Lidc Idri
Papers and Code
Generation of Chest CT pulmonary Nodule Images by Latent Diffusion Models using the LIDC-IDRI Dataset
Jan 16, 2026Recently, computer-aided diagnosis systems have been developed to support diagnosis, but their performance depends heavily on the quality and quantity of training data. However, in clinical practice, it is difficult to collect the large amount of CT images for specific cases, such as small cell carcinoma with low epidemiological incidence or benign tumors that are difficult to distinguish from malignant ones. This leads to the challenge of data imbalance. In this study, to address this issue, we proposed a method to automatically generate chest CT nodule images that capture target features using latent diffusion models (LDM) and verified its effectiveness. Using the LIDC-IDRI dataset, we created pairs of nodule images and finding-based text prompts based on physician evaluations. For the image generation models, we used Stable Diffusion version 1.5 (SDv1) and 2.0 (SDv2), which are types of LDM. Each model was fine-tuned using the created dataset. During the generation process, we adjusted the guidance scale (GS), which indicates the fidelity to the input text. Both quantitative and subjective evaluations showed that SDv2 (GS = 5) achieved the best performance in terms of image quality, diversity, and text consistency. In the subjective evaluation, no statistically significant differences were observed between the generated images and real images, confirming that the quality was equivalent to real clinical images. We proposed a method for generating chest CT nodule images based on input text using LDM. Evaluation results demonstrated that the proposed method could generate high-quality images that successfully capture specific medical features.
Visual question answering-based image-finding generation for pulmonary nodules on chest CT from structured annotations
Jan 16, 2026Interpretation of imaging findings based on morphological characteristics is important for diagnosing pulmonary nodules on chest computed tomography (CT) images. In this study, we constructed a visual question answering (VQA) dataset from structured data in an open dataset and investigated an image-finding generation method for chest CT images, with the aim of enabling interactive diagnostic support that presents findings based on questions that reflect physicians' interests rather than fixed descriptions. In this study, chest CT images included in the Lung Image Database Consortium and Image Database Resource Initiative (LIDC-IDRI) datasets were used. Regions of interest surrounding the pulmonary nodules were extracted from these images, and image findings and questions were defined based on morphological characteristics recorded in the database. A dataset comprising pairs of cropped images, corresponding questions, and image findings was constructed, and the VQA model was fine-tuned on it. Language evaluation metrics such as BLEU were used to evaluate the generated image findings. The VQA dataset constructed using the proposed method contained image findings with natural expressions as radiological descriptions. In addition, the generated image findings showed a high CIDEr score of 3.896, and a high agreement with the reference findings was obtained through evaluation based on morphological characteristics. We constructed a VQA dataset for chest CT images using structured information on the morphological characteristics from the LIDC-IDRI dataset. Methods for generating image findings in response to these questions have also been investigated. Based on the generated results and evaluation metric scores, the proposed method was effective as an interactive diagnostic support system that can present image findings according to physicians' interests.
ProSona: Prompt-Guided Personalization for Multi-Expert Medical Image Segmentation
Nov 11, 2025Automated medical image segmentation suffers from high inter-observer variability, particularly in tasks such as lung nodule delineation, where experts often disagree. Existing approaches either collapse this variability into a consensus mask or rely on separate model branches for each annotator. We introduce ProSona, a two-stage framework that learns a continuous latent space of annotation styles, enabling controllable personalization via natural language prompts. A probabilistic U-Net backbone captures diverse expert hypotheses, while a prompt-guided projection mechanism navigates this latent space to generate personalized segmentations. A multi-level contrastive objective aligns textual and visual representations, promoting disentangled and interpretable expert styles. Across the LIDC-IDRI lung nodule and multi-institutional prostate MRI datasets, ProSona reduces the Generalized Energy Distance by 17% and improves mean Dice by more than one point compared with DPersona. These results demonstrate that natural-language prompts can provide flexible, accurate, and interpretable control over personalized medical image segmentation. Our implementation is available online 1 .
Minimum Data, Maximum Impact: 20 annotated samples for explainable lung nodule classification
Aug 01, 2025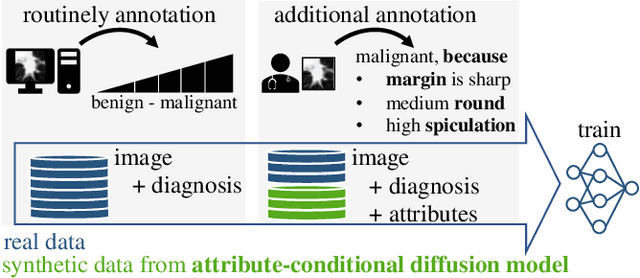
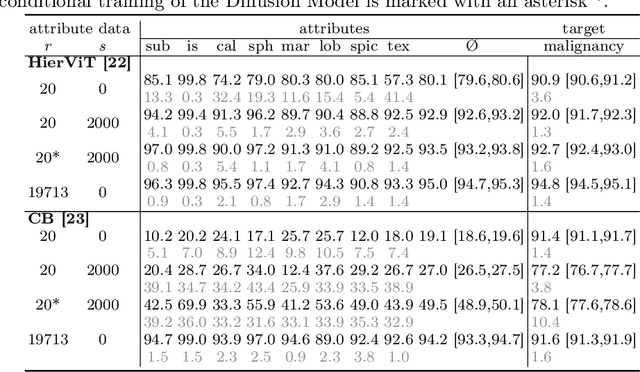
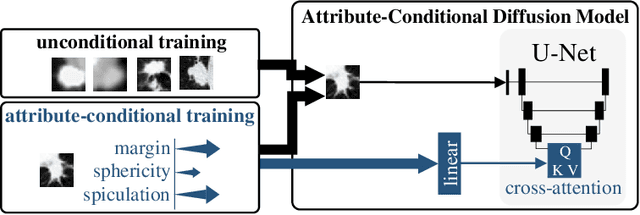
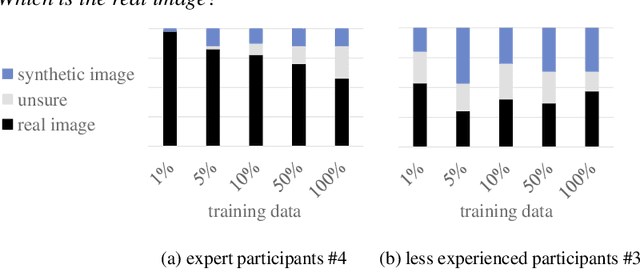
Classification models that provide human-interpretable explanations enhance clinicians' trust and usability in medical image diagnosis. One research focus is the integration and prediction of pathology-related visual attributes used by radiologists alongside the diagnosis, aligning AI decision-making with clinical reasoning. Radiologists use attributes like shape and texture as established diagnostic criteria and mirroring these in AI decision-making both enhances transparency and enables explicit validation of model outputs. However, the adoption of such models is limited by the scarcity of large-scale medical image datasets annotated with these attributes. To address this challenge, we propose synthesizing attribute-annotated data using a generative model. We enhance the Diffusion Model with attribute conditioning and train it using only 20 attribute-labeled lung nodule samples from the LIDC-IDRI dataset. Incorporating its generated images into the training of an explainable model boosts performance, increasing attribute prediction accuracy by 13.4% and target prediction accuracy by 1.8% compared to training with only the small real attribute-annotated dataset. This work highlights the potential of synthetic data to overcome dataset limitations, enhancing the applicability of explainable models in medical image analysis.
Multi-Attention Stacked Ensemble for Lung Cancer Detection in CT Scans
Jul 27, 2025



In this work, we address the challenge of binary lung nodule classification (benign vs malignant) using CT images by proposing a multi-level attention stacked ensemble of deep neural networks. Three pretrained backbones - EfficientNet V2 S, MobileViT XXS, and DenseNet201 - are each adapted with a custom classification head tailored to 96 x 96 pixel inputs. A two-stage attention mechanism learns both model-wise and class-wise importance scores from concatenated logits, and a lightweight meta-learner refines the final prediction. To mitigate class imbalance and improve generalization, we employ dynamic focal loss with empirically calculated class weights, MixUp augmentation during training, and test-time augmentation at inference. Experiments on the LIDC-IDRI dataset demonstrate exceptional performance, achieving 98.09 accuracy and 0.9961 AUC, representing a 35 percent reduction in error rate compared to state-of-the-art methods. The model exhibits balanced performance across sensitivity (98.73) and specificity (98.96), with particularly strong results on challenging cases where radiologist disagreement was high. Statistical significance testing confirms the robustness of these improvements across multiple experimental runs. Our approach can serve as a robust, automated aid for radiologists in lung cancer screening.
DiffOSeg: Omni Medical Image Segmentation via Multi-Expert Collaboration Diffusion Model
Jul 17, 2025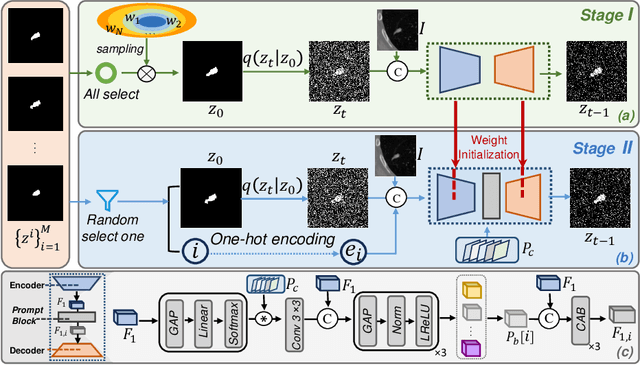
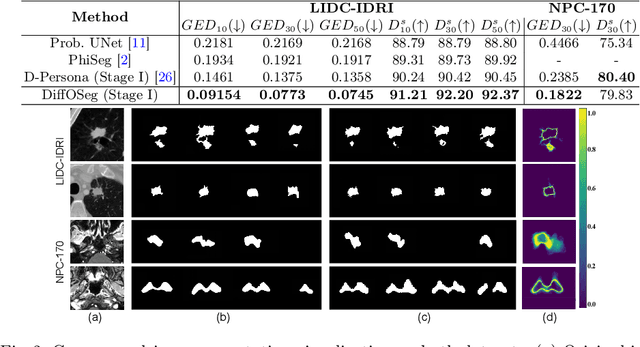
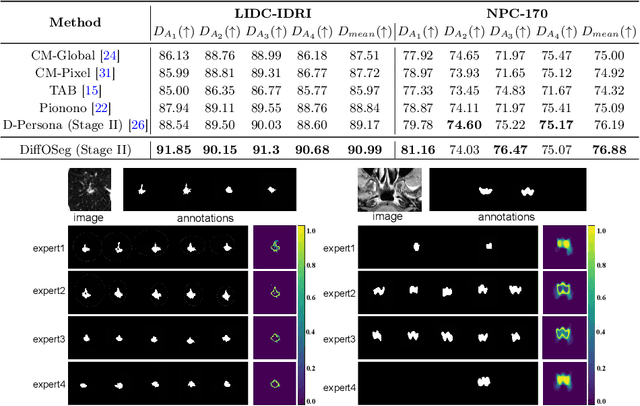
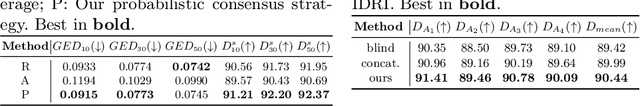
Annotation variability remains a substantial challenge in medical image segmentation, stemming from ambiguous imaging boundaries and diverse clinical expertise. Traditional deep learning methods producing single deterministic segmentation predictions often fail to capture these annotator biases. Although recent studies have explored multi-rater segmentation, existing methods typically focus on a single perspective -- either generating a probabilistic ``gold standard'' consensus or preserving expert-specific preferences -- thus struggling to provide a more omni view. In this study, we propose DiffOSeg, a two-stage diffusion-based framework, which aims to simultaneously achieve both consensus-driven (combining all experts' opinions) and preference-driven (reflecting experts' individual assessments) segmentation. Stage I establishes population consensus through a probabilistic consensus strategy, while Stage II captures expert-specific preference via adaptive prompts. Demonstrated on two public datasets (LIDC-IDRI and NPC-170), our model outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods across all evaluated metrics. Source code is available at https://github.com/string-ellipses/DiffOSeg .
A Narrative Review on Large AI Models in Lung Cancer Screening, Diagnosis, and Treatment Planning
Jun 08, 2025Lung cancer remains one of the most prevalent and fatal diseases worldwide, demanding accurate and timely diagnosis and treatment. Recent advancements in large AI models have significantly enhanced medical image understanding and clinical decision-making. This review systematically surveys the state-of-the-art in applying large AI models to lung cancer screening, diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment. We categorize existing models into modality-specific encoders, encoder-decoder frameworks, and joint encoder architectures, highlighting key examples such as CLIP, BLIP, Flamingo, BioViL-T, and GLoRIA. We further examine their performance in multimodal learning tasks using benchmark datasets like LIDC-IDRI, NLST, and MIMIC-CXR. Applications span pulmonary nodule detection, gene mutation prediction, multi-omics integration, and personalized treatment planning, with emerging evidence of clinical deployment and validation. Finally, we discuss current limitations in generalizability, interpretability, and regulatory compliance, proposing future directions for building scalable, explainable, and clinically integrated AI systems. Our review underscores the transformative potential of large AI models to personalize and optimize lung cancer care.
Describe Anything in Medical Images
May 09, 2025Localized image captioning has made significant progress with models like the Describe Anything Model (DAM), which can generate detailed region-specific descriptions without explicit region-text supervision. However, such capabilities have yet to be widely applied to specialized domains like medical imaging, where diagnostic interpretation relies on subtle regional findings rather than global understanding. To mitigate this gap, we propose MedDAM, the first comprehensive framework leveraging large vision-language models for region-specific captioning in medical images. MedDAM employs medical expert-designed prompts tailored to specific imaging modalities and establishes a robust evaluation benchmark comprising a customized assessment protocol, data pre-processing pipeline, and specialized QA template library. This benchmark evaluates both MedDAM and other adaptable large vision-language models, focusing on clinical factuality through attribute-level verification tasks, thereby circumventing the absence of ground-truth region-caption pairs in medical datasets. Extensive experiments on the VinDr-CXR, LIDC-IDRI, and SkinCon datasets demonstrate MedDAM's superiority over leading peers (including GPT-4o, Claude 3.7 Sonnet, LLaMA-3.2 Vision, Qwen2.5-VL, GPT-4Rol, and OMG-LLaVA) in the task, revealing the importance of region-level semantic alignment in medical image understanding and establishing MedDAM as a promising foundation for clinical vision-language integration.
Diffusion Based Ambiguous Image Segmentation
Apr 08, 2025Medical image segmentation often involves inherent uncertainty due to variations in expert annotations. Capturing this uncertainty is an important goal and previous works have used various generative image models for the purpose of representing the full distribution of plausible expert ground truths. In this work, we explore the design space of diffusion models for generative segmentation, investigating the impact of noise schedules, prediction types, and loss weightings. Notably, we find that making the noise schedule harder with input scaling significantly improves performance. We conclude that x- and v-prediction outperform epsilon-prediction, likely because the diffusion process is in the discrete segmentation domain. Many loss weightings achieve similar performance as long as they give enough weight to the end of the diffusion process. We base our experiments on the LIDC-IDRI lung lesion dataset and obtain state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance. Additionally, we introduce a randomly cropped variant of the LIDC-IDRI dataset that is better suited for uncertainty in image segmentation. Our model also achieves SOTA in this harder setting.
Hybrid CNN with Chebyshev Polynomial Expansion for Medical Image Analysis
Apr 09, 2025Lung cancer remains one of the leading causes of cancer-related mortality worldwide, with early and accurate diagnosis playing a pivotal role in improving patient outcomes. Automated detection of pulmonary nodules in computed tomography (CT) scans is a challenging task due to variability in nodule size, shape, texture, and location. Traditional Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have shown considerable promise in medical image analysis; however, their limited ability to capture fine-grained spatial-spectral variations restricts their performance in complex diagnostic scenarios. In this study, we propose a novel hybrid deep learning architecture that incorporates Chebyshev polynomial expansions into CNN layers to enhance expressive power and improve the representation of underlying anatomical structures. The proposed Chebyshev-CNN leverages the orthogonality and recursive properties of Chebyshev polynomials to extract high-frequency features and approximate complex nonlinear functions with greater fidelity. The model is trained and evaluated on benchmark lung cancer imaging datasets, including LUNA16 and LIDC-IDRI, achieving superior performance in classifying pulmonary nodules as benign or malignant. Quantitative results demonstrate significant improvements in accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity compared to traditional CNN-based approaches. This integration of polynomial-based spectral approximation within deep learning provides a robust framework for enhancing automated medical diagnostics and holds potential for broader applications in clinical decision support systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge