Andreas Tolias
NeuroAI for AI Safety
Nov 27, 2024



Abstract:As AI systems become increasingly powerful, the need for safe AI has become more pressing. Humans are an attractive model for AI safety: as the only known agents capable of general intelligence, they perform robustly even under conditions that deviate significantly from prior experiences, explore the world safely, understand pragmatics, and can cooperate to meet their intrinsic goals. Intelligence, when coupled with cooperation and safety mechanisms, can drive sustained progress and well-being. These properties are a function of the architecture of the brain and the learning algorithms it implements. Neuroscience may thus hold important keys to technical AI safety that are currently underexplored and underutilized. In this roadmap, we highlight and critically evaluate several paths toward AI safety inspired by neuroscience: emulating the brain's representations, information processing, and architecture; building robust sensory and motor systems from imitating brain data and bodies; fine-tuning AI systems on brain data; advancing interpretability using neuroscience methods; and scaling up cognitively-inspired architectures. We make several concrete recommendations for how neuroscience can positively impact AI safety.
Avalanche: an End-to-End Library for Continual Learning
Apr 01, 2021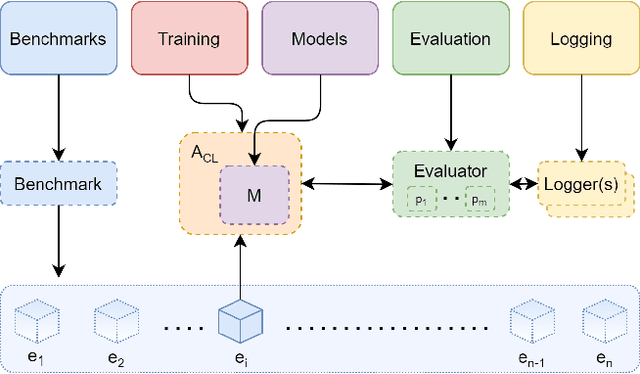
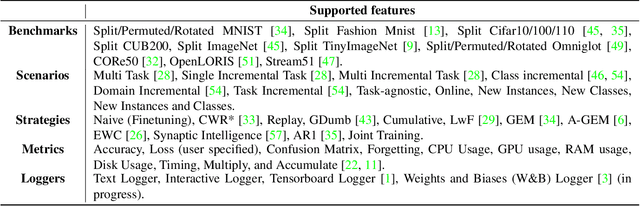
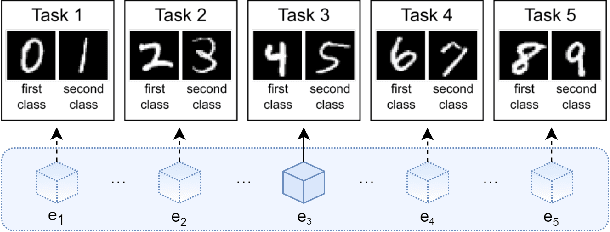
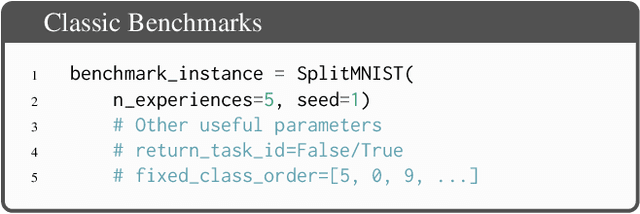
Abstract:Learning continually from non-stationary data streams is a long-standing goal and a challenging problem in machine learning. Recently, we have witnessed a renewed and fast-growing interest in continual learning, especially within the deep learning community. However, algorithmic solutions are often difficult to re-implement, evaluate and port across different settings, where even results on standard benchmarks are hard to reproduce. In this work, we propose Avalanche, an open-source end-to-end library for continual learning research based on PyTorch. Avalanche is designed to provide a shared and collaborative codebase for fast prototyping, training, and reproducible evaluation of continual learning algorithms.
Penalized matrix decomposition for denoising, compression, and improved demixing of functional imaging data
Jul 17, 2018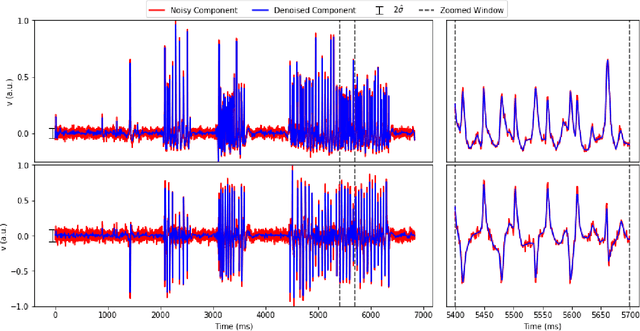
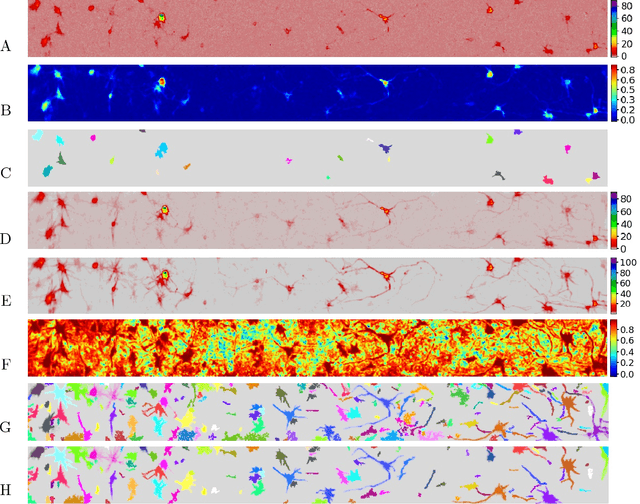
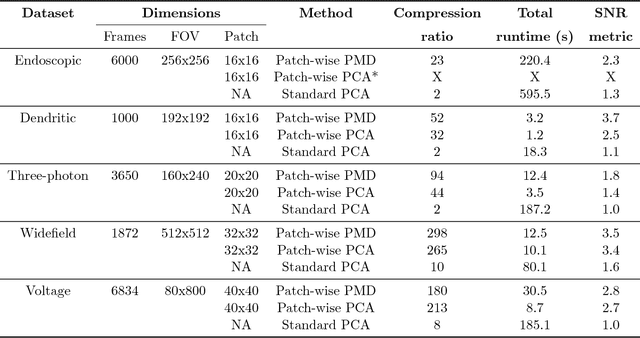

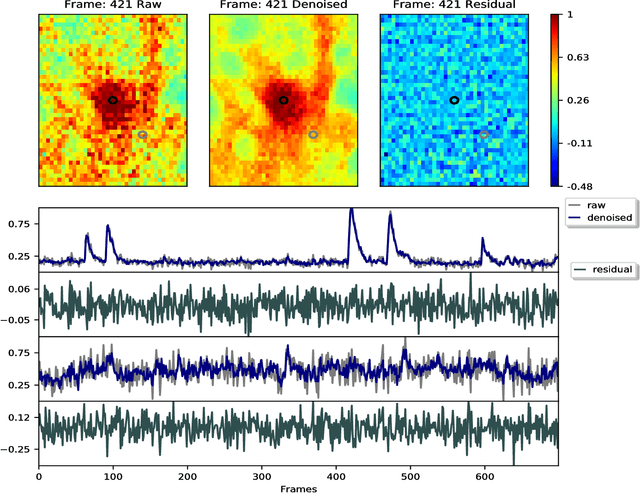
Abstract:Calcium imaging has revolutionized systems neuroscience, providing the ability to image large neural populations with single-cell resolution. The resulting datasets are quite large, which has presented a barrier to routine open sharing of this data, slowing progress in reproducible research. State of the art methods for analyzing this data are based on non-negative matrix factorization (NMF); these approaches solve a non-convex optimization problem, and are effective when good initializations are available, but can break down in low-SNR settings where common initialization approaches fail. Here we introduce an approach to compressing and denoising functional imaging data. The method is based on a spatially-localized penalized matrix decomposition (PMD) of the data to separate (low-dimensional) signal from (temporally-uncorrelated) noise. This approach can be applied in parallel on local spatial patches and is therefore highly scalable, does not impose non-negativity constraints or require stringent identifiability assumptions (leading to significantly more robust results compared to NMF), and estimates all parameters directly from the data, so no hand-tuning is required. We have applied the method to a wide range of functional imaging data (including one-photon, two-photon, three-photon, widefield, somatic, axonal, dendritic, calcium, and voltage imaging datasets): in all cases, we observe ~2-4x increases in SNR and compression rates of 20-300x with minimal visible loss of signal, with no adjustment of hyperparameters; this in turn facilitates the process of demixing the observed activity into contributions from individual neurons. We focus on two challenging applications: dendritic calcium imaging data and voltage imaging data in the context of optogenetic stimulation. In both cases, we show that our new approach leads to faster and much more robust extraction of activity from the data.
Supervised learning sets benchmark for robust spike detection from calcium imaging signals
Feb 28, 2015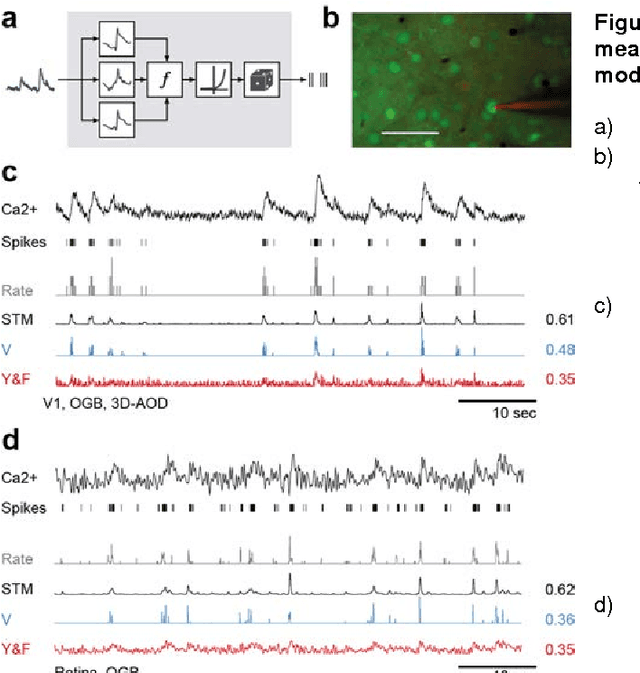
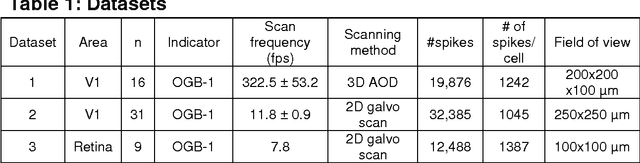
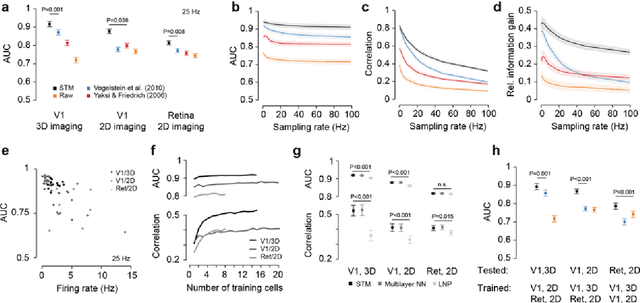
Abstract:A fundamental challenge in calcium imaging has been to infer the timing of action potentials from the measured noisy calcium fluorescence traces. We systematically evaluate a range of spike inference algorithms on a large benchmark dataset recorded from varying neural tissue (V1 and retina) using different calcium indicators (OGB-1 and GCamp6). We show that a new algorithm based on supervised learning in flexible probabilistic models outperforms all previously published techniques, setting a new standard for spike inference from calcium signals. Importantly, it performs better than other algorithms even on datasets not seen during training. Future data acquired in new experimental conditions can easily be used to further improve its spike prediction accuracy and generalization performance. Finally, we show that comparing algorithms on artificial data is not informative about performance on real population imaging data, suggesting that a benchmark dataset may greatly facilitate future algorithmic developments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge