Meinrad Beer
FunnyNodules: A Customizable Medical Dataset Tailored for Evaluating Explainable AI
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:Densely annotated medical image datasets that capture not only diagnostic labels but also the underlying reasoning behind these diagnoses are scarce. Such reasoning-related annotations are essential for developing and evaluating explainable AI (xAI) models that reason similarly to radiologists: making correct predictions for the right reasons. To address this gap, we introduce FunnyNodules, a fully parameterized synthetic dataset designed for systematic analysis of attribute-based reasoning in medical AI models. The dataset generates abstract, lung nodule-like shapes with controllable visual attributes such as roundness, margin sharpness, and spiculation. Target class is derived from a predefined attribute combination, allowing full control over the decision rule that links attributes to the diagnostic class. We demonstrate how FunnyNodules can be used in model-agnostic evaluations to assess whether models learn correct attribute-target relations, to interpret over- or underperformance in attribute prediction, and to analyze attention alignment with attribute-specific regions of interest. The framework is fully customizable, supporting variations in dataset complexity, target definitions, class balance, and beyond. With complete ground truth information, FunnyNodules provides a versatile foundation for developing, benchmarking, and conducting in-depth analyses of explainable AI methods in medical image analysis.
Minimum Data, Maximum Impact: 20 annotated samples for explainable lung nodule classification
Aug 01, 2025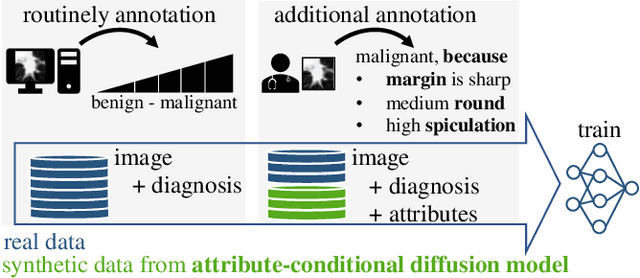
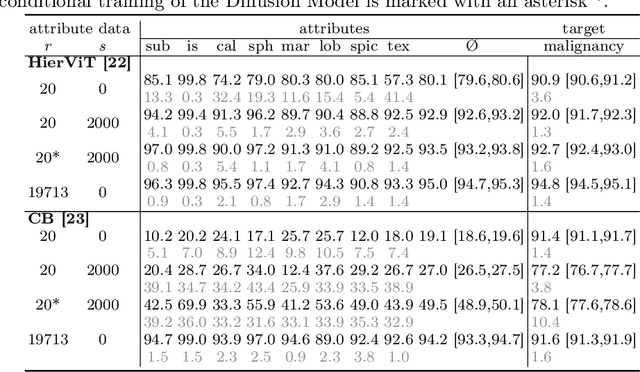
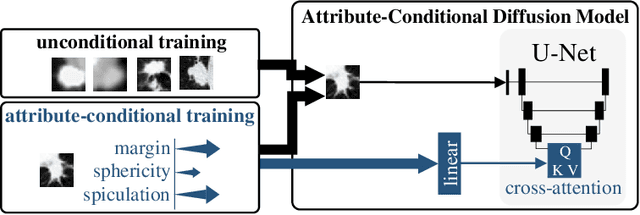
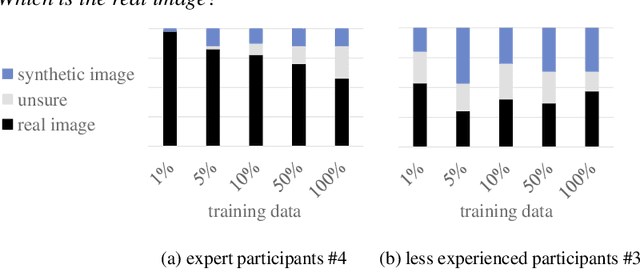
Abstract:Classification models that provide human-interpretable explanations enhance clinicians' trust and usability in medical image diagnosis. One research focus is the integration and prediction of pathology-related visual attributes used by radiologists alongside the diagnosis, aligning AI decision-making with clinical reasoning. Radiologists use attributes like shape and texture as established diagnostic criteria and mirroring these in AI decision-making both enhances transparency and enables explicit validation of model outputs. However, the adoption of such models is limited by the scarcity of large-scale medical image datasets annotated with these attributes. To address this challenge, we propose synthesizing attribute-annotated data using a generative model. We enhance the Diffusion Model with attribute conditioning and train it using only 20 attribute-labeled lung nodule samples from the LIDC-IDRI dataset. Incorporating its generated images into the training of an explainable model boosts performance, increasing attribute prediction accuracy by 13.4% and target prediction accuracy by 1.8% compared to training with only the small real attribute-annotated dataset. This work highlights the potential of synthetic data to overcome dataset limitations, enhancing the applicability of explainable models in medical image analysis.
Hierarchical Vision Transformer with Prototypes for Interpretable Medical Image Classification
Feb 13, 2025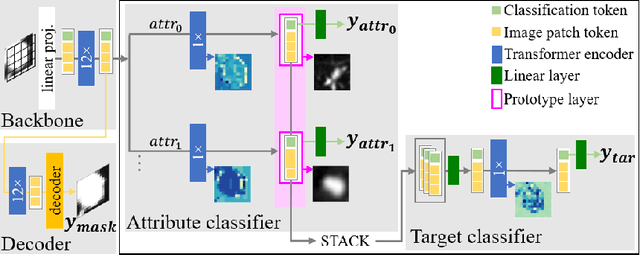
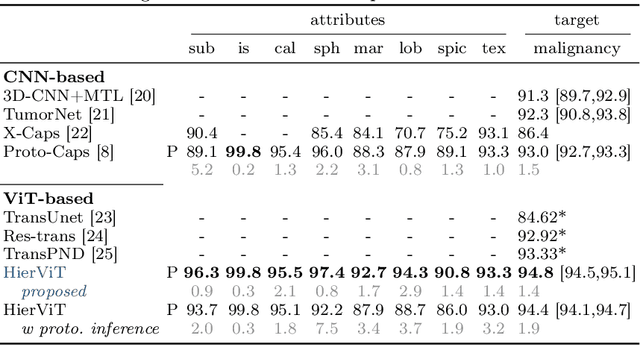
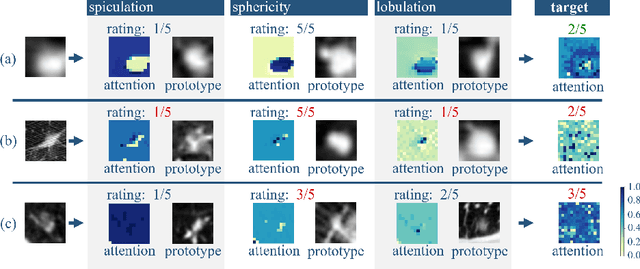
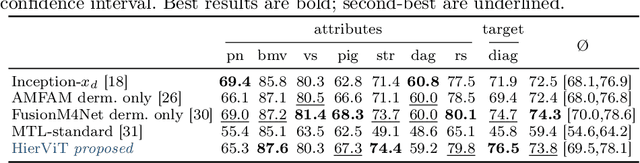
Abstract:Explainability is a highly demanded requirement for applications in high-risk areas such as medicine. Vision Transformers have mainly been limited to attention extraction to provide insight into the model's reasoning. Our approach combines the high performance of Vision Transformers with the introduction of new explainability capabilities. We present HierViT, a Vision Transformer that is inherently interpretable and adapts its reasoning to that of humans. A hierarchical structure is used to process domain-specific features for prediction. It is interpretable by design, as it derives the target output with human-defined features that are visualized by exemplary images (prototypes). By incorporating domain knowledge about these decisive features, the reasoning is semantically similar to human reasoning and therefore intuitive. Moreover, attention heatmaps visualize the crucial regions for identifying each feature, thereby providing HierViT with a versatile tool for validating predictions. Evaluated on two medical benchmark datasets, LIDC-IDRI for lung nodule assessment and derm7pt for skin lesion classification, HierViT achieves superior and comparable prediction accuracy, respectively, while offering explanations that align with human reasoning.
Less is More: Selective Reduction of CT Data for Self-Supervised Pre-Training of Deep Learning Models with Contrastive Learning Improves Downstream Classification Performance
Oct 18, 2024Abstract:Self-supervised pre-training of deep learning models with contrastive learning is a widely used technique in image analysis. Current findings indicate a strong potential for contrastive pre-training on medical images. However, further research is necessary to incorporate the particular characteristics of these images. We hypothesize that the similarity of medical images hinders the success of contrastive learning in the medical imaging domain. To this end, we investigate different strategies based on deep embedding, information theory, and hashing in order to identify and reduce redundancy in medical pre-training datasets. The effect of these different reduction strategies on contrastive learning is evaluated on two pre-training datasets and several downstream classification tasks. In all of our experiments, dataset reduction leads to a considerable performance gain in downstream tasks, e.g., an AUC score improvement from 0.78 to 0.83 for the COVID CT Classification Grand Challenge, 0.97 to 0.98 for the OrganSMNIST Classification Challenge and 0.73 to 0.83 for a brain hemorrhage classification task. Furthermore, pre-training is up to nine times faster due to the dataset reduction. In conclusion, the proposed approach highlights the importance of dataset quality and provides a transferable approach to improve contrastive pre-training for classification downstream tasks on medical images.
* Published in Computers in Biology and Medicine
Evaluating the Explainability of Attributes and Prototypes for a Medical Classification Model
Apr 15, 2024Abstract:Due to the sensitive nature of medicine, it is particularly important and highly demanded that AI methods are explainable. This need has been recognised and there is great research interest in xAI solutions with medical applications. However, there is a lack of user-centred evaluation regarding the actual impact of the explanations. We evaluate attribute- and prototype-based explanations with the Proto-Caps model. This xAI model reasons the target classification with human-defined visual features of the target object in the form of scores and attribute-specific prototypes. The model thus provides a multimodal explanation that is intuitively understandable to humans thanks to predefined attributes. A user study involving six radiologists shows that the explanations are subjectivly perceived as helpful, as they reflect their decision-making process. The results of the model are considered a second opinion that radiologists can discuss using the model's explanations. However, it was shown that the inclusion and increased magnitude of model explanations objectively can increase confidence in the model's predictions when the model is incorrect. We can conclude that attribute scores and visual prototypes enhance confidence in the model. However, additional development and repeated user studies are needed to tailor the explanation to the respective use case.
Interpretable Medical Image Classification using Prototype Learning and Privileged Information
Oct 24, 2023Abstract:Interpretability is often an essential requirement in medical imaging. Advanced deep learning methods are required to address this need for explainability and high performance. In this work, we investigate whether additional information available during the training process can be used to create an understandable and powerful model. We propose an innovative solution called Proto-Caps that leverages the benefits of capsule networks, prototype learning and the use of privileged information. Evaluating the proposed solution on the LIDC-IDRI dataset shows that it combines increased interpretability with above state-of-the-art prediction performance. Compared to the explainable baseline model, our method achieves more than 6 % higher accuracy in predicting both malignancy (93.0 %) and mean characteristic features of lung nodules. Simultaneously, the model provides case-based reasoning with prototype representations that allow visual validation of radiologist-defined attributes.
* MICCAI 2023 Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention
Dealing with Small Datasets for Deep Learning in Medical Imaging: An Evaluation of Self-Supervised Pre-Training on CT Scans Comparing Contrastive and Masked Autoencoder Methods for Convolutional Models
Aug 24, 2023Abstract:Deep learning in medical imaging has the potential to minimize the risk of diagnostic errors, reduce radiologist workload, and accelerate diagnosis. Training such deep learning models requires large and accurate datasets, with annotations for all training samples. However, in the medical imaging domain, annotated datasets for specific tasks are often small due to the high complexity of annotations, limited access, or the rarity of diseases. To address this challenge, deep learning models can be pre-trained on large image datasets without annotations using methods from the field of self-supervised learning. After pre-training, small annotated datasets are sufficient to fine-tune the models for a specific task. The most popular self-supervised pre-training approaches in medical imaging are based on contrastive learning. However, recent studies in natural image processing indicate a strong potential for masked autoencoder approaches. Our work compares state-of-the-art contrastive learning methods with the recently introduced masked autoencoder approach "SparK" for convolutional neural networks (CNNs) on medical images. Therefore we pre-train on a large unannotated CT image dataset and fine-tune on several CT classification tasks. Due to the challenge of obtaining sufficient annotated training data in medical imaging, it is of particular interest to evaluate how the self-supervised pre-training methods perform when fine-tuning on small datasets. By experimenting with gradually reducing the training dataset size for fine-tuning, we find that the reduction has different effects depending on the type of pre-training chosen. The SparK pre-training method is more robust to the training dataset size than the contrastive methods. Based on our results, we propose the SparK pre-training for medical imaging tasks with only small annotated datasets.
Improving COVID-19 CXR Detection with Synthetic Data Augmentation
Dec 14, 2021



Abstract:Since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, researchers have developed deep learning models to classify COVID-19 induced pneumonia. As with many medical imaging tasks, the quality and quantity of the available data is often limited. In this work we train a deep learning model on publicly available COVID-19 image data and evaluate the model on local hospital chest X-ray data. The data has been reviewed and labeled by two radiologists to ensure a high quality estimation of the generalization capabilities of the model. Furthermore, we are using a Generative Adversarial Network to generate synthetic X-ray images based on this data. Our results show that using those synthetic images for data augmentation can improve the model's performance significantly. This can be a promising approach for many sparse data domains.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge