Xueting Wang
The RoboSense Challenge: Sense Anything, Navigate Anywhere, Adapt Across Platforms
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Autonomous systems are increasingly deployed in open and dynamic environments -- from city streets to aerial and indoor spaces -- where perception models must remain reliable under sensor noise, environmental variation, and platform shifts. However, even state-of-the-art methods often degrade under unseen conditions, highlighting the need for robust and generalizable robot sensing. The RoboSense 2025 Challenge is designed to advance robustness and adaptability in robot perception across diverse sensing scenarios. It unifies five complementary research tracks spanning language-grounded decision making, socially compliant navigation, sensor configuration generalization, cross-view and cross-modal correspondence, and cross-platform 3D perception. Together, these tasks form a comprehensive benchmark for evaluating real-world sensing reliability under domain shifts, sensor failures, and platform discrepancies. RoboSense 2025 provides standardized datasets, baseline models, and unified evaluation protocols, enabling large-scale and reproducible comparison of robust perception methods. The challenge attracted 143 teams from 85 institutions across 16 countries, reflecting broad community engagement. By consolidating insights from 23 winning solutions, this report highlights emerging methodological trends, shared design principles, and open challenges across all tracks, marking a step toward building robots that can sense reliably, act robustly, and adapt across platforms in real-world environments.
Unveiling Intrinsic Text Bias in Multimodal Large Language Models through Attention Key-Space Analysis
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) exhibit a pronounced preference for textual inputs when processing vision-language data, limiting their ability to reason effectively from visual evidence. Unlike prior studies that attribute this text bias to external factors such as data imbalance or instruction tuning, we propose that the bias originates from the model's internal architecture. Specifically, we hypothesize that visual key vectors (Visual Keys) are out-of-distribution (OOD) relative to the text key space learned during language-only pretraining. Consequently, these visual keys receive systematically lower similarity scores during attention computation, leading to their under-utilization in the context representation. To validate this hypothesis, we extract key vectors from LLaVA and Qwen2.5-VL and analyze their distributional structures using qualitative (t-SNE) and quantitative (Jensen-Shannon divergence) methods. The results provide direct evidence that visual and textual keys occupy markedly distinct subspaces within the attention space. The inter-modal divergence is statistically significant, exceeding intra-modal variation by several orders of magnitude. These findings reveal that text bias arises from an intrinsic misalignment within the attention key space rather than solely from external data factors.
Exploring Palette based Color Guidance in Diffusion Models
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:With the advent of diffusion models, Text-to-Image (T2I) generation has seen substantial advancements. Current T2I models allow users to specify object colors using linguistic color names, and some methods aim to personalize color-object association through prompt learning. However, existing models struggle to provide comprehensive control over the color schemes of an entire image, especially for background elements and less prominent objects not explicitly mentioned in prompts. This paper proposes a novel approach to enhance color scheme control by integrating color palettes as a separate guidance mechanism alongside prompt instructions. We investigate the effectiveness of palette guidance by exploring various palette representation methods within a diffusion-based image colorization framework. To facilitate this exploration, we construct specialized palette-text-image datasets and conduct extensive quantitative and qualitative analyses. Our results demonstrate that incorporating palette guidance significantly improves the model's ability to generate images with desired color schemes, enabling a more controlled and refined colorization process.
Training Data Synthesis with Difficulty Controlled Diffusion Model
Nov 27, 2024



Abstract:Semi-supervised learning (SSL) can improve model performance by leveraging unlabeled images, which can be collected from public image sources with low costs. In recent years, synthetic images have become increasingly common in public image sources due to rapid advances in generative models. Therefore, it is becoming inevitable to include existing synthetic images in the unlabeled data for SSL. How this kind of contamination will affect SSL remains unexplored. In this paper, we introduce a new task, Real-Synthetic Hybrid SSL (RS-SSL), to investigate the impact of unlabeled data contaminated by synthetic images for SSL. First, we set up a new RS-SSL benchmark to evaluate current SSL methods and found they struggled to improve by unlabeled synthetic images, sometimes even negatively affected. To this end, we propose RSMatch, a novel SSL method specifically designed to handle the challenges of RS-SSL. RSMatch effectively identifies unlabeled synthetic data and further utilizes them for improvement. Extensive experimental results show that RSMatch can transfer synthetic unlabeled data from `obstacles' to `resources.' The effectiveness is further verified through ablation studies and visualization.
Reward Incremental Learning in Text-to-Image Generation
Nov 26, 2024Abstract:The recent success of denoising diffusion models has significantly advanced text-to-image generation. While these large-scale pretrained models show excellent performance in general image synthesis, downstream objectives often require fine-tuning to meet specific criteria such as aesthetics or human preference. Reward gradient-based strategies are promising in this context, yet existing methods are limited to single-reward tasks, restricting their applicability in real-world scenarios that demand adapting to multiple objectives introduced incrementally over time. In this paper, we first define this more realistic and unexplored problem, termed Reward Incremental Learning (RIL), where models are desired to adapt to multiple downstream objectives incrementally. Additionally, while the models adapt to the ever-emerging new objectives, we observe a unique form of catastrophic forgetting in diffusion model fine-tuning, affecting both metric-wise and visual structure-wise image quality. To address this catastrophic forgetting challenge, we propose Reward Incremental Distillation (RID), a method that mitigates forgetting with minimal computational overhead, enabling stable performance across sequential reward tasks. The experimental results demonstrate the efficacy of RID in achieving consistent, high-quality generation in RIL scenarios. The source code of our work will be publicly available upon acceptance.
ContextBLIP: Doubly Contextual Alignment for Contrastive Image Retrieval from Linguistically Complex Descriptions
May 29, 2024Abstract:Image retrieval from contextual descriptions (IRCD) aims to identify an image within a set of minimally contrastive candidates based on linguistically complex text. Despite the success of VLMs, they still significantly lag behind human performance in IRCD. The main challenges lie in aligning key contextual cues in two modalities, where these subtle cues are concealed in tiny areas of multiple contrastive images and within the complex linguistics of textual descriptions. This motivates us to propose ContextBLIP, a simple yet effective method that relies on a doubly contextual alignment scheme for challenging IRCD. Specifically, 1) our model comprises a multi-scale adapter, a matching loss, and a text-guided masking loss. The adapter learns to capture fine-grained visual cues. The two losses enable iterative supervision for the adapter, gradually highlighting the focal patches of a single image to the key textual cues. We term such a way as intra-contextual alignment. 2) Then, ContextBLIP further employs an inter-context encoder to learn dependencies among candidates, facilitating alignment between the text to multiple images. We term this step as inter-contextual alignment. Consequently, the nuanced cues concealed in each modality can be effectively aligned. Experiments on two benchmarks show the superiority of our method. We observe that ContextBLIP can yield comparable results with GPT-4V, despite involving about 7,500 times fewer parameters.
Self-supervised 6-DoF Robot Grasping by Demonstration via Augmented Reality Teleoperation System
Apr 03, 2024



Abstract:Most existing 6-DoF robot grasping solutions depend on strong supervision on grasp pose to ensure satisfactory performance, which could be laborious and impractical when the robot works in some restricted area. To this end, we propose a self-supervised 6-DoF grasp pose detection framework via an Augmented Reality (AR) teleoperation system that can efficiently learn human demonstrations and provide 6-DoF grasp poses without grasp pose annotations. Specifically, the system collects the human demonstration from the AR environment and contrastively learns the grasping strategy from the demonstration. For the real-world experiment, the proposed system leads to satisfactory grasping abilities and learning to grasp unknown objects within three demonstrations.
Semantic-Driven Initial Image Construction for Guided Image Synthesis in Diffusion Model
Dec 13, 2023



Abstract:The initial noise image has demonstrated a significant influence on image generation, and manipulating the initial noise image can effectively increase control over the generation. All of the current generation is based only on a single initial noise drawn from a normal distribution, which may not be suited to the desired content specified by the prompt. In this research, we propose a novel approach using pre-collected, semantically-informed pixel blocks from multiple initial noises for the initial image construction to enhance control over the image generation. The inherent tendencies of these pixel blocks can easily generate specific content, thus effectively guiding the generation process towards the desired content. The pursuit of tailored initial image construction inevitably leads to deviations from the normal distribution, and our experimental results show that the diffusion model exhibits a certain degree of tolerance towards the distribution of initial images. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance in the training-free layout-to-image synthesis task, demonstrating the adaptability of the initial image construction in guiding the content of the generated image. Our code will be made publicly available.
Angle Range and Identity Similarity Enhanced Gaze and Head Redirection based on Synthetic data
Sep 11, 2023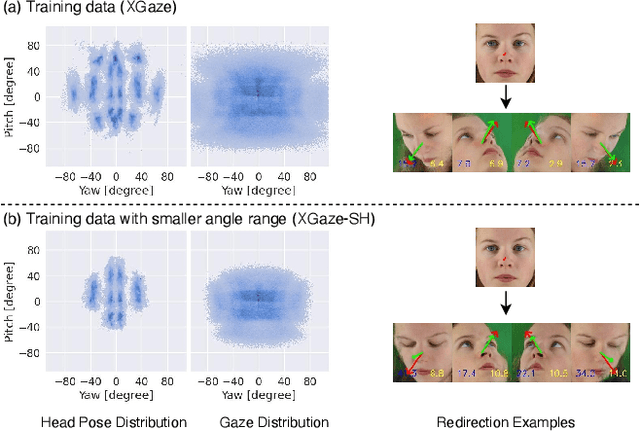
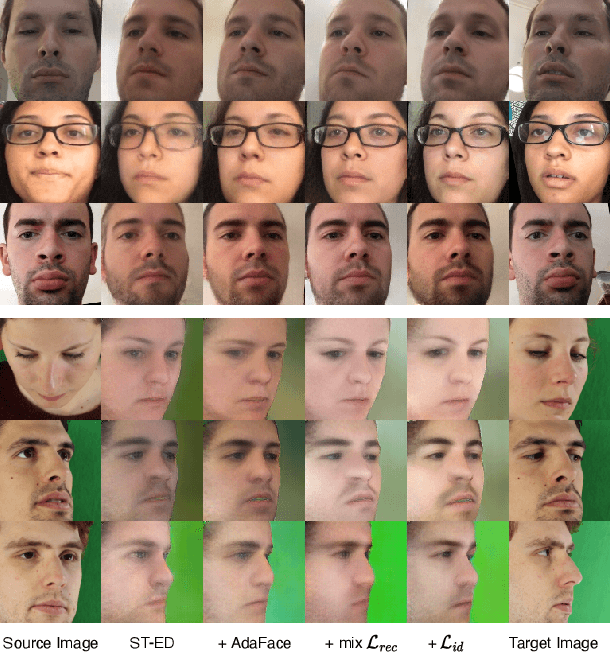

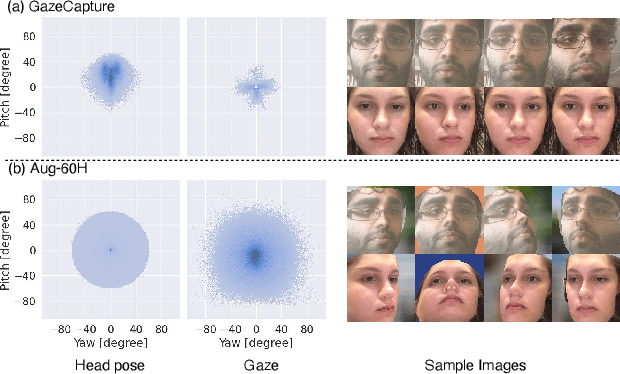
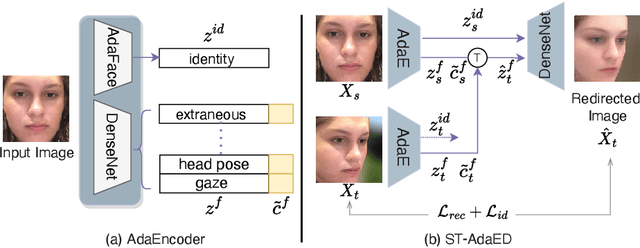
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a method for improving the angular accuracy and photo-reality of gaze and head redirection in full-face images. The problem with current models is that they cannot handle redirection at large angles, and this limitation mainly comes from the lack of training data. To resolve this problem, we create data augmentation by monocular 3D face reconstruction to extend the head pose and gaze range of the real data, which allows the model to handle a wider redirection range. In addition to the main focus on data augmentation, we also propose a framework with better image quality and identity preservation of unseen subjects even training with synthetic data. Experiments show that our method significantly improves redirection performance in terms of redirection angular accuracy while maintaining high image quality, especially when redirecting to large angles.
Multimodal Color Recommendation in Vector Graphic Documents
Aug 08, 2023



Abstract:Color selection plays a critical role in graphic document design and requires sufficient consideration of various contexts. However, recommending appropriate colors which harmonize with the other colors and textual contexts in documents is a challenging task, even for experienced designers. In this study, we propose a multimodal masked color model that integrates both color and textual contexts to provide text-aware color recommendation for graphic documents. Our proposed model comprises self-attention networks to capture the relationships between colors in multiple palettes, and cross-attention networks that incorporate both color and CLIP-based text representations. Our proposed method primarily focuses on color palette completion, which recommends colors based on the given colors and text. Additionally, it is applicable for another color recommendation task, full palette generation, which generates a complete color palette corresponding to the given text. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed approach surpasses previous color palette completion methods on accuracy, color distribution, and user experience, as well as full palette generation methods concerning color diversity and similarity to the ground truth palettes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge