Zerun Wang
Mirai: Autoregressive Visual Generation Needs Foresight
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Autoregressive (AR) visual generators model images as sequences of discrete tokens and are trained with next token likelihood. This strict causality supervision optimizes each step only by its immediate next token, which diminishes global coherence and slows convergence. We ask whether foresight, training signals that originate from later tokens, can help AR visual generation. We conduct a series of controlled diagnostics along the injection level, foresight layout, and foresight source axes, unveiling a key insight: aligning foresight to AR models' internal representation on the 2D image grids improves causality modeling. We formulate this insight with Mirai (meaning "future" in Japanese), a general framework that injects future information into AR training with no architecture change and no extra inference overhead: Mirai-E uses explicit foresight from multiple future positions of unidirectional representations, whereas Mirai-I leverages implicit foresight from matched bidirectional representations. Extensive experiments show that Mirai significantly accelerates convergence and improves generation quality. For instance, Mirai can speed up LlamaGen-B's convergence by up to 10$\times$ and reduce the generation FID from 5.34 to 4.34 on the ImageNet class-condition image generation benchmark. Our study highlights that visual autoregressive models need foresight.
Training Data Synthesis with Difficulty Controlled Diffusion Model
Nov 27, 2024



Abstract:Semi-supervised learning (SSL) can improve model performance by leveraging unlabeled images, which can be collected from public image sources with low costs. In recent years, synthetic images have become increasingly common in public image sources due to rapid advances in generative models. Therefore, it is becoming inevitable to include existing synthetic images in the unlabeled data for SSL. How this kind of contamination will affect SSL remains unexplored. In this paper, we introduce a new task, Real-Synthetic Hybrid SSL (RS-SSL), to investigate the impact of unlabeled data contaminated by synthetic images for SSL. First, we set up a new RS-SSL benchmark to evaluate current SSL methods and found they struggled to improve by unlabeled synthetic images, sometimes even negatively affected. To this end, we propose RSMatch, a novel SSL method specifically designed to handle the challenges of RS-SSL. RSMatch effectively identifies unlabeled synthetic data and further utilizes them for improvement. Extensive experimental results show that RSMatch can transfer synthetic unlabeled data from `obstacles' to `resources.' The effectiveness is further verified through ablation studies and visualization.
SCOMatch: Alleviating Overtrusting in Open-set Semi-supervised Learning
Sep 26, 2024



Abstract:Open-set semi-supervised learning (OSSL) leverages practical open-set unlabeled data, comprising both in-distribution (ID) samples from seen classes and out-of-distribution (OOD) samples from unseen classes, for semi-supervised learning (SSL). Prior OSSL methods initially learned the decision boundary between ID and OOD with labeled ID data, subsequently employing self-training to refine this boundary. These methods, however, suffer from the tendency to overtrust the labeled ID data: the scarcity of labeled data caused the distribution bias between the labeled samples and the entire ID data, which misleads the decision boundary to overfit. The subsequent self-training process, based on the overfitted result, fails to rectify this problem. In this paper, we address the overtrusting issue by treating OOD samples as an additional class, forming a new SSL process. Specifically, we propose SCOMatch, a novel OSSL method that 1) selects reliable OOD samples as new labeled data with an OOD memory queue and a corresponding update strategy and 2) integrates the new SSL process into the original task through our Simultaneous Close-set and Open-set self-training. SCOMatch refines the decision boundary of ID and OOD classes across the entire dataset, thereby leading to improved results. Extensive experimental results show that SCOMatch significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art methods on various benchmarks. The effectiveness is further verified through ablation studies and visualization.
From Obstacle to Opportunity: Enhancing Semi-supervised Learning with Synthetic Data
May 27, 2024



Abstract:Semi-supervised learning (SSL) can utilize unlabeled data to enhance model performance. In recent years, with increasingly powerful generative models becoming available, a large number of synthetic images have been uploaded to public image sets. Therefore, when collecting unlabeled data from these sources, the inclusion of synthetic images is inevitable. This prompts us to consider the impact of unlabeled data mixed with real and synthetic images on SSL. In this paper, we set up a new task, Real and Synthetic hybrid SSL (RS-SSL), to investigate this problem. We discover that current SSL methods are unable to fully utilize synthetic data and are sometimes negatively affected. Then, by analyzing the issues caused by synthetic images, we propose a new SSL method, RSMatch, to tackle the RS-SSL problem. Extensive experimental results show that RSMatch can better utilize the synthetic data in unlabeled images to improve the SSL performance. The effectiveness is further verified through ablation studies and visualization.
Online Open-set Semi-supervised Object Detection via Semi-supervised Outlier Filtering
May 23, 2023
Abstract:Open-set semi-supervised object detection (OSSOD) methods aim to utilize practical unlabeled datasets with out-of-distribution (OOD) instances for object detection. The main challenge in OSSOD is distinguishing and filtering the OOD instances from the in-distribution (ID) instances during pseudo-labeling. The previous method uses an offline OOD detection network trained only with labeled data for solving this problem. However, the scarcity of available data limits the potential for improvement. Meanwhile, training separately leads to low efficiency. To alleviate the above issues, this paper proposes a novel end-to-end online framework that improves performance and efficiency by mining more valuable instances from unlabeled data. Specifically, we first propose a semi-supervised OOD detection strategy to mine valuable ID and OOD instances in unlabeled datasets for training. Then, we constitute an online end-to-end trainable OSSOD framework by integrating the OOD detection head into the object detector, making it jointly trainable with the original detection task. Our experimental results show that our method works well on several benchmarks, including the partially labeled COCO dataset with open-set classes and the fully labeled COCO dataset with the additional large-scale open-set unlabeled dataset, OpenImages. Compared with previous OSSOD methods, our approach achieves the best performance on COCO with OpenImages by +0.94 mAP, reaching 44.07 mAP.
LODE: Deep Local Deblurring and A New Benchmark
Sep 19, 2021
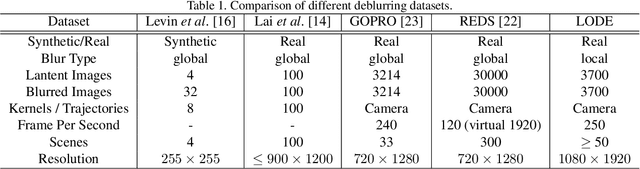
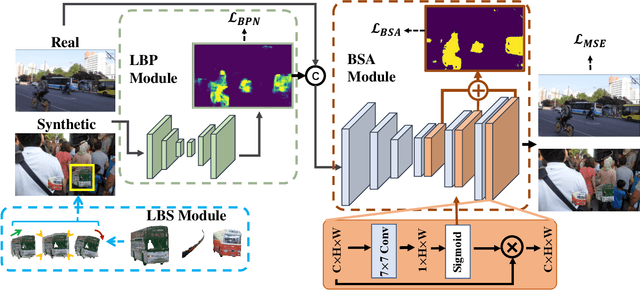

Abstract:While recent deep deblurring algorithms have achieved remarkable progress, most existing methods focus on the global deblurring problem, where the image blur mostly arises from severe camera shake. We argue that the local blur, which is mostly derived from moving objects with a relatively static background, is prevalent but remains under-explored. In this paper, we first lay the data foundation for local deblurring by constructing, for the first time, a LOcal-DEblur (LODE) dataset consisting of 3,700 real-world captured locally blurred images and their corresponding ground-truth. Then, we propose a novel framework, termed BLur-Aware DEblurring network (BladeNet), which contains three components: the Local Blur Synthesis module generates locally blurred training pairs, the Local Blur Perception module automatically captures the locally blurred region and the Blur-guided Spatial Attention module guides the deblurring network with spatial attention. This framework is flexible such that it can be combined with many existing SotA algorithms. We carry out extensive experiments on REDS and LODE datasets showing that BladeNet improves PSNR by 2.5dB over SotAs for local deblurring while keeping comparable performance for global deblurring. We will publish the dataset and codes.
PANDA: A Gigapixel-level Human-centric Video Dataset
Mar 10, 2020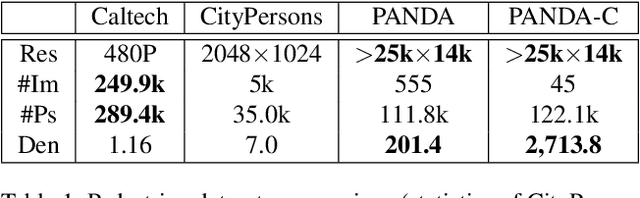

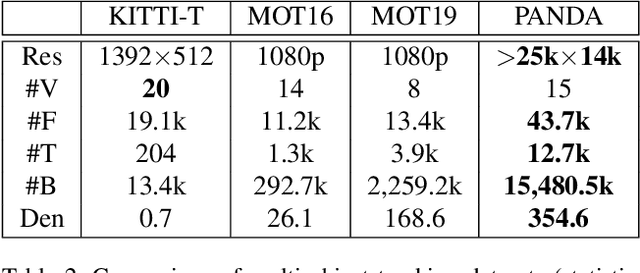
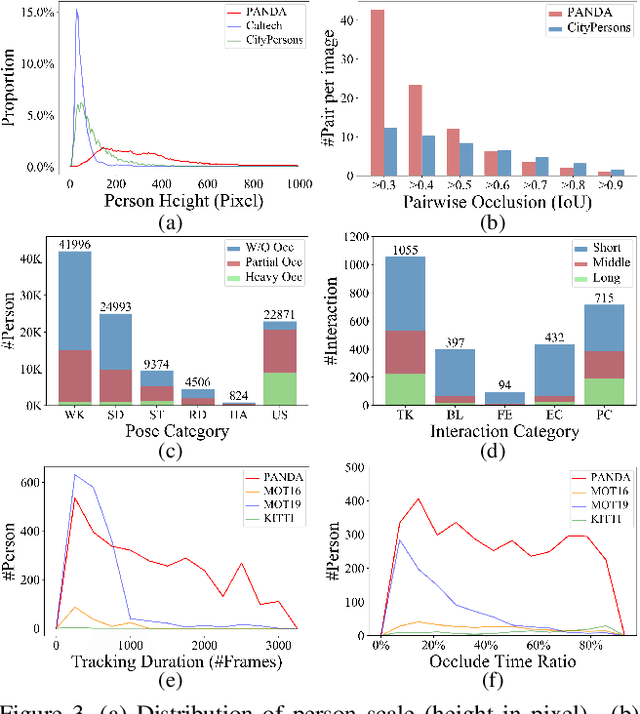
Abstract:We present PANDA, the first gigaPixel-level humAN-centric viDeo dAtaset, for large-scale, long-term, and multi-object visual analysis. The videos in PANDA were captured by a gigapixel camera and cover real-world scenes with both wide field-of-view (~1 square kilometer area) and high-resolution details (~gigapixel-level/frame). The scenes may contain 4k head counts with over 100x scale variation. PANDA provides enriched and hierarchical ground-truth annotations, including 15,974.6k bounding boxes, 111.8k fine-grained attribute labels, 12.7k trajectories, 2.2k groups and 2.9k interactions. We benchmark the human detection and tracking tasks. Due to the vast variance of pedestrian pose, scale, occlusion and trajectory, existing approaches are challenged by both accuracy and efficiency. Given the uniqueness of PANDA with both wide FoV and high resolution, a new task of interaction-aware group detection is introduced. We design a 'global-to-local zoom-in' framework, where global trajectories and local interactions are simultaneously encoded, yielding promising results. We believe PANDA will contribute to the community of artificial intelligence and praxeology by understanding human behaviors and interactions in large-scale real-world scenes. PANDA Website: http://www.panda-dataset.com.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge