Marta Couto
Building Persuasive Robots with Social Power Strategies
Jul 12, 2023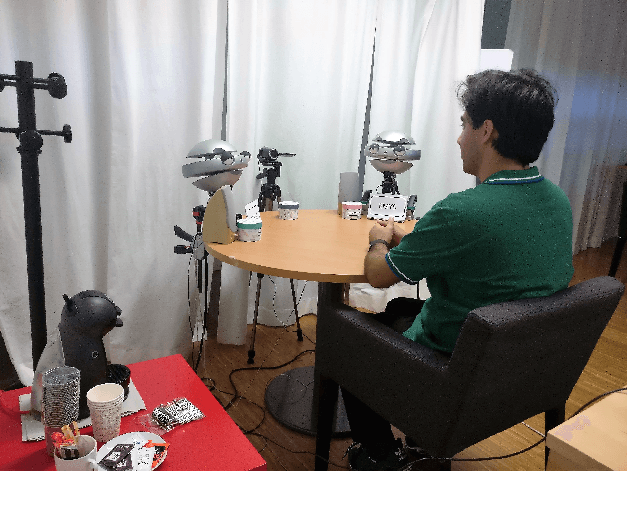
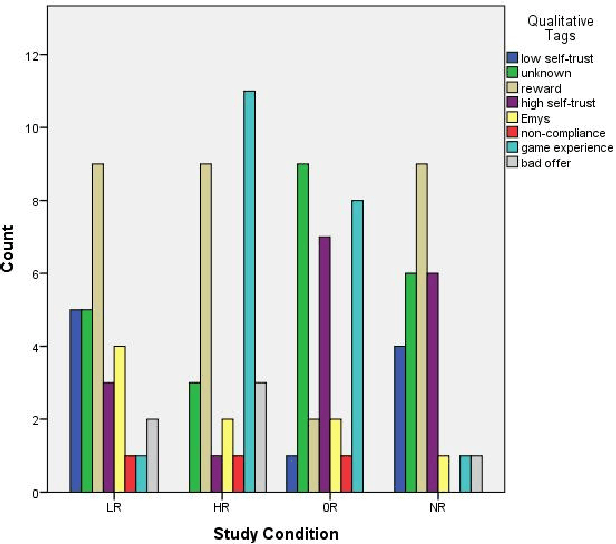
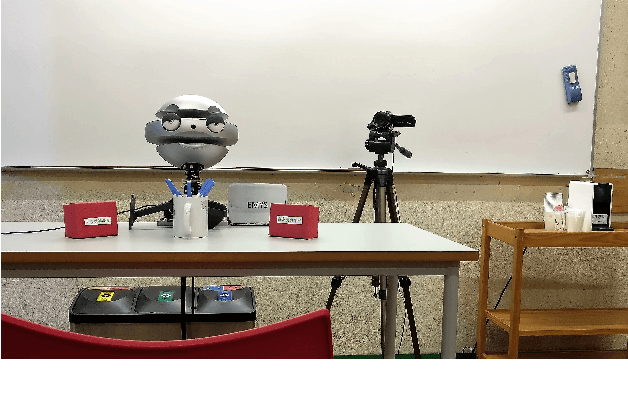
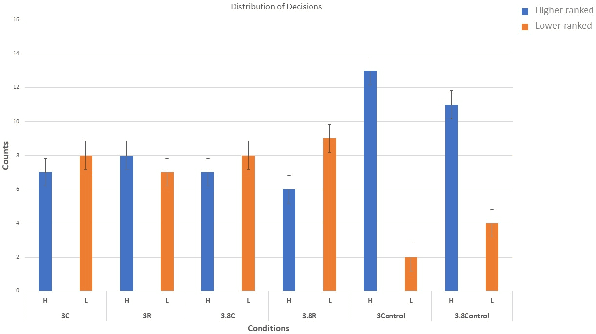
Abstract:Can social power endow social robots with the capacity to persuade? This paper represents our recent endeavor to design persuasive social robots. We have designed and run three different user studies to investigate the effectiveness of different bases of social power (inspired by French and Raven's theory) on peoples' compliance to the requests of social robots. The results show that robotic persuaders that exert social power (specifically from expert, reward, and coercion bases) demonstrate increased ability to influence humans. The first study provides a positive answer and shows that under the same circumstances, people with different personalities prefer robots using a specific social power base. In addition, social rewards can be useful in persuading individuals. The second study suggests that by employing social power, social robots are capable of persuading people objectively to select a less desirable choice among others. Finally, the third study shows that the effect of power on persuasion does not decay over time and might strengthen under specific circumstances. Moreover, exerting stronger social power does not necessarily lead to higher persuasion. Overall, we argue that the results of these studies are relevant for designing human--robot-interaction scenarios especially the ones aiming at behavioral change.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge