one of the predominant challenges in modern control system design. Moreover, it is crucial to robustly ensure safety without inducing unnecessary conservativeness that degrades performance. In this work we present a constructive approach for safety-critical control synthesis via Control Barrier Functions (CBF). By filtering a hand-designed controller via a CBF, we are able to attain performant behavior while providing rigorous guarantees of safety. In the face of disturbances, robust safety and performance are simultaneously achieved through the notion of Input-to-State Safety (ISSf). We take a tutorial approach by developing the CBF-design methodology in parallel with an inverted pendulum example, making the challenges and sensitivities in the design process concrete. To establish the capability of the proposed approach, we consider the practical setting of safety-critical design via CBFs for a connected automated vehicle (CAV) in the form of a class-8 truck without a trailer. Through experimentation we see the impact of unmodeled disturbances in the truck's actuation system on the safety guarantees provided by CBFs. We characterize these disturbances and using ISSf, produce a robust controller that achieves safety without conceding performance. We evaluate our design both in simulation, and for the first time on an automotive system, experimentally.
Safety of Sampled-Data Systems with Control Barrier Functions via Approximate Discrete Time Models
Mar 22, 2022



Abstract:Control Barrier Functions (CBFs) have been demonstrated to be a powerful tool for safety-critical controller design for nonlinear systems. Existing design paradigms do not address the gap between theory (controller design with continuous time models) and practice (the discrete time sampled implementation of the resulting controllers); this can lead to poor performance and violations of safety for hardware instantiations. We propose an approach to close this gap by synthesizing sampled-data counterparts to these CBF-based controllers using approximate discrete time models and Sampled-Data Control Barrier Functions (SD-CBFs). Using properties of a system's continuous time model, we establish a relationship between SD-CBFs and a notion of practical safety for sampled-data systems. Furthermore, we construct convex optimization-based controllers that formally endow nonlinear systems with safety guarantees in practice. We demonstrate the efficacy of these controllers in simulation.
Bipedal Locomotion with Nonlinear Model Predictive Control: Online Gait Generation using Whole-Body Dynamics
Mar 14, 2022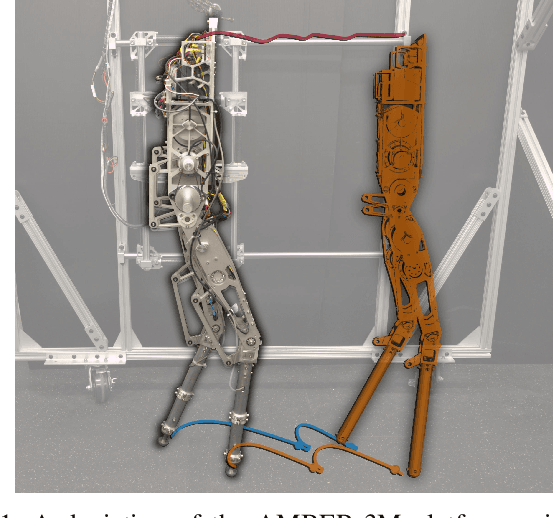



Abstract:The ability to generate dynamic walking in real-time for bipedal robots with compliance and underactuation has the potential to enable locomotion in complex and unstructured environments. Yet, the high-dimensional nature of bipedal robots has limited the use of full-order rigid body dynamics to gaits which are synthesized offline and then tracked online, e.g., via whole-body controllers. In this work we develop an online nonlinear model predictive control approach that leverages the full-order dynamics to realize diverse walking behaviors. Additionally, this approach can be coupled with gaits synthesized offline via a terminal cost that enables a shorter prediction horizon; this makes rapid online re-planning feasible and bridges the gap between online reactive control and offline gait planning. We demonstrate the proposed method on the planar robot AMBER-3M, both in simulation and on hardware.
Safety-Aware Preference-Based Learning for Safety-Critical Control
Dec 15, 2021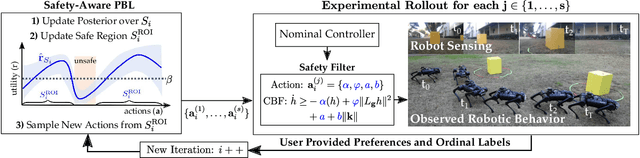
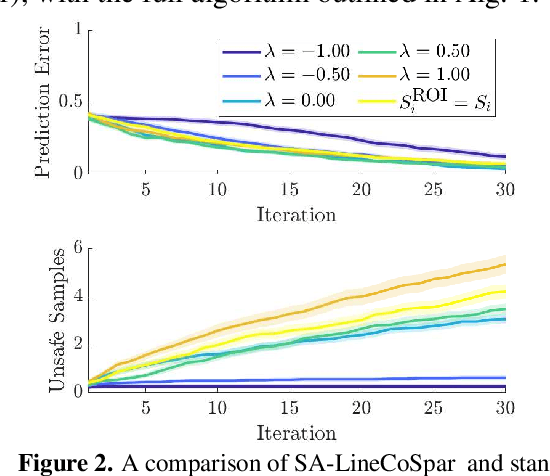
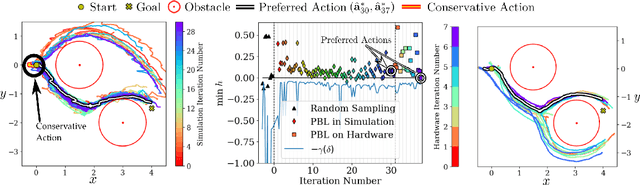
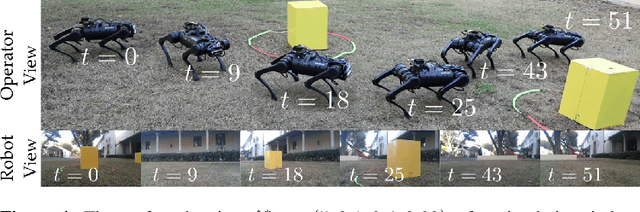
Abstract:Bringing dynamic robots into the wild requires a tenuous balance between performance and safety. Yet controllers designed to provide robust safety guarantees often result in conservative behavior, and tuning these controllers to find the ideal trade-off between performance and safety typically requires domain expertise or a carefully constructed reward function. This work presents a design paradigm for systematically achieving behaviors that balance performance and robust safety by integrating safety-aware Preference-Based Learning (PBL) with Control Barrier Functions (CBFs). Fusing these concepts -- safety-aware learning and safety-critical control -- gives a robust means to achieve safe behaviors on complex robotic systems in practice. We demonstrate the capability of this design paradigm to achieve safe and performant perception-based autonomous operation of a quadrupedal robot both in simulation and experimentally on hardware.
Episodic Learning for Safe Bipedal Locomotion with Control Barrier Functions and Projection-to-State Safety
May 04, 2021



Abstract:This paper combines episodic learning and control barrier functions in the setting of bipedal locomotion. The safety guarantees that control barrier functions provide are only valid with perfect model knowledge; however, this assumption cannot be met on hardware platforms. To address this, we utilize the notion of projection-to-state safety paired with a machine learning framework in an attempt to learn the model uncertainty as it affects the barrier functions. The proposed approach is demonstrated both in simulation and on hardware for the AMBER-3M bipedal robot in the context of the stepping-stone problem, which requires precise foot placement while walking dynamically.
Towards Robust Data-Driven Control Synthesis for Nonlinear Systems with Actuation Uncertainty
Nov 21, 2020
Abstract:Modern nonlinear control theory seeks to endow systems with properties such as stability and safety, and has been deployed successfully across various domains. Despite this success, model uncertainty remains a significant challenge in ensuring that model-based controllers transfer to real world systems. This paper develops a data-driven approach to robust control synthesis in the presence of model uncertainty using Control Certificate Functions (CCFs), resulting in a convex optimization based controller for achieving properties like stability and safety. An important benefit of our framework is nuanced data-dependent guarantees, which in principle can yield sample-efficient data collection approaches that need not fully determine the input-to-state relationship. This work serves as a starting point for addressing important questions at the intersection of nonlinear control theory and non-parametric learning, both theoretical and in application. We validate the proposed method in simulation with an inverted pendulum in multiple experimental configurations.
Multi-Layered Safety for Legged Robots via Control Barrier Functions and Model Predictive Control
Oct 30, 2020



Abstract:The problem of dynamic locomotion over rough terrain requires both accurate foot placement together with an emphasis on dynamic stability. Existing approaches to this problem prioritize immediate safe foot placement over longer term dynamic stability considerations, or relegate the coordination of foot placement and dynamic stability to heuristic methods. We propose a multi-layered locomotion framework that unifies Control Barrier Functions (CBFs) with Model Predictive Control (MPC) to simultaneously achieve safe foot placement and dynamic stability. Our approach incorporates CBF based safety constraints both in a low frequency kino-dynamic MPC formulation and a high frequency inverse dynamics tracking controller. This ensures that safety-critical execution is considered when optimizing locomotion over a longer horizon. We validate the proposed method in a 3D stepping-stone scenario in simulation and experimentally on the ANYmal quadruped platform.
Guaranteeing Safety of Learned Perception Modules via Measurement-Robust Control Barrier Functions
Oct 30, 2020


Abstract:Modern nonlinear control theory seeks to develop feedback controllers that endow systems with properties such as safety and stability. The guarantees ensured by these controllers often rely on accurate estimates of the system state for determining control actions. In practice, measurement model uncertainty can lead to error in state estimates that degrades these guarantees. In this paper, we seek to unify techniques from control theory and machine learning to synthesize controllers that achieve safety in the presence of measurement model uncertainty. We define the notion of a Measurement-Robust Control Barrier Function (MR-CBF) as a tool for determining safe control inputs when facing measurement model uncertainty. Furthermore, MR-CBFs are used to inform sampling methodologies for learning-based perception systems and quantify tolerable error in the resulting learned models. We demonstrate the efficacy of MR-CBFs in achieving safety with measurement model uncertainty on a simulated Segway system.
Nonlinear Model Predictive Control of Robotic Systems with Control Lyapunov Functions
Jun 01, 2020



Abstract:The theoretical unification of Nonlinear Model Predictive Control (NMPC) with Control Lyapunov Functions (CLFs) provides a framework for achieving optimal control performance while ensuring stability guarantees. In this paper we present the first real-time realization of a unified NMPC and CLF controller on a robotic system with limited computational resources. These limitations motivate a set of approaches for efficiently incorporating CLF stability constraints into a general NMPC formulation. We evaluate the performance of the proposed methods compared to baseline CLF and NMPC controllers with a robotic Segway platform both in simulation and on hardware. The addition of a prediction horizon provides a performance advantage over CLF based controllers, which operate optimally point-wise in time. Moreover, the explicitly imposed stability constraints remove the need for difficult cost function and parameter tuning required by NMPC. Therefore the unified controller improves the performance of each isolated controller and simplifies the overall design process.
A Control Lyapunov Perspective on Episodic Learning via Projection to State Stability
Mar 18, 2019

Abstract:The goal of this paper is to understand the impact of learning on control synthesis from a Lyapunov function perspective. In particular, rather than consider uncertainties in the full system dynamics, we employ Control Lyapunov Functions (CLFs) as low-dimensional projections. To understand and characterize the uncertainty that these projected dynamics introduce in the system, we introduce a new notion: Projection to State Stability (PSS). PSS can be viewed as a variant of Input to State Stability defined on projected dynamics, and enables characterizing robustness of a CLF with respect to the data used to learn system uncertainties. We use PSS to bound uncertainty in affine control, and demonstrate that a practical episodic learning approach can use PSS to characterize uncertainty in the CLF for robust control synthesis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge