Zhigang Chang
Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Revisiting Multi-Granularity Representation via Group Contrastive Learning for Unsupervised Vehicle Re-identification
Oct 29, 2024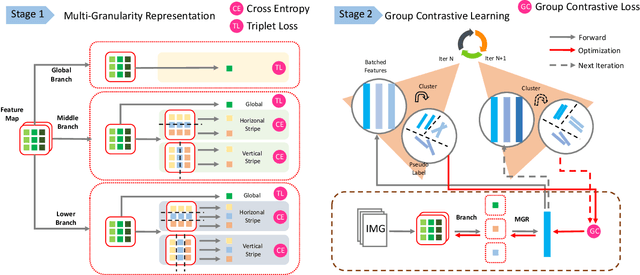



Abstract:Vehicle re-identification (Vehicle ReID) aims at retrieving vehicle images across disjoint surveillance camera views. The majority of vehicle ReID research is heavily reliant upon supervisory labels from specific human-collected datasets for training. When applied to the large-scale real-world scenario, these models will experience dreadful performance declines due to the notable domain discrepancy between the source dataset and the target. To address this challenge, in this paper, we propose an unsupervised vehicle ReID framework (MGR-GCL). It integrates a multi-granularity CNN representation for learning discriminative transferable features and a contrastive learning module responsible for efficient domain adaptation in the unlabeled target domain. Specifically, after training the proposed Multi-Granularity Representation (MGR) on the labeled source dataset, we propose a group contrastive learning module (GCL) to generate pseudo labels for the target dataset, facilitating the domain adaptation process. We conducted extensive experiments and the results demonstrated our superiority against existing state-of-the-art methods.
HorGait: Advancing Gait Recognition with Efficient High-Order Spatial Interactions in LiDAR Point Clouds
Oct 11, 2024Abstract:Gait recognition is a remote biometric technology that utilizes the dynamic characteristics of human movement to identify individuals even under various extreme lighting conditions. Due to the limitation in spatial perception capability inherent in 2D gait representations, LiDAR can directly capture 3D gait features and represent them as point clouds, reducing environmental and lighting interference in recognition while significantly advancing privacy protection. For complex 3D representations, shallow networks fail to achieve accurate recognition, making vision Transformers the foremost prevalent method. However, the prevalence of dumb patches has limited the widespread use of Transformer architecture in gait recognition. This paper proposes a method named HorGait, which utilizes a hybrid model with a Transformer architecture for gait recognition on the planar projection of 3D point clouds from LiDAR. Specifically, it employs a hybrid model structure called LHM Block to achieve input adaptation, long-range, and high-order spatial interaction of the Transformer architecture. Additionally, it uses large convolutional kernel CNNs to segment the input representation, replacing attention windows to reduce dumb patches. We conducted extensive experiments, and the results show that HorGait achieves state-of-the-art performance among Transformer architecture methods on the SUSTech1K dataset, verifying that the hybrid model can complete the full Transformer process and perform better in point cloud planar projection. The outstanding performance of HorGait offers new insights for the future application of the Transformer architecture in gait recognition.
SpheriGait: Enriching Spatial Representation via Spherical Projection for LiDAR-based Gait Recognition
Sep 18, 2024Abstract:Gait recognition is a rapidly progressing technique for the remote identification of individuals. Prior research predominantly employing 2D sensors to gather gait data has achieved notable advancements; nonetheless, they have unavoidably neglected the influence of 3D dynamic characteristics on recognition. Gait recognition utilizing LiDAR 3D point clouds not only directly captures 3D spatial features but also diminishes the impact of lighting conditions while ensuring privacy protection.The essence of the problem lies in how to effectively extract discriminative 3D dynamic representation from point clouds.In this paper, we proposes a method named SpheriGait for extracting and enhancing dynamic features from point clouds for Lidar-based gait recognition. Specifically, it substitutes the conventional point cloud plane projection method with spherical projection to augment the perception of dynamic feature.Additionally, a network block named DAM-L is proposed to extract gait cues from the projected point cloud data. We conducted extensive experiments and the results demonstrated the SpheriGait achieved state-of-the-art performance on the SUSTech1K dataset, and verified that the spherical projection method can serve as a universal data preprocessing technique to enhance the performance of other LiDAR-based gait recognition methods, exhibiting exceptional flexibility and practicality.
Hierarchical Semantic Perceptual Listener Head Video Generation: A High-performance Pipeline
Jul 19, 2023Abstract:In dyadic speaker-listener interactions, the listener's head reactions along with the speaker's head movements, constitute an important non-verbal semantic expression together. The listener Head generation task aims to synthesize responsive listener's head videos based on audios of the speaker and reference images of the listener. Compared to the Talking-head generation, it is more challenging to capture the correlation clues from the speaker's audio and visual information. Following the ViCo baseline scheme, we propose a high-performance solution by enhancing the hierarchical semantic extraction capability of the audio encoder module and improving the decoder part, renderer and post-processing modules. Our solution gets the first place on the official leaderboard for the track of listening head generation. This paper is a technical report of ViCo@2023 Conversational Head Generation Challenge in ACM Multimedia 2023 conference.
Seq-Masks: Bridging the gap between appearance and gait modeling for video-based person re-identification
Dec 10, 2021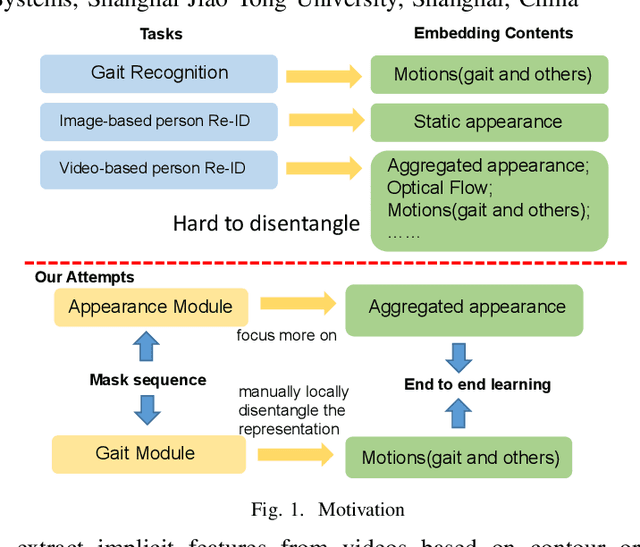
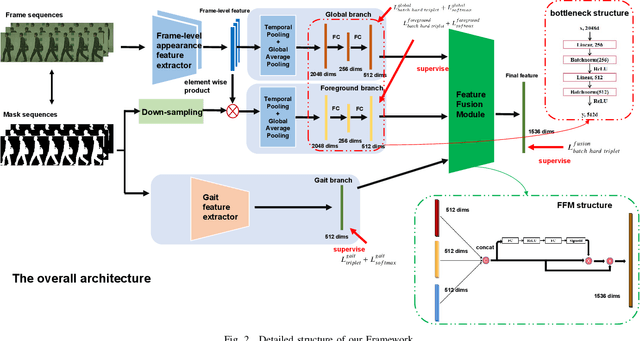
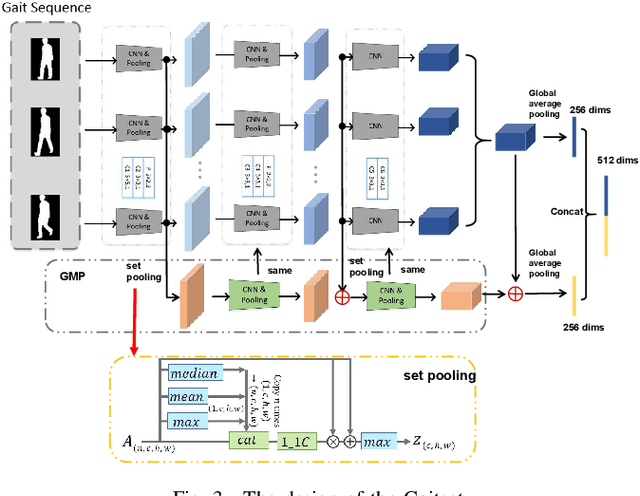
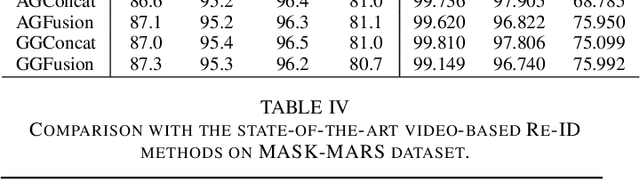
Abstract:ideo-based person re-identification (Re-ID) aims to match person images in video sequences captured by disjoint surveillance cameras. Traditional video-based person Re-ID methods focus on exploring appearance information, thus, vulnerable against illumination changes, scene noises, camera parameters, and especially clothes/carrying variations. Gait recognition provides an implicit biometric solution to alleviate the above headache. Nonetheless, it experiences severe performance degeneration as camera view varies. In an attempt to address these problems, in this paper, we propose a framework that utilizes the sequence masks (SeqMasks) in the video to integrate appearance information and gait modeling in a close fashion. Specifically, to sufficiently validate the effectiveness of our method, we build a novel dataset named MaskMARS based on MARS. Comprehensive experiments on our proposed large wild video Re-ID dataset MaskMARS evidenced our extraordinary performance and generalization capability. Validations on the gait recognition metric CASIA-B dataset further demonstrated the capability of our hybrid model.
TransHash: Transformer-based Hamming Hashing for Efficient Image Retrieval
May 05, 2021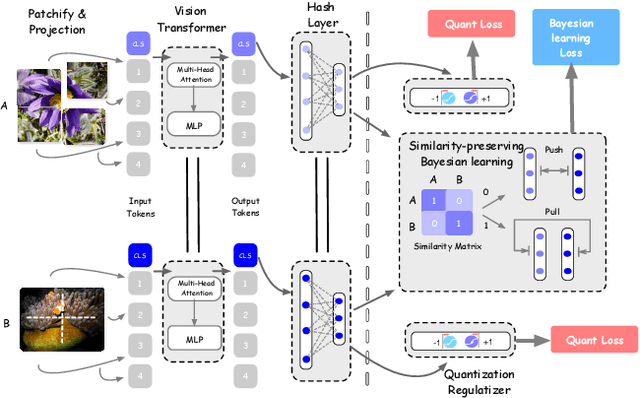
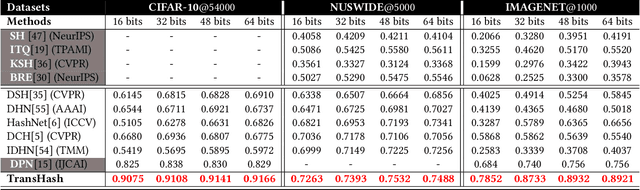
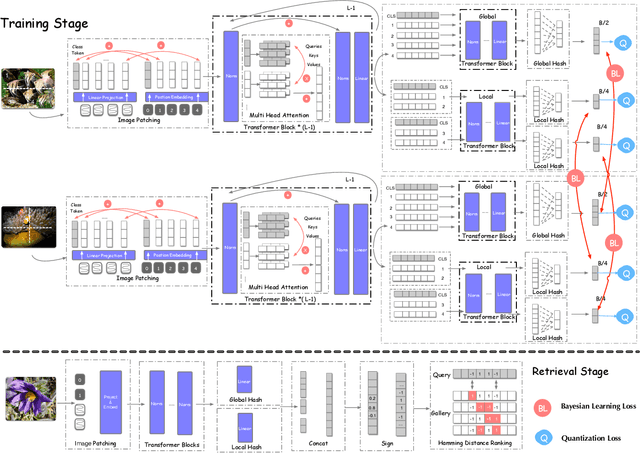
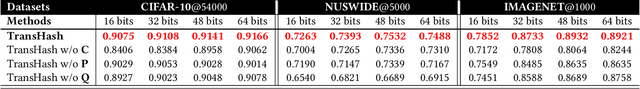
Abstract:Deep hamming hashing has gained growing popularity in approximate nearest neighbour search for large-scale image retrieval. Until now, the deep hashing for the image retrieval community has been dominated by convolutional neural network architectures, e.g. \texttt{Resnet}\cite{he2016deep}. In this paper, inspired by the recent advancements of vision transformers, we present \textbf{Transhash}, a pure transformer-based framework for deep hashing learning. Concretely, our framework is composed of two major modules: (1) Based on \textit{Vision Transformer} (ViT), we design a siamese vision transformer backbone for image feature extraction. To learn fine-grained features, we innovate a dual-stream feature learning on top of the transformer to learn discriminative global and local features. (2) Besides, we adopt a Bayesian learning scheme with a dynamically constructed similarity matrix to learn compact binary hash codes. The entire framework is jointly trained in an end-to-end manner.~To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to tackle deep hashing learning problems without convolutional neural networks (\textit{CNNs}). We perform comprehensive experiments on three widely-studied datasets: \textbf{CIFAR-10}, \textbf{NUSWIDE} and \textbf{IMAGENET}. The experiments have evidenced our superiority against the existing state-of-the-art deep hashing methods. Specifically, we achieve 8.2\%, 2.6\%, 12.7\% performance gains in terms of average \textit{mAP} for different hash bit lengths on three public datasets, respectively.
Distribution Context Aware Loss for Person Re-identification
Nov 17, 2019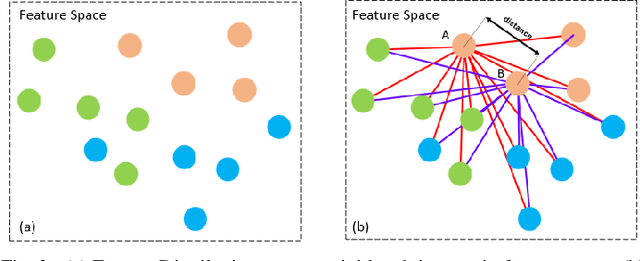
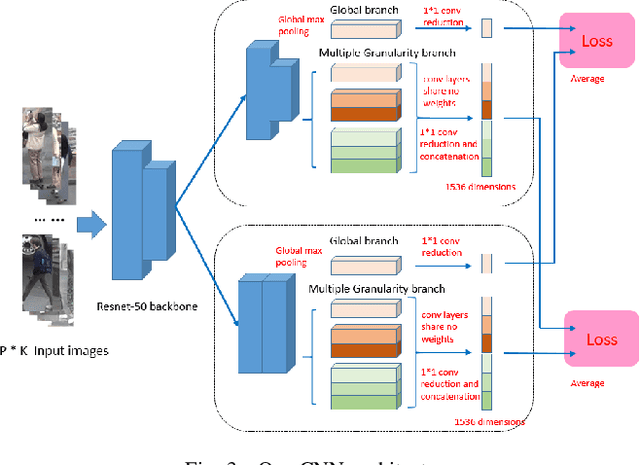

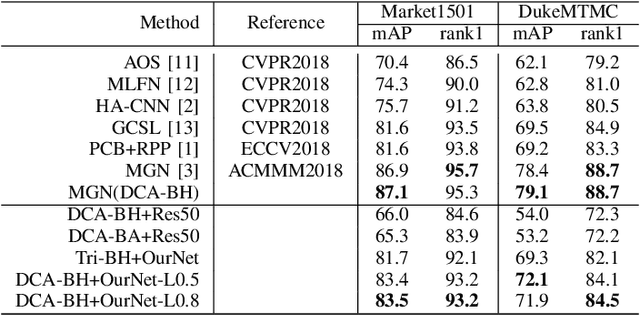
Abstract:To learn the optimal similarity function between probe and gallery images in Person re-identification, effective deep metric learning methods have been extensively explored to obtain discriminative feature embedding. However, existing metric loss like triplet loss and its variants always emphasize pair-wise relations but ignore the distribution context in feature space, leading to inconsistency and sub-optimal. In fact, the similarity of one pair not only decides the match of this pair, but also has potential impacts on other sample pairs. In this paper, we propose a novel Distribution Context Aware (DCA) loss based on triplet loss to combine both numerical similarity and relation similarity in feature space for better clustering. Extensive experiments on three benchmarks including Market-1501, DukeMTMC-reID and MSMT17, evidence the favorable performance of our method against the corresponding baseline and other state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge