Zhiyong Liu
Hierarchical Image Matching for UAV Absolute Visual Localization via Semantic and Structural Constraints
Jun 11, 2025

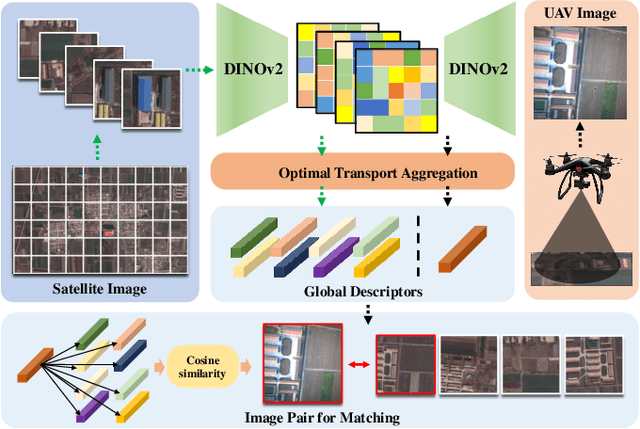

Abstract:Absolute localization, aiming to determine an agent's location with respect to a global reference, is crucial for unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) in various applications, but it becomes challenging when global navigation satellite system (GNSS) signals are unavailable. Vision-based absolute localization methods, which locate the current view of the UAV in a reference satellite map to estimate its position, have become popular in GNSS-denied scenarios. However, existing methods mostly rely on traditional and low-level image matching, suffering from difficulties due to significant differences introduced by cross-source discrepancies and temporal variations. To overcome these limitations, in this paper, we introduce a hierarchical cross-source image matching method designed for UAV absolute localization, which integrates a semantic-aware and structure-constrained coarse matching module with a lightweight fine-grained matching module. Specifically, in the coarse matching module, semantic features derived from a vision foundation model first establish region-level correspondences under semantic and structural constraints. Then, the fine-grained matching module is applied to extract fine features and establish pixel-level correspondences. Building upon this, a UAV absolute visual localization pipeline is constructed without any reliance on relative localization techniques, mainly by employing an image retrieval module before the proposed hierarchical image matching modules. Experimental evaluations on public benchmark datasets and a newly introduced CS-UAV dataset demonstrate superior accuracy and robustness of the proposed method under various challenging conditions, confirming its effectiveness.
Boosting Open-Vocabulary Object Detection by Handling Background Samples
Oct 11, 2024



Abstract:Open-vocabulary object detection is the task of accurately detecting objects from a candidate vocabulary list that includes both base and novel categories. Currently, numerous open-vocabulary detectors have achieved success by leveraging the impressive zero-shot capabilities of CLIP. However, we observe that CLIP models struggle to effectively handle background images (i.e. images without corresponding labels) due to their language-image learning methodology. This limitation results in suboptimal performance for open-vocabulary detectors that rely on CLIP when processing background samples. In this paper, we propose Background Information Representation for open-vocabulary Detector (BIRDet), a novel approach to address the limitations of CLIP in handling background samples. Specifically, we design Background Information Modeling (BIM) to replace the single, fixed background embedding in mainstream open-vocabulary detectors with dynamic scene information, and prompt it into image-related background representations. This method effectively enhances the ability to classify oversized regions as background. Besides, we introduce Partial Object Suppression (POS), an algorithm that utilizes the ratio of overlap area to address the issue of misclassifying partial regions as foreground. Experiments on OV-COCO and OV-LVIS benchmarks demonstrate that our proposed model is capable of achieving performance enhancements across various open-vocabulary detectors.
AIGC Empowering Telecom Sector White Paper_chinese
Jul 24, 2023Abstract:In the global craze of GPT, people have deeply realized that AI, as a transformative technology and key force in economic and social development, will bring great leaps and breakthroughs to the global industry and profoundly influence the future world competition pattern. As the builder and operator of information and communication infrastructure, the telecom sector provides infrastructure support for the development of AI, and even takes the lead in the implementation of AI applications. How to enable the application of AIGC (GPT) and implement AIGC in the telecom sector are questions that telecom practitioners must ponder and answer. Through the study of GPT, a typical representative of AIGC, the authors have analyzed how GPT empowers the telecom sector in the form of scenarios, discussed the gap between the current GPT general model and telecom services, proposed for the first time a Telco Augmented Cognition capability system, provided answers to how to construct a telecom service GPT in the telecom sector, and carried out various practices. Our counterparts in the industry are expected to focus on collaborative innovation around telecom and AI, build an open and shared innovation ecosystem, promote the deep integration of AI and telecom sector, and accelerate the construction of next-generation information infrastructure, in an effort to facilitate the digital transformation of the economy and society.
Refined Pseudo labeling for Source-free Domain Adaptive Object Detection
Mar 07, 2023



Abstract:Domain adaptive object detection (DAOD) assumes that both labeled source data and unlabeled target data are available for training, but this assumption does not always hold in real-world scenarios. Thus, source-free DAOD is proposed to adapt the source-trained detectors to target domains with only unlabeled target data. Existing source-free DAOD methods typically utilize pseudo labeling, where the performance heavily relies on the selection of confidence threshold. However, most prior works adopt a single fixed threshold for all classes to generate pseudo labels, which ignore the imbalanced class distribution, resulting in biased pseudo labels. In this work, we propose a refined pseudo labeling framework for source-free DAOD. First, to generate unbiased pseudo labels, we present a category-aware adaptive threshold estimation module, which adaptively provides the appropriate threshold for each category. Second, to alleviate incorrect box regression, a localization-aware pseudo label assignment strategy is introduced to divide labels into certain and uncertain ones and optimize them separately. Finally, extensive experiments on four adaptation tasks demonstrate the effectiveness of our method.
FIT: Frequency-based Image Translation for Domain Adaptive Object Detection
Mar 07, 2023Abstract:Domain adaptive object detection (DAOD) aims to adapt the detector from a labelled source domain to an unlabelled target domain. In recent years, DAOD has attracted massive attention since it can alleviate performance degradation due to the large shift of data distributions in the wild. To align distributions between domains, adversarial learning is widely used in existing DAOD methods. However, the decision boundary for the adversarial domain discriminator may be inaccurate, causing the model biased towards the source domain. To alleviate this bias, we propose a novel Frequency-based Image Translation (FIT) framework for DAOD. First, by keeping domain-invariant frequency components and swapping domain-specific ones, we conduct image translation to reduce domain shift at the input level. Second, hierarchical adversarial feature learning is utilized to further mitigate the domain gap at the feature level. Finally, we design a joint loss to train the entire network in an end-to-end manner without extra training to obtain translated images. Extensive experiments on three challenging DAOD benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of our method.
Automatically Discovering Novel Visual Categories with Self-supervised Prototype Learning
Aug 01, 2022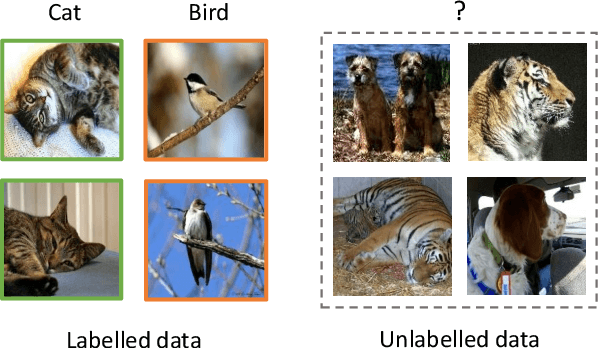
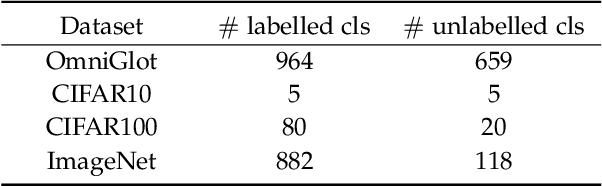
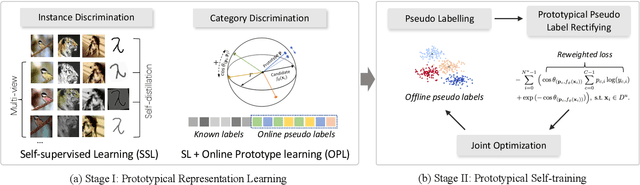
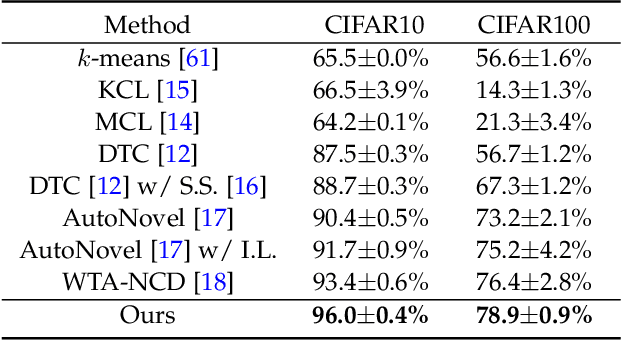
Abstract:This paper tackles the problem of novel category discovery (NCD), which aims to discriminate unknown categories in large-scale image collections. The NCD task is challenging due to the closeness to the real-world scenarios, where we have only encountered some partial classes and images. Unlike other works on the NCD, we leverage the prototypes to emphasize the importance of category discrimination and alleviate the issue of missing annotations of novel classes. Concretely, we propose a novel adaptive prototype learning method consisting of two main stages: prototypical representation learning and prototypical self-training. In the first stage, we obtain a robust feature extractor, which could serve for all images with base and novel categories. This ability of instance and category discrimination of the feature extractor is boosted by self-supervised learning and adaptive prototypes. In the second stage, we utilize the prototypes again to rectify offline pseudo labels and train a final parametric classifier for category clustering. We conduct extensive experiments on four benchmark datasets and demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed method with state-of-the-art performance.
Zero-shot object goal visual navigation
Jun 15, 2022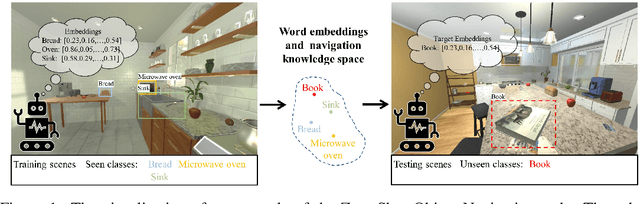
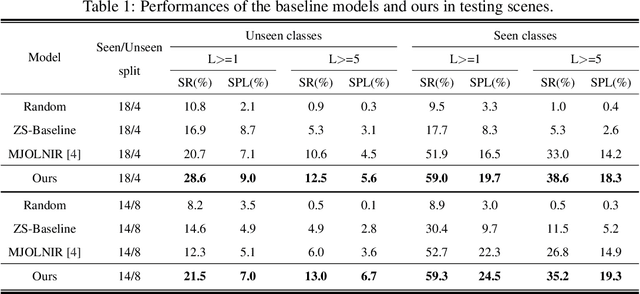
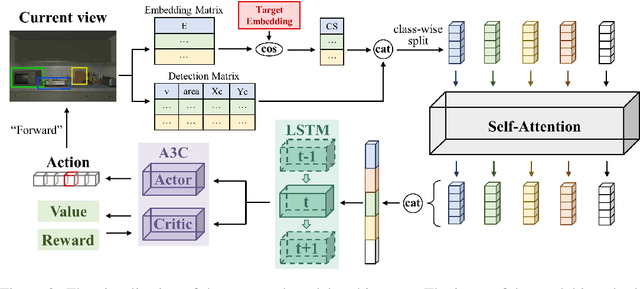
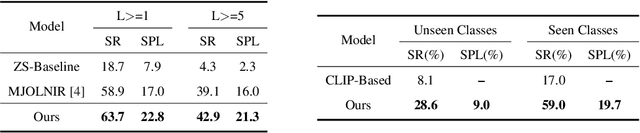
Abstract:Object goal visual navigation is a challenging task that aims to guide a robot to find the target object only based on its visual observation, and the target is limited to the classes specified in the training stage. However, in real households, there may exist numerous object classes that the robot needs to deal with, and it is hard for all of these classes to be contained in the training stage. To address this challenge, we propose a zero-shot object navigation task by combining zero-shot learning with object goal visual navigation, which aims at guiding robots to find objects belonging to novel classes without any training samples. This task gives rise to the need to generalize the learned policy to novel classes, which is a less addressed issue of object navigation using deep reinforcement learning. To address this issue, we utilize "class-unrelated" data as input to alleviate the overfitting of the classes specified in the training stage. The class-unrelated input consists of detection results and cosine similarity of word embeddings, and does not contain any class-related visual features or knowledge graphs. Extensive experiments on the AI2-THOR platform show that our model outperforms the baseline models in both seen and unseen classes, which proves that our model is less class-sensitive and generalizes better. Our code is available at https://github.com/pioneer-innovation/Zero-Shot-Object-Navigation
Weakly Aligned Feature Fusion for Multimodal Object Detection
Apr 21, 2022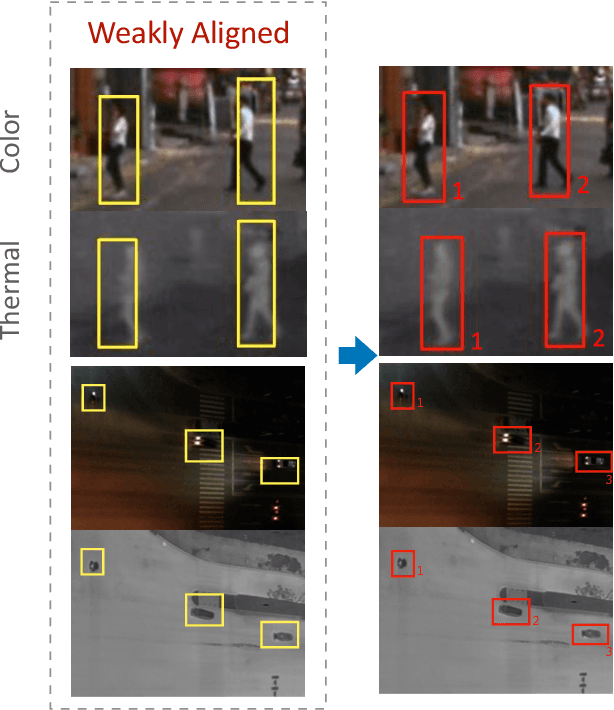
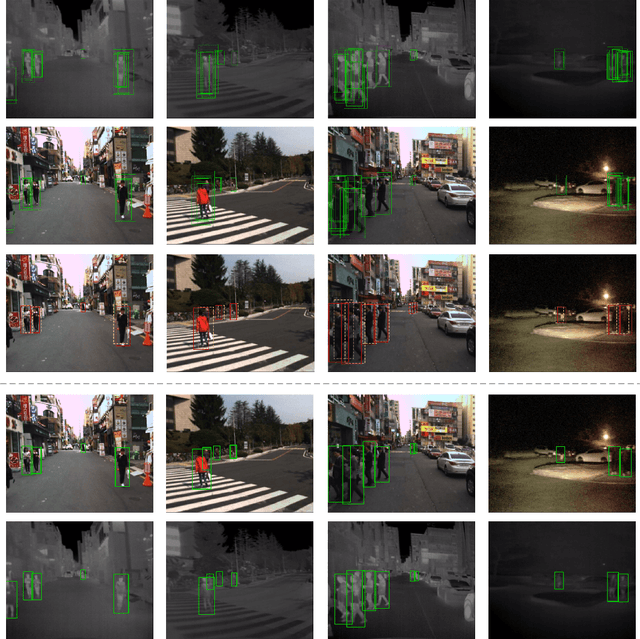
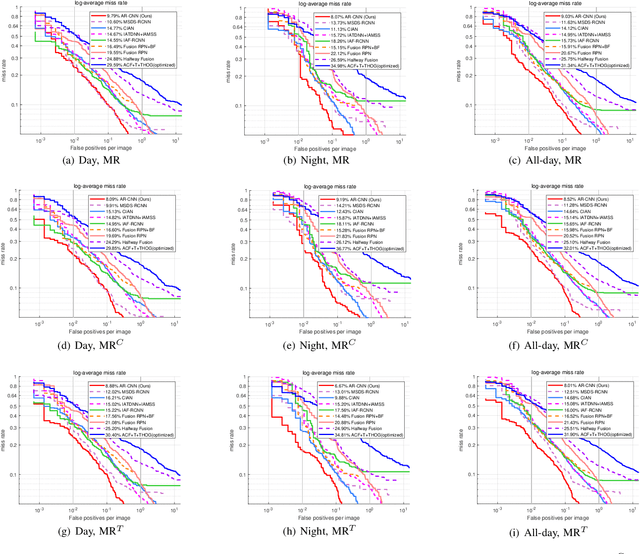


Abstract:To achieve accurate and robust object detection in the real-world scenario, various forms of images are incorporated, such as color, thermal, and depth. However, multimodal data often suffer from the position shift problem, i.e., the image pair is not strictly aligned, making one object has different positions in different modalities. For the deep learning method, this problem makes it difficult to fuse multimodal features and puzzles the convolutional neural network (CNN) training. In this article, we propose a general multimodal detector named aligned region CNN (AR-CNN) to tackle the position shift problem. First, a region feature (RF) alignment module with adjacent similarity constraint is designed to consistently predict the position shift between two modalities and adaptively align the cross-modal RFs. Second, we propose a novel region of interest (RoI) jitter strategy to improve the robustness to unexpected shift patterns. Third, we present a new multimodal feature fusion method that selects the more reliable feature and suppresses the less useful one via feature reweighting. In addition, by locating bounding boxes in both modalities and building their relationships, we provide novel multimodal labeling named KAIST-Paired. Extensive experiments on 2-D and 3-D object detection, RGB-T, and RGB-D datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of our method.
Unseen Object Instance Segmentation with Fully Test-time RGB-D Embeddings Adaptation
Apr 21, 2022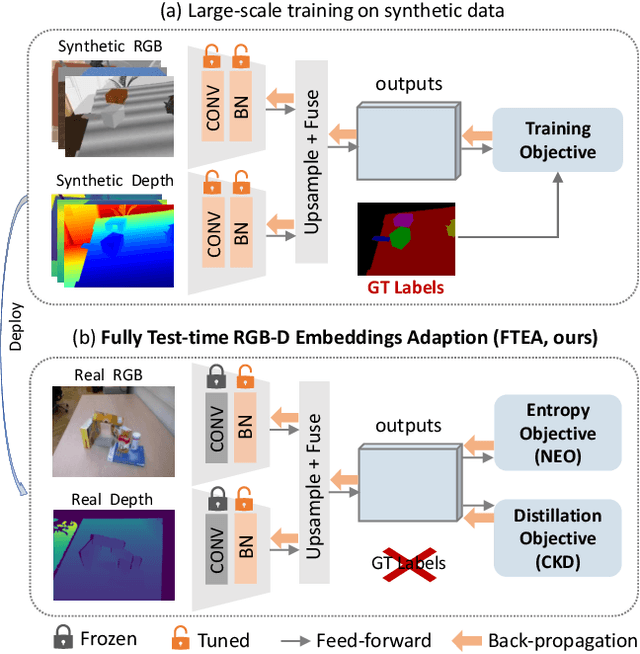
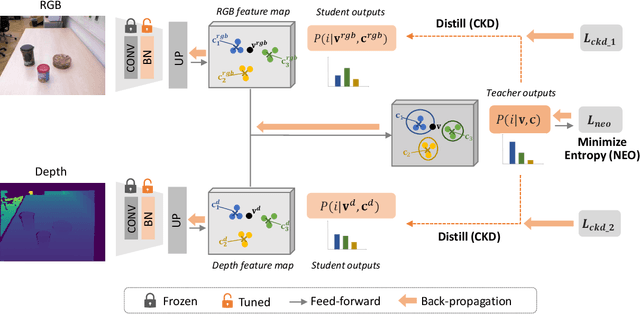
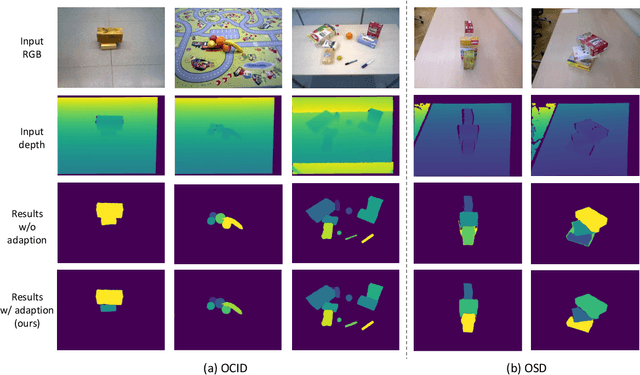
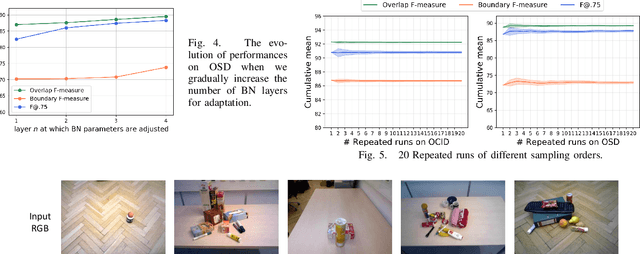
Abstract:Segmenting unseen objects is a crucial ability for the robot since it may encounter new environments during the operation. Recently, a popular solution is leveraging RGB-D features of large-scale synthetic data and directly applying the model to unseen real-world scenarios. However, even though depth data have fair generalization ability, the domain shift due to the Sim2Real gap is inevitable, which presents a key challenge to the unseen object instance segmentation (UOIS) model. To tackle this problem, we re-emphasize the adaptation process across Sim2Real domains in this paper. Specifically, we propose a framework to conduct the Fully Test-time RGB-D Embeddings Adaptation (FTEA) based on parameters of the BatchNorm layer. To construct the learning objective for test-time back-propagation, we propose a novel non-parametric entropy objective that can be implemented without explicit classification layers. Moreover, we design a cross-modality knowledge distillation module to encourage the information transfer during test time. The proposed method can be efficiently conducted with test-time images, without requiring annotations or revisiting the large-scale synthetic training data. Besides significant time savings, the proposed method consistently improves segmentation results on both overlap and boundary metrics, achieving state-of-the-art performances on two real-world RGB-D image datasets. We hope our work could draw attention to the test-time adaptation and reveal a promising direction for robot perception in unseen environments.
The Cross-Modality Disparity Problem in Multispectral Pedestrian Detection
Jan 09, 2019



Abstract:Aggregating extra features of novel modality brings great advantages for building robust pedestrian detector under adverse illumination conditions. However, misaligned imagery still persists in multispectral scenario and will depress the performance of detector in a non-trivial way. In this paper, we first present and explore the cross-modality disparity problem in multispectral pedestrian detection, providing insights into the utilization of multimodal inputs. Then, to further address this issue, we propose a novel framework including a region feature alignment module and the region of interest (RoI) jittering training strategy. Moreover, dense, high-quality, and modality-independent color-thermal annotation pairs are provided to scrub the large-scale KAIST dataset to benefit future multispectral detection research. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed approach improves the robustness of detector with a large margin and achieves state-of-the-art performance with high efficiency. Code and data will be publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge