Ana Paiva
Building Persuasive Robots with Social Power Strategies
Jul 12, 2023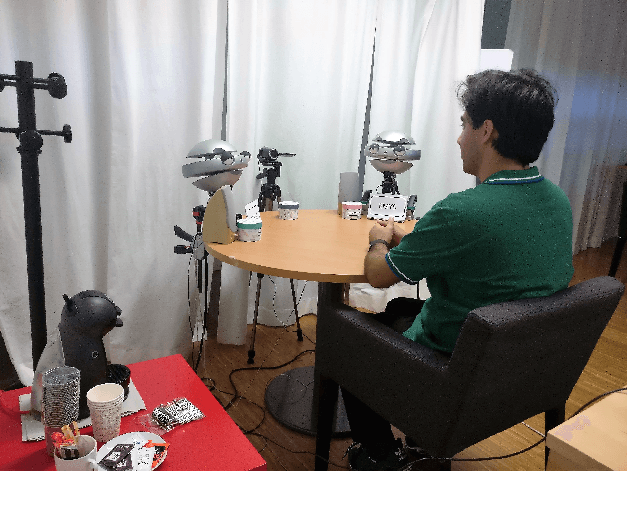
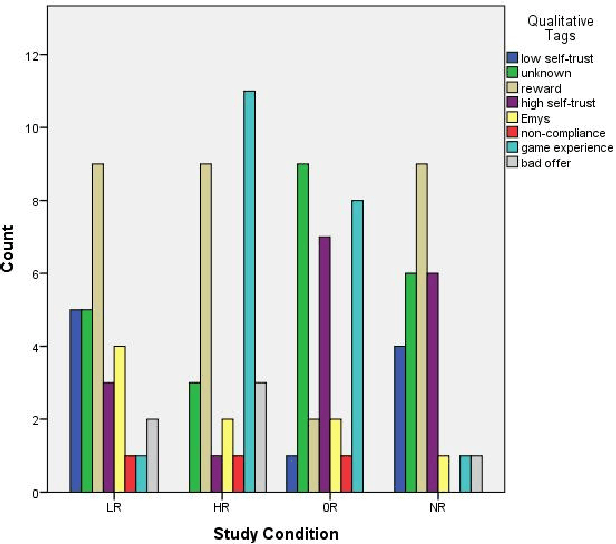
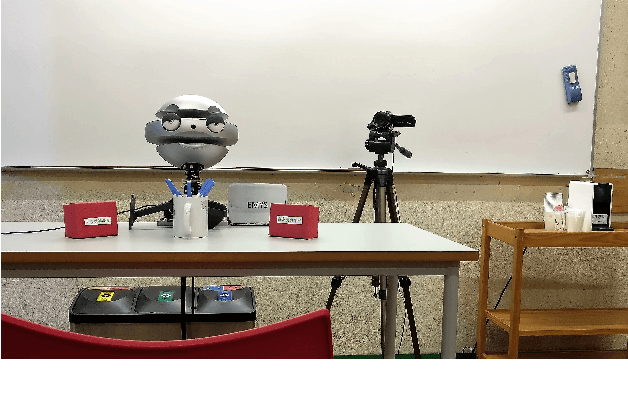
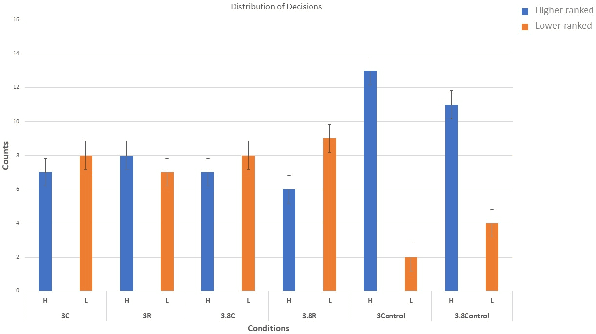
Abstract:Can social power endow social robots with the capacity to persuade? This paper represents our recent endeavor to design persuasive social robots. We have designed and run three different user studies to investigate the effectiveness of different bases of social power (inspired by French and Raven's theory) on peoples' compliance to the requests of social robots. The results show that robotic persuaders that exert social power (specifically from expert, reward, and coercion bases) demonstrate increased ability to influence humans. The first study provides a positive answer and shows that under the same circumstances, people with different personalities prefer robots using a specific social power base. In addition, social rewards can be useful in persuading individuals. The second study suggests that by employing social power, social robots are capable of persuading people objectively to select a less desirable choice among others. Finally, the third study shows that the effect of power on persuasion does not decay over time and might strengthen under specific circumstances. Moreover, exerting stronger social power does not necessarily lead to higher persuasion. Overall, we argue that the results of these studies are relevant for designing human--robot-interaction scenarios especially the ones aiming at behavioral change.
From Modelling to Understanding Children's Behaviour in the Context of Robotics and Social Artificial Intelligence
Oct 20, 2022Abstract:Understanding and modelling children's cognitive processes and their behaviour in the context of their interaction with robots and social artificial intelligence systems is a fundamental prerequisite for meaningful and effective robot interventions. However, children's development involve complex faculties such as exploration, creativity and curiosity which are challenging to model. Also, often children express themselves in a playful way which is different from a typical adult behaviour. Different children also have different needs, and it remains a challenge in the current state of the art that those of neurodiverse children are under-addressed. With this workshop, we aim to promote a common ground among different disciplines such as developmental sciences, artificial intelligence and social robotics and discuss cutting-edge research in the area of user modelling and adaptive systems for children.
Centralized Training with Hybrid Execution in Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Oct 12, 2022
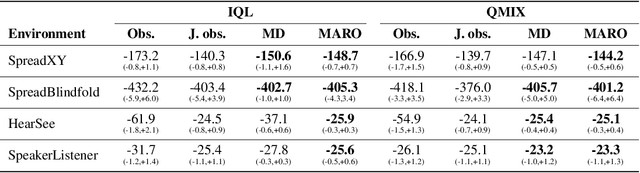

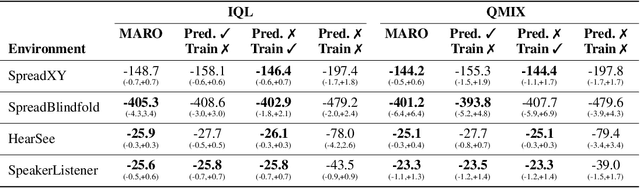
Abstract:We introduce hybrid execution in multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL), a new paradigm in which agents aim to successfully perform cooperative tasks with any communication level at execution time by taking advantage of information-sharing among the agents. Under hybrid execution, the communication level can range from a setting in which no communication is allowed between agents (fully decentralized), to a setting featuring full communication (fully centralized). To formalize our setting, we define a new class of multi-agent partially observable Markov decision processes (POMDPs) that we name hybrid-POMDPs, which explicitly models a communication process between the agents. We contribute MARO, an approach that combines an autoregressive predictive model to estimate missing agents' observations, and a dropout-based RL training scheme that simulates different communication levels during the centralized training phase. We evaluate MARO on standard scenarios and extensions of previous benchmarks tailored to emphasize the negative impact of partial observability in MARL. Experimental results show that our method consistently outperforms baselines, allowing agents to act with faulty communication while successfully exploiting shared information.
"Guess what I'm doing": Extending legibility to sequential decision tasks
Sep 19, 2022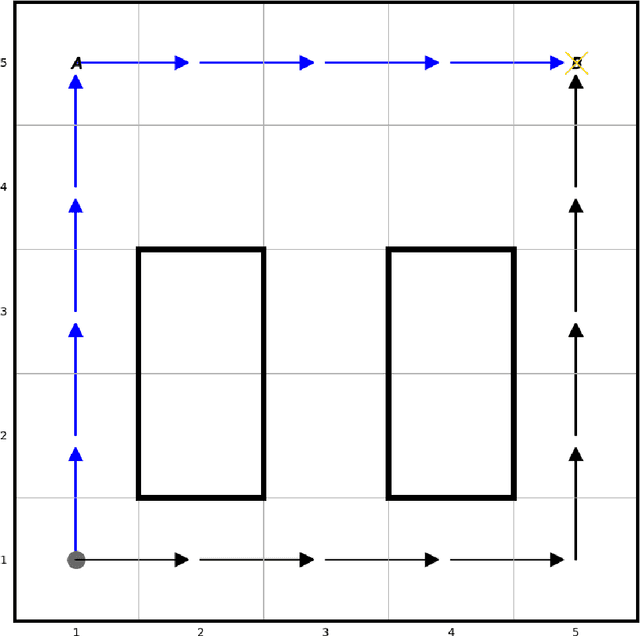

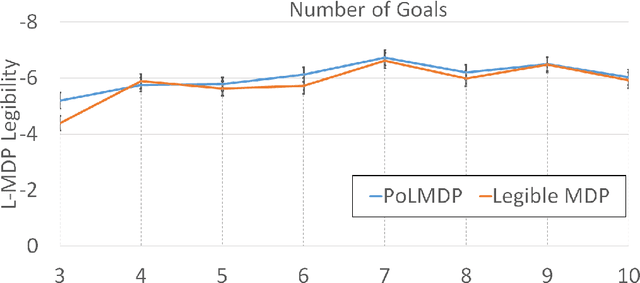

Abstract:In this paper we investigate the notion of legibility in sequential decision tasks under uncertainty. Previous works that extend legibility to scenarios beyond robot motion either focus on deterministic settings or are computationally too expensive. Our proposed approach, dubbed PoL-MDP, is able to handle uncertainty while remaining computationally tractable. We establish the advantages of our approach against state-of-the-art approaches in several simulated scenarios of different complexity. We also showcase the use of our legible policies as demonstrations for an inverse reinforcement learning agent, establishing their superiority against the commonly used demonstrations based on the optimal policy. Finally, we assess the legibility of our computed policies through a user study where people are asked to infer the goal of a mobile robot following a legible policy by observing its actions.
Avant-Satie! Using ERIK to encode task-relevant expressivity into the animation of autonomous social robots
Mar 02, 2022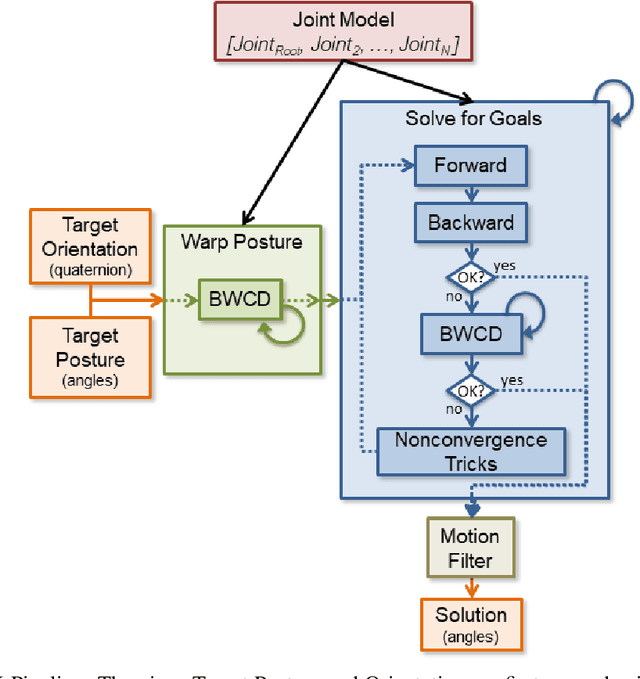
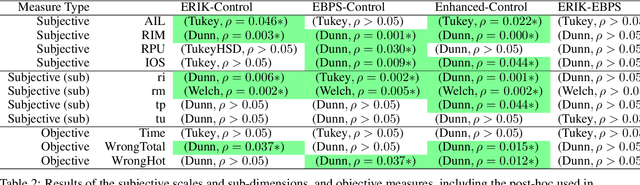
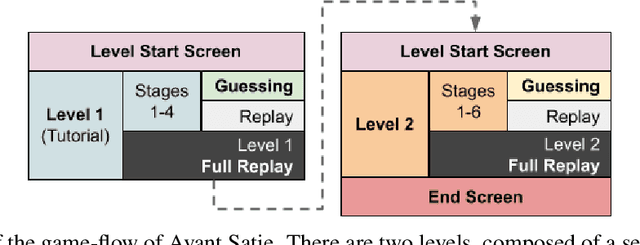
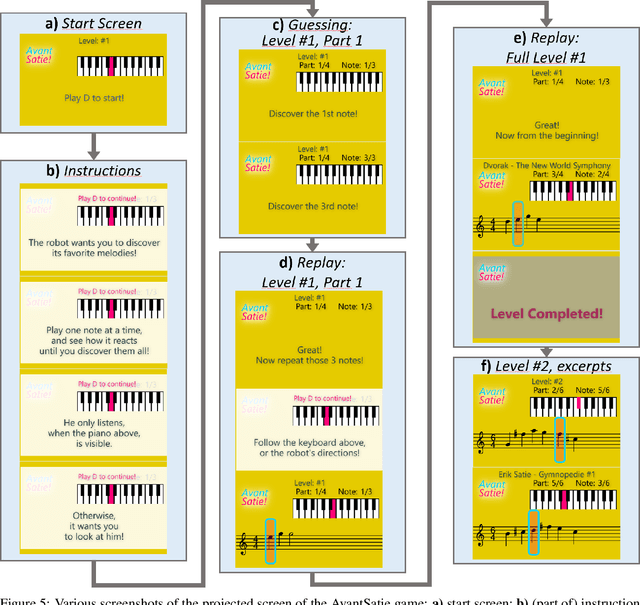
Abstract:ERIK is an expressive inverse kinematics technique that has been previously presented and evaluated both algorithmically and in a limited user-interaction scenario. It allows autonomous social robots to convey posture-based expressive information while gaze-tracking users. We have developed a new scenario aimed at further validating some of the unsupported claims from the previous scenario. Our experiment features a fully autonomous Adelino robot, and concludes that ERIK can be used to direct a user's choice of actions during execution of a given task, fully through its non-verbal expressive queues.
GMC -- Geometric Multimodal Contrastive Representation Learning
Feb 08, 2022
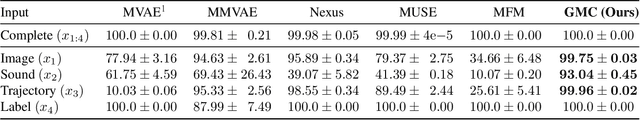
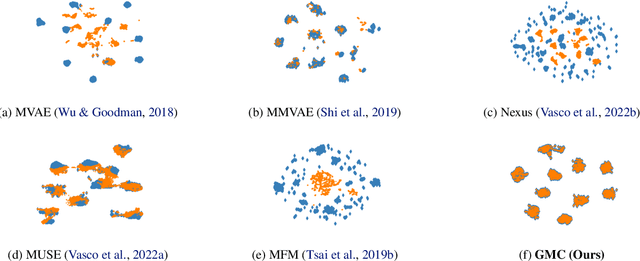

Abstract:Learning representations of multimodal data that are both informative and robust to missing modalities at test time remains a challenging problem due to the inherent heterogeneity of data obtained from different channels. To address it, we present a novel Geometric Multimodal Contrastive (GMC) representation learning method comprised of two main components: i) a two-level architecture consisting of modality-specific base encoder, allowing to process an arbitrary number of modalities to an intermediate representation of fixed dimensionality, and a shared projection head, mapping the intermediate representations to a latent representation space; ii) a multimodal contrastive loss function that encourages the geometric alignment of the learned representations. We experimentally demonstrate that GMC representations are semantically rich and achieve state-of-the-art performance with missing modality information on three different learning problems including prediction and reinforcement learning tasks.
How to Sense the World: Leveraging Hierarchy in Multimodal Perception for Robust Reinforcement Learning Agents
Oct 07, 2021
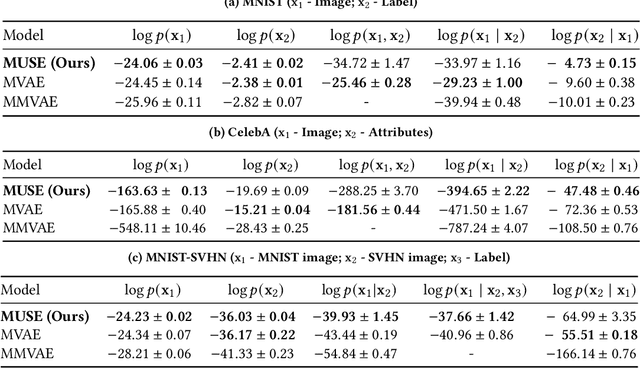
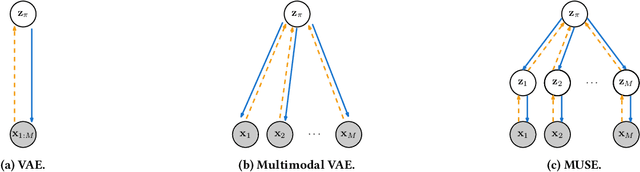

Abstract:This work addresses the problem of sensing the world: how to learn a multimodal representation of a reinforcement learning agent's environment that allows the execution of tasks under incomplete perceptual conditions. To address such problem, we argue for hierarchy in the design of representation models and contribute with a novel multimodal representation model, MUSE. The proposed model learns hierarchical representations: low-level modality-specific representations, encoded from raw observation data, and a high-level multimodal representation, encoding joint-modality information to allow robust state estimation. We employ MUSE as the sensory representation model of deep reinforcement learning agents provided with multimodal observations in Atari games. We perform a comparative study over different designs of reinforcement learning agents, showing that MUSE allows agents to perform tasks under incomplete perceptual experience with minimal performance loss. Finally, we evaluate the performance of MUSE in literature-standard multimodal scenarios with higher number and more complex modalities, showing that it outperforms state-of-the-art multimodal variational autoencoders in single and cross-modality generation.
FAtiMA Toolkit -- Toward an effective and accessible tool for the development of intelligent virtual agents and social robots
Mar 04, 2021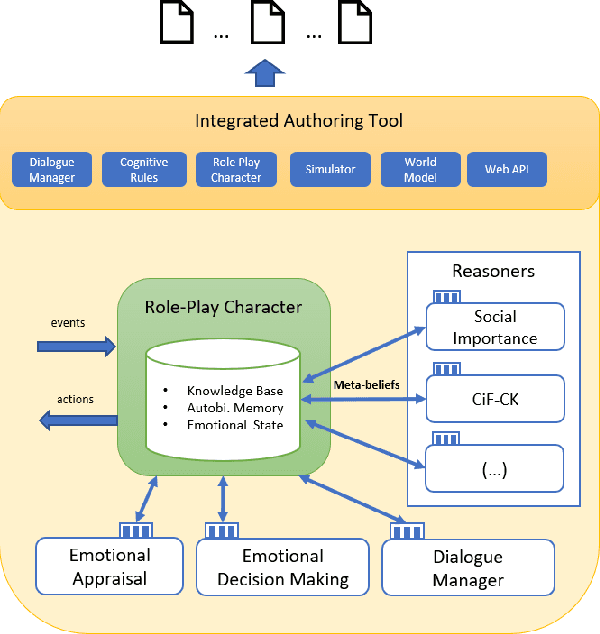
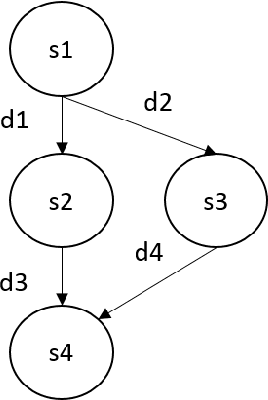
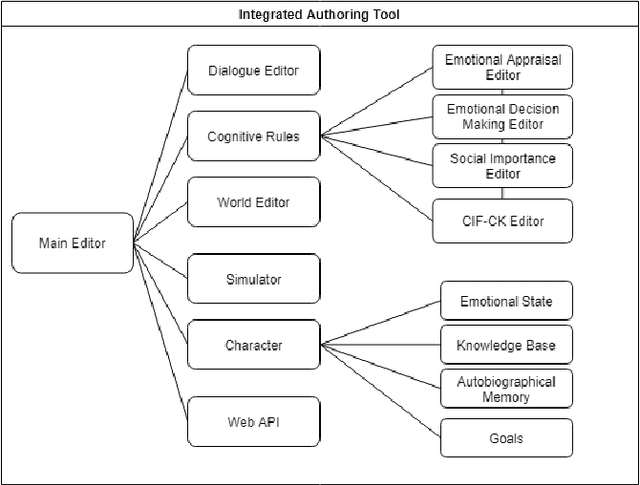
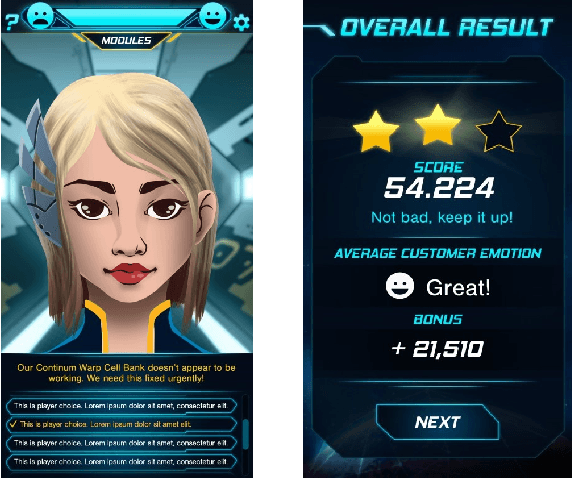
Abstract:More than a decade has passed since the development of FearNot!, an application designed to help children deal with bullying through role-playing with virtual characters. It was also the application that led to the creation of FAtiMA, an affective agent architecture for creating autonomous characters that can evoke empathic responses. In this paper, we describe FAtiMA Toolkit, a collection of open-source tools that is designed to help researchers, game developers and roboticists incorporate a computational model of emotion and decision-making in their work. The toolkit was developed with the goal of making FAtiMA more accessible, easier to incorporate into different projects and more flexible in its capabilities for human-agent interaction, based upon the experience gathered over the years across different virtual environments and human-robot interaction scenarios. As a result, this work makes several different contributions to the field of Agent-Based Architectures. More precisely, FAtiMA Toolkit's library based design allows developers to easily integrate it with other frameworks, its meta-cognitive model affords different internal reasoners and affective components and its explicit dialogue structure gives control to the author even within highly complex scenarios. To demonstrate the use of FAtiMA Toolkit, several different use cases where the toolkit was successfully applied are described and discussed.
MHVAE: a Human-Inspired Deep Hierarchical Generative Model for Multimodal Representation Learning
Jun 04, 2020

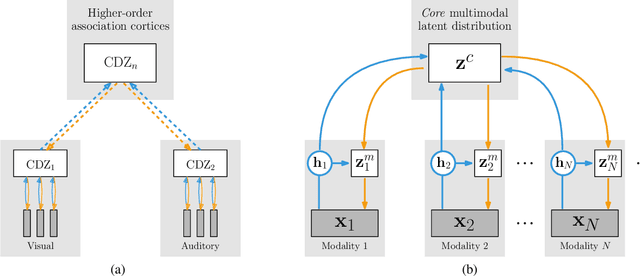

Abstract:Humans are able to create rich representations of their external reality. Their internal representations allow for cross-modality inference, where available perceptions can induce the perceptual experience of missing input modalities. In this paper, we contribute the Multimodal Hierarchical Variational Auto-encoder (MHVAE), a hierarchical multimodal generative model for representation learning. Inspired by human cognitive models, the MHVAE is able to learn modality-specific distributions, of an arbitrary number of modalities, and a joint-modality distribution, responsible for cross-modality inference. We formally derive the model's evidence lower bound and propose a novel methodology to approximate the joint-modality posterior based on modality-specific representation dropout. We evaluate the MHVAE on standard multimodal datasets. Our model performs on par with other state-of-the-art generative models regarding joint-modality reconstruction from arbitrary input modalities and cross-modality inference.
Explainable Agents Through Social Cues: A Review
Mar 11, 2020
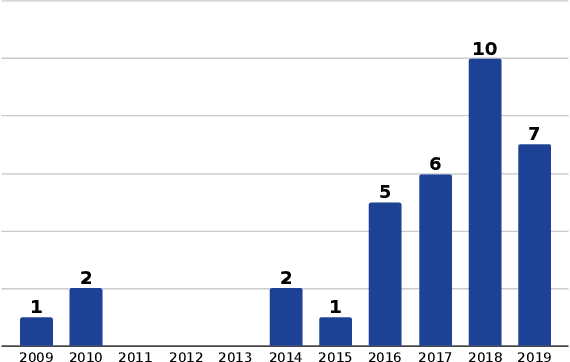

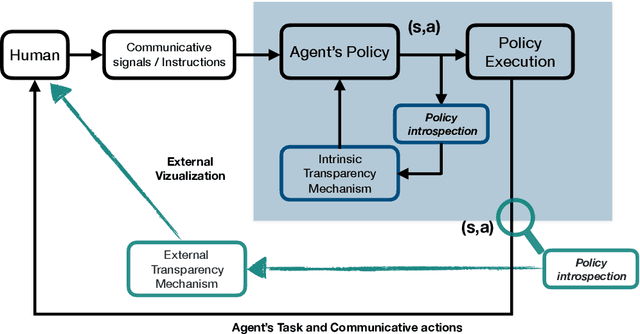
Abstract:How to provide explanations has experienced a surge of interest in Human-Robot Interaction (HRI) over the last three years. In HRI this is known as explainability, expressivity, transparency or sometimes legibility, and the challenge for embodied agents is that they offer a unique array of modalities to communicate this information thanks to their embodiment. Responding to this surge of interest, we review the existing literature in explainability and organize it by (1) providing an overview of existing definitions, (2) showing how explainability is implemented and how it exploits different modalities, and (3) showing how the impact of explainability is measured. Additionally, we present a list of open questions and challenges that highlight areas that require further investigation by the community. This provides the interested scholar with an overview of the current state-of-the-art.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge