Zhen Mei
Deep Transfer Learning-based Detection for Flash Memory Channels
Oct 08, 2024



Abstract:The NAND flash memory channel is corrupted by different types of noises, such as the data retention noise and the wear-out noise, which lead to unknown channel offset and make the flash memory channel non-stationary. In the literature, machine learning-based methods have been proposed for data detection for flash memory channels. However, these methods require a large number of training samples and labels to achieve a satisfactory performance, which is costly. Furthermore, with a large unknown channel offset, it may be impossible to obtain enough correct labels. In this paper, we reformulate the data detection for the flash memory channel as a transfer learning (TL) problem. We then propose a model-based deep TL (DTL) algorithm for flash memory channel detection. It can effectively reduce the training data size from $10^6$ samples to less than 104 samples. Moreover, we propose an unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA)-based DTL algorithm using moment alignment, which can detect data without any labels. Hence, it is suitable for scenarios where the decoding of error-correcting code fails and no labels can be obtained. Finally, a UDA-based threshold detector is proposed to eliminate the need for a neural network. Both the channel raw error rate analysis and simulation results demonstrate that the proposed DTL-based detection schemes can achieve near-optimal bit error rate (BER) performance with much less training data and/or without using any labels.
Deep Learning-Based Decoding of Linear Block Codes for Spin-Torque Transfer Magnetic Random Access Memory (STT-MRAM)
Oct 08, 2024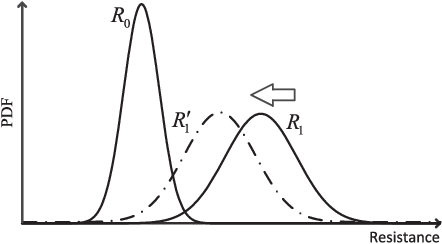
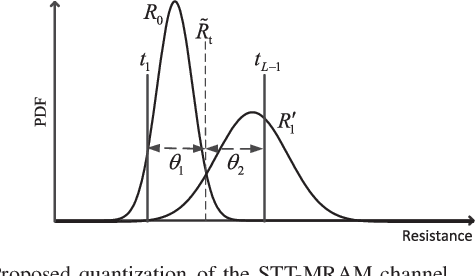
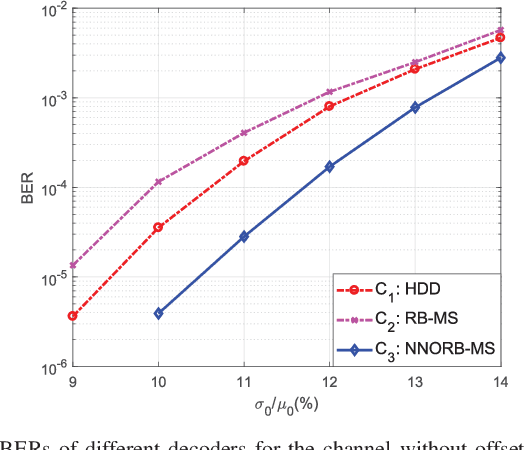
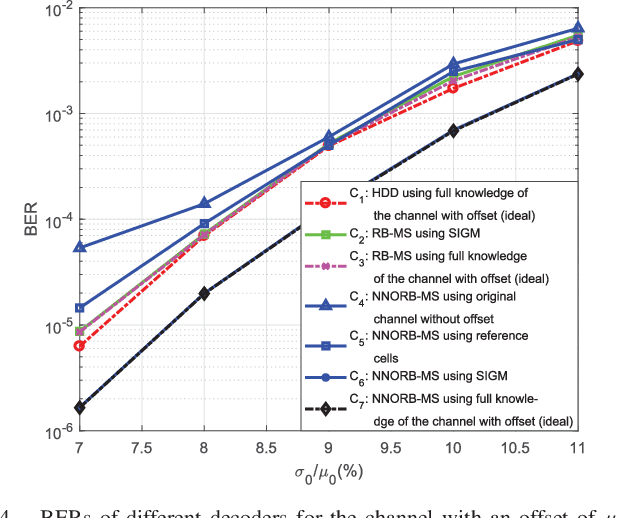
Abstract:Thanks to its superior features of fast read/write speed and low power consumption, spin-torque transfer magnetic random access memory (STT-MRAM) has become a promising non-volatile memory (NVM) technology that is suitable for many applications. However, the reliability of STT-MRAM is seriously affected by the variation of the memory fabrication process and the working temperature, and the later will lead to an unknown offset of the channel. Hence, there is a pressing need to develop more effective error correction coding techniques to tackle these imperfections and improve the reliability of STT-MRAM. In this work, we propose, for the first time, the application of deep-learning (DL) based algorithms and techniques to improve the decoding performance of linear block codes with short codeword lengths for STT-MRAM. We formulate the belief propagation (BP) decoding of linear block code as a neural network (NN), and propose a novel neural normalized-offset reliability-based min-sum (NNORB-MS) decoding algorithm. We successfully apply our proposed decoding algorithm to the STT-MRAM channel through channel symmetrization to overcome the channel asymmetry. We also propose an NN-based soft information generation method (SIGM) to take into account the unknown offset of the channel. Simulation results demonstrate that our proposed NNORB-MS decoding algorithm can achieve significant performance gain over both the hard-decision decoding (HDD) and the regular reliability-based min-sum (RB-MS) decoding algorithm, for cases without and with the unknown channel offset. Moreover, the decoder structure and time complexity of the NNORB-MS algorithm remain similar to those of the regular RB-MS algorithm.
Federated Meta-Learning for Few-Shot Fault Diagnosis with Representation Encoding
Oct 13, 2023



Abstract:Deep learning-based fault diagnosis (FD) approaches require a large amount of training data, which are difficult to obtain since they are located across different entities. Federated learning (FL) enables multiple clients to collaboratively train a shared model with data privacy guaranteed. However, the domain discrepancy and data scarcity problems among clients deteriorate the performance of the global FL model. To tackle these issues, we propose a novel framework called representation encoding-based federated meta-learning (REFML) for few-shot FD. First, a novel training strategy based on representation encoding and meta-learning is developed. It harnesses the inherent heterogeneity among training clients, effectively transforming it into an advantage for out-of-distribution generalization on unseen working conditions or equipment types. Additionally, an adaptive interpolation method that calculates the optimal combination of local and global models as the initialization of local training is proposed. This helps to further utilize local information to mitigate the negative effects of domain discrepancy. As a result, high diagnostic accuracy can be achieved on unseen working conditions or equipment types with limited training data. Compared with the state-of-the-art methods, such as FedProx, the proposed REFML framework achieves an increase in accuracy by 2.17%-6.50% when tested on unseen working conditions of the same equipment type and 13.44%-18.33% when tested on totally unseen equipment types, respectively.
Analysis and Optimization of Wireless Federated Learning with Data Heterogeneity
Aug 04, 2023



Abstract:With the rapid proliferation of smart mobile devices, federated learning (FL) has been widely considered for application in wireless networks for distributed model training. However, data heterogeneity, e.g., non-independently identically distributions and different sizes of training data among clients, poses major challenges to wireless FL. Limited communication resources complicate the implementation of fair scheduling which is required for training on heterogeneous data, and further deteriorate the overall performance. To address this issue, this paper focuses on performance analysis and optimization for wireless FL, considering data heterogeneity, combined with wireless resource allocation. Specifically, we first develop a closed-form expression for an upper bound on the FL loss function, with a particular emphasis on data heterogeneity described by a dataset size vector and a data divergence vector. Then we formulate the loss function minimization problem, under constraints on long-term energy consumption and latency, and jointly optimize client scheduling, resource allocation, and the number of local training epochs (CRE). Next, via the Lyapunov drift technique, we transform the CRE optimization problem into a series of tractable problems. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate that the proposed algorithm outperforms other benchmarks in terms of the learning accuracy and energy consumption.
Efficient Joint-Dimensional Search with Solution Space Regularization for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation
Aug 10, 2022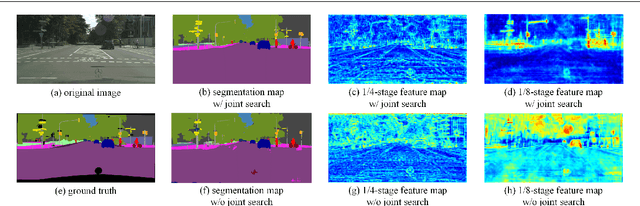
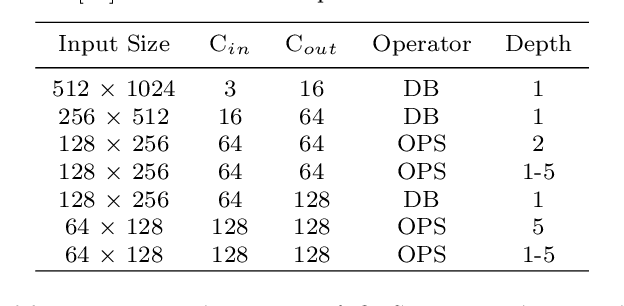
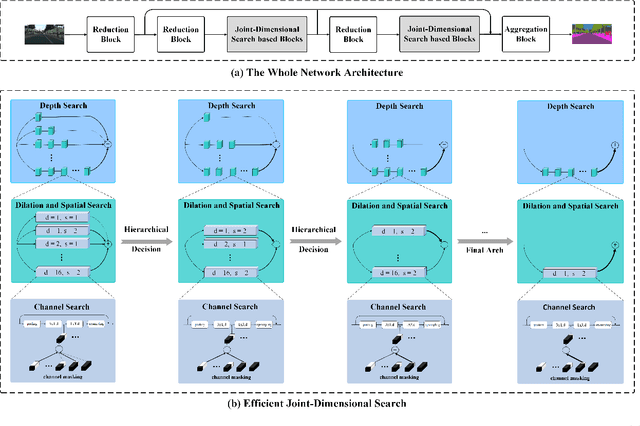
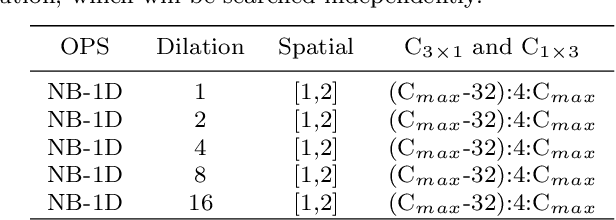
Abstract:Semantic segmentation is a popular research topic in computer vision, and many efforts have been made on it with impressive results. In this paper, we intend to search an optimal network structure that can run in real-time for this problem. Towards this goal, we jointly search the depth, channel, dilation rate and feature spatial resolution, which results in a search space consisting of about 2.78*10^324 possible choices. To handle such a large search space, we leverage differential architecture search methods. However, the architecture parameters searched using existing differential methods need to be discretized, which causes the discretization gap between the architecture parameters found by the differential methods and their discretized version as the final solution for the architecture search. Hence, we relieve the problem of discretization gap from the innovative perspective of solution space regularization. Specifically, a novel Solution Space Regularization (SSR) loss is first proposed to effectively encourage the supernet to converge to its discrete one. Then, a new Hierarchical and Progressive Solution Space Shrinking method is presented to further achieve high efficiency of searching. In addition, we theoretically show that the optimization of SSR loss is equivalent to the L_0-norm regularization, which accounts for the improved search-evaluation gap. Comprehensive experiments show that the proposed search scheme can efficiently find an optimal network structure that yields an extremely fast speed (175 FPS) of segmentation with a small model size (1 M) while maintaining comparable accuracy.
DNN-aided Read-voltage Threshold Optimization for MLC Flash Memory with Finite Block Length
Apr 11, 2020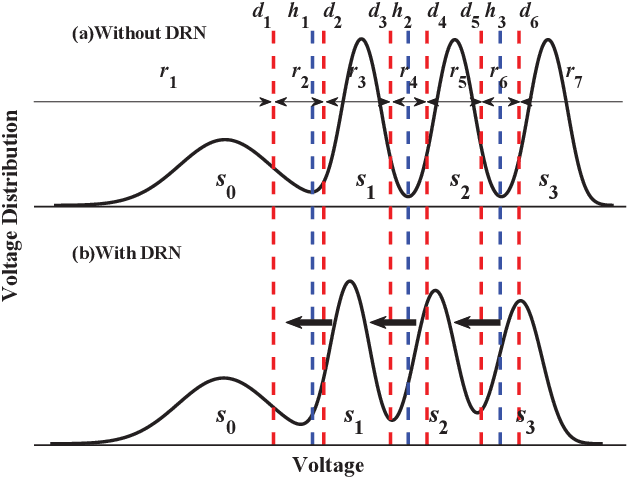
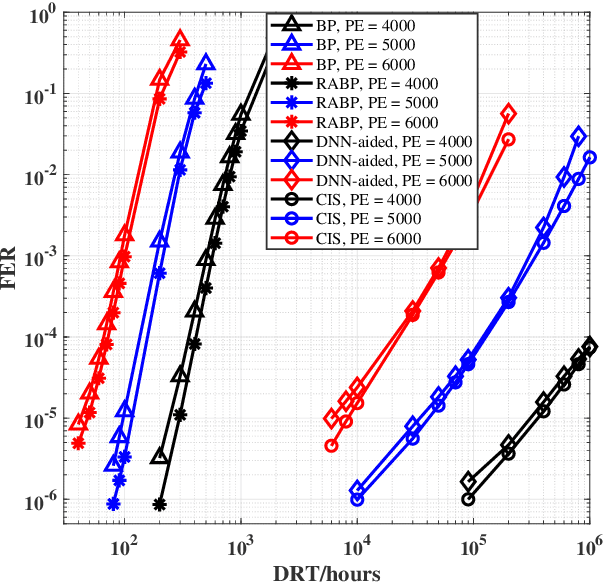
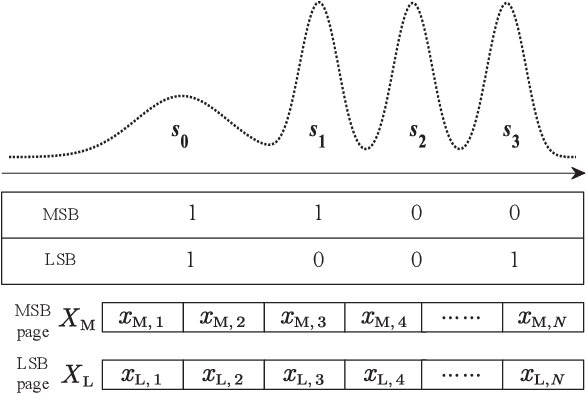
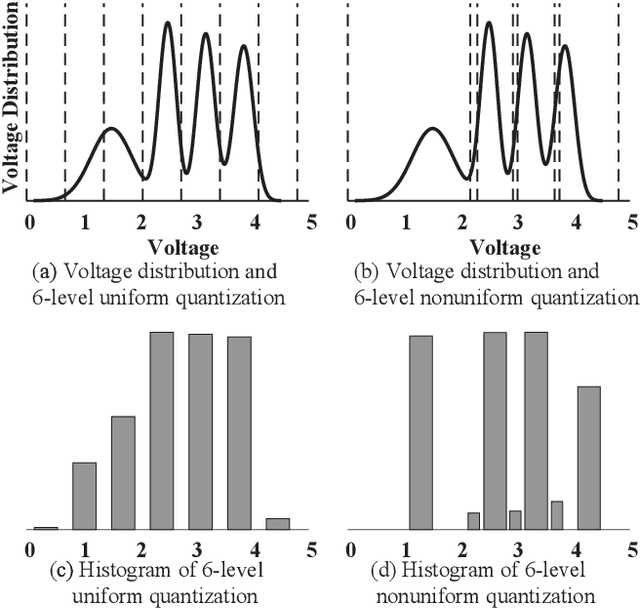
Abstract:The error correcting performance of multi-level-cell (MLC) NAND flash memory is closely related to the block length of error correcting codes (ECCs) and log-likelihood-ratios (LLRs) of the read-voltage thresholds. Driven by this issue, this paper optimizes the read-voltage thresholds for MLC flash memory to improve the decoding performance of ECCs with finite block length. First, through the analysis of channel coding rate (CCR) and decoding error probability under finite block length, we formulate the optimization problem of read-voltage thresholds to minimize the maximum decoding error probability. Second, we develop a cross iterative search (CIS) algorithm to optimize read-voltage thresholds under the perfect knowledge of flash memory channel. However, it is challenging to analytically characterize the voltage distribution under the effect of data retention noise (DRN), since the data retention time (DRT) is hard to be recorded for flash memory in reality. To address this problem, we develop a deep neural network (DNN) aided optimization strategy to optimize the read-voltage thresholds, where a multi-layer perception (MLP) network is employed to learn the relationship between voltage distribution and read-voltage thresholds. Simulation results show that, compared with the existing schemes, the proposed DNN-aided read-voltage threshold optimization strategy with a well-designed LDPC code can not only improve the program-and-erase (PE) endurance but also reduce the read latency.
Neural Network-Based Dynamic Threshold Detection for Non-Volatile Memories
Feb 17, 2019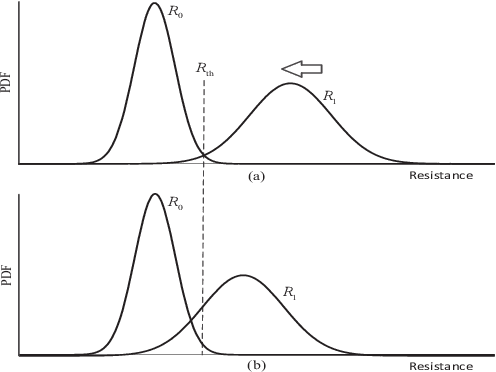
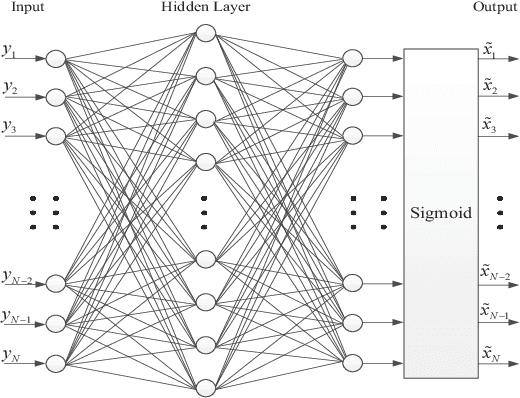
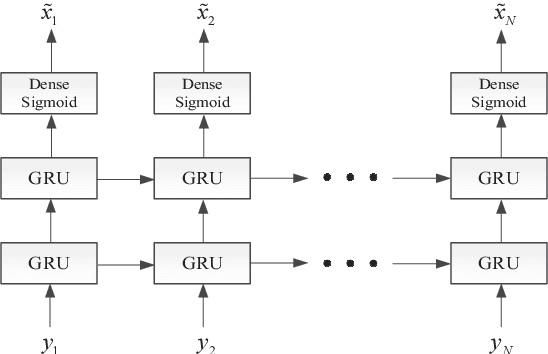
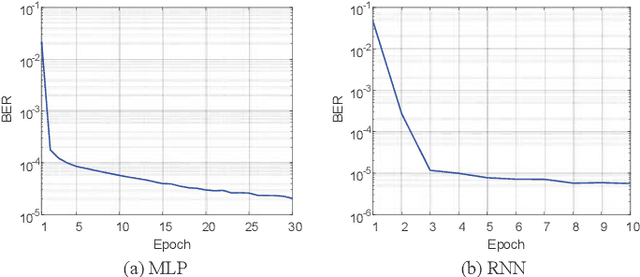
Abstract:The memory physics induced unknown offset of the channel is a critical and difficult issue to be tackled for many non-volatile memories (NVMs). In this paper, we first propose novel neural network (NN) detectors by using the multilayer perceptron (MLP) network and the recurrent neural network (RNN), which can effectively tackle the unknown offset of the channel. However, compared with the conventional threshold detector, the NN detectors will incur a significant delay of the read latency and more power consumption. Therefore, we further propose a novel dynamic threshold detector (DTD), whose detection threshold can be derived based on the outputs of the proposed NN detectors. In this way, the NN-based detection only needs to be invoked when the error correction code (ECC) decoder fails, or periodically when the system is in the idle state. Thereafter, the threshold detector will still be adopted by using the adjusted detection threshold derived base on the outputs of the NN detector, until a further adjustment of the detection threshold is needed. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed DTD based on the RNN detection can achieve the error performance of the optimum detector, without the prior knowledge of the channel.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge